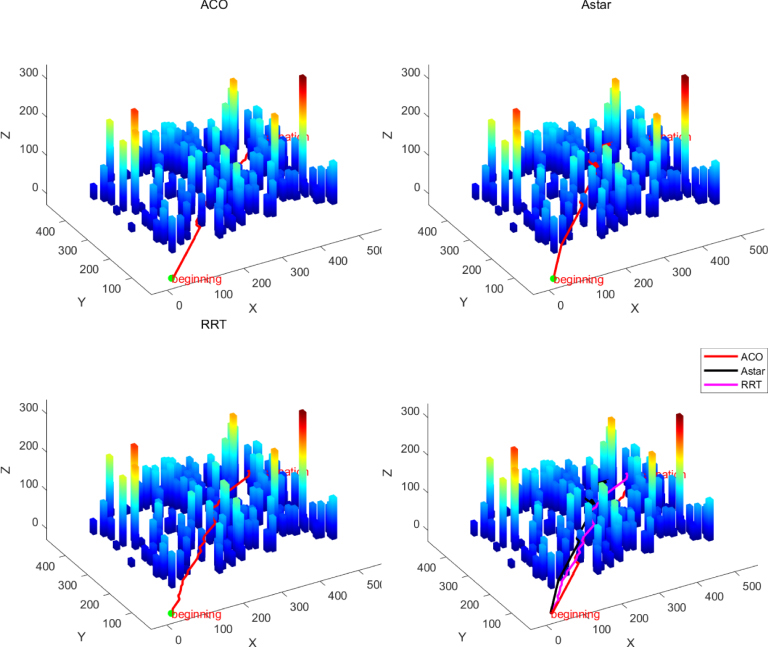
To address the issue of low accuracy in 3D modeling of images captured by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), the authors propose an enhanced 3D reconstruction model for a mountain in Yuanmou by employing an improved Structure from Motion–Multiview Stereo (SFM–MVS) algorithm. In the process of converting 2D into 3D data, the key challenges lie in feature point extraction and matching. The authors introduce an algorithm for optimizing Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF) by combining the SURF descriptor operator with a fast feature point algorithm. The use of the Laplace operator to refine the extraction of weighted feature points along with integration into the robust SURF descriptor simultaneously improves both matching speed and accuracy. This solution mitigates issues related to excessive image data and the low accuracy and efficiency of 3D reconstruction models in UAV applications. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method extracts more feature points, increases matching speed, and significantly enhances accuracy compared to both the original SURF and traditional Scale-Invariant Feature Transform algorithms. When compared to the unoptimized SFM–MVS algorithm, the accuracy of the optimized 3D reconstruction using the SURF-based algorithm improves by approximately 44.68%, with a 30% increase in processing speed. Additionally, to evaluate UAV path planning performance on complex terrain, the authors first employ the optimized SURF-based 3D reconstruction method to precisely reconstruct the terrain map of the target area. This method improves both the accuracy and efficiency of 3D terrain reconstruction, providing high-precision data for subsequent path planning algorithm performance testing. Subsequently, three classical path planning algorithms—Ant Colony Optimization, A*, and Rapidly exploring Random Tree—are selected for comparative analysis of UAV path planning capabilities on complex terrain.
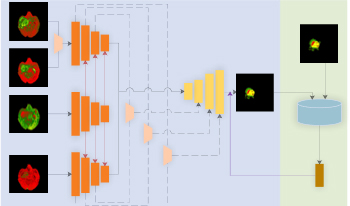
Accurate segmentation of brain tumors is essential in the planning of neurosurgical treatments as it can significantly enhance their effectiveness. In this paper, the authors propose a modified Residual U-shaped network (ResUnet) based on multimodal fusion and a Generative Adversarial Network for multimodal brain tumor Magnetic Resonance Imaging segmentation. First, they propose a three-path structure for the encoding stage to address the issue of inadequate utilization of multimodal features, which leads to suboptimal segmentation results. The structure comprises three components: the T1 path, the T1ce path, and the fusion path combining Flair and T2 modalities. They then utilize average pooling to integrate the global information from the T1 path into both the T1ce and the fusion path, enhancing the feature fusion across different modalities and strengthening the robustness of the network. Subsequently, the features from the T1ce path and the fusion path are connected to the decoding stage through skip connections to enhance the utilization of model features and improve segmentation accuracy. Finally, the authors leverage the Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network (DCGAN) to further enhance the accuracy of the network. They improve the loss function of the DCGAN by introducing an adaptive coefficient, which reduces the loss value in the early stages of model training and increases it in the later stages. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively improves segmentation accuracy compared to related methods.
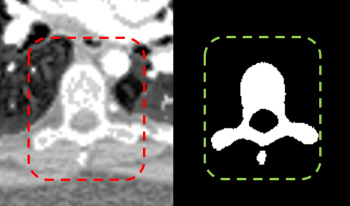
Spinal CT image segmentation is actively researched in the field of medical image processing. However, due to factors such as high variability among spinal CT slices and image artifacts, and so on, automatic and accurate spinal CT segmentation tasks are extremely challenging. To address these issues, we propose a cascaded U-shaped framework that combines multi-scale features and attention mechanisms (MA-WNet) for the automatic segmentation of spinal CT images. Specifically, our framework combines two U-shaped networks to achieve coarse and fine segmentation separately for spinal CT images. Within each U-shaped network, we add multi-scale feature extraction modules during both the encoding and decoding phases to address variations in spine shape across different slices. Additionally, various attention mechanisms are embedded to mitigate the effects of image artifacts and irrelevant information on segmentation outcomes. Experimental results show that our proposed method achieves average segmentation Dice similarity coefficients of 94.53% and 91.38% on the CSI 2014 and VerSe 2020 datasets, respectively, indicating highly accurate segmentation performance, which is valuable for potential clinical applications.
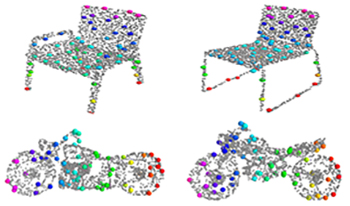
Sparse representation is the key part of shape registration, compression, and regeneration. Most existing models generate sparse representation by detecting salient points directly from input point clouds, but they are susceptible to noise, deformations, and outliers. The authors propose a novel alternative solution that combines global distribution probabilities and local contextual features to learn semantic structural consistency and adaptively generate sparse structural representation for arbitrary 3D point clouds. First, they construct a 3D variational auto-encoder network to learn an optimal latent space aligned with multiple anisotropic Gaussian mixture models (GMMs). Then, they combine GMM parameters with contextual properties to construct enhanced point features that effectively resist noise and geometric deformations, better revealing underlying semantic structural consistency. Second, they design a weight scoring unit that computes a contribution matrix to the semantic structure and adaptively generates sparse structural points. Finally, the authors enforce semantic correspondence and structural consistency to ensure that the generated structural points have stronger discriminative ability in both feature and distribution domains. Extensive experiments on shape benchmarks have shown that the proposed network outperforms state-of-the-art methods, with lower costs and more significant performance in shape segmentation and classification.
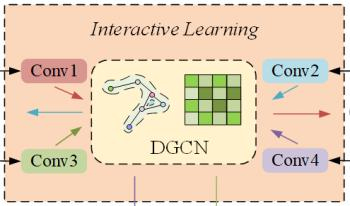
Accurate traffic flow forecasting plays a crucial role in alleviating road congestion and optimizing traffic management. Although numerous effective models have been proposed in existing research to predict future traffic flow, most models exhibit certain limitations in modeling spatiotemporal dependencies, especially in capturing multiscale spatiotemporal relationships. To address this, we propose a novel model called Spatiotemporal Augmented Interactive Learning and Temporal Attention (STAIL-TA) for traffic flow prediction, which is designed for dynamic and interactive adaptive modeling of spatiotemporal features in traffic flow data. Specifically, we first design a feature augmentation layer that enhances the interaction of time-based features. Next, we introduce an interactive dynamic graph convolutional network, which uses an interactive learning strategy to simultaneously capture spatiotemporal characteristics of traffic data. Additionally, a new dynamic graph generation method is employed to design a dynamic graph convolutional block, which is capable of capturing the spatial correlations that change dynamically within the traffic network. Finally, we construct a novel temporal attention mechanism that effectively leverages local contextual information and is specifically designed for transforming numerical sequence representations. This enables the prediction model to capture the dynamic temporal dependencies of traffic flow better, thus facilitating long-term forecasting. The experimental results show that the STAIL-TA model improves the mean absolute error and root mean squared error on the PEMS-BAY dataset by 7.75%, 3.68% and 5.59%, 2.72% in the 15-minute and 30-minute predictions, respectively, when compared to the existing optimal baseline method, MRA-BGCN.
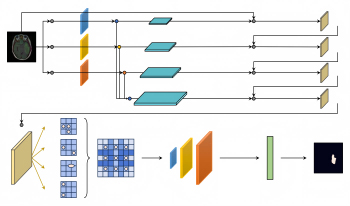
Purpose: Gliomas, particularly brain tumors, pose significant challenges due to their complex pathology and life-threatening potential. The goal of this study is to introduce LU-net, a novel semantic segmentation algorithm designed to enhance the diagnosis and treatment planning of gliomas. This research seeks to address the limitations of traditional classification and detection methods by improving the accuracy and robustness of tumor boundary delineation in medical images. Methods: LU-net employs a multiscale image pyramid along with a Bayesian-inference-based multiscale probability search to capture complex tumor features. The algorithm is further strengthened by integrating a Conditional Random Field model, enabling more precise segmentation. The performance of LU-net is evaluated against existing segmentation algorithms using standard metrics such as accuracy, Intersection over Union (IoU), and Dice score. Results: The experimental results demonstrate that LU-net outperforms current segmentation algorithms in terms of both accuracy and robustness. Specifically, LU-net achieves an accuracy of 0.9953, an IoU of 0.667, and a Dice score of 0.566, effectively addressing the pathological heterogeneity and invasiveness of gliomas. These results highlight LU-net’s superior ability to delineate tumor boundaries and improve diagnostic accuracy. Conclusion: LU-net sets a new benchmark in glioma lesion detection, offering a more effective approach for brain tumor segmentation. By improving the accuracy, reliability, and interpretability of brain tumor boundary delineation, LU-net enhances diagnostic and treatment strategies, providing significant benefits to patients, clinicians, and healthcare providers. Overall, this work marks a significant contribution to the field of medical imaging and glioma diagnosis.
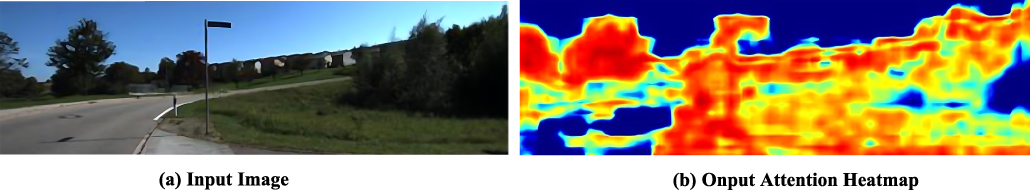
This paper presents a self-supervised monocular visual odometry (VO) method guided by attention feature maps, aimed at effectively mitigating the impact of redundant pixels during network training. Existing self-supervised VO methods typically treat all pixels equally when computing photometric error, which can lead to increased sensitivity to noise from irrelevant pixels and, consequently, training errors. To address this issue, the authors adopt a soft-attention mechanism to generate attention feature maps that allow the model to focus on more relevant pixels while downweighting the influence of disruptive ones. This approach enhances the robustness and accuracy of depth estimation and pose tracking. The proposed method achieves competitive results on the KITTI dataset, with Sequences 09 and 10 demonstrating relative rotation errors of 0.022 and 0.032 and relative translation errors of 5.56 and 7.29, respectively.
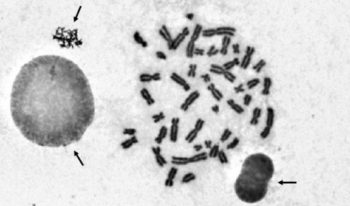
For the automated analysis of metaphase chromosome images, the chromosomes on the images need to be segmented first. However, the segmentation results often contain several non-chromosome objects. Elimination of non-chromosome objects is essential in automated chromosome image analysis. This study aims to exclude non-chromosome objects from segmented chromosome candidates for further analysis. A feature-based method was developed to eliminate non-chromosome objects from metaphase chromosome images. In a metaphase chromosome image, the chromosome candidates were segmented by a threshold first. After segmenting the chromosome candidates, four classes of features, namely, area, density-based features, roughness-based features, and widths, of the segmented candidates were extracted to discriminate between chromosomes and non-chromosome objects. Seven classifiers were used and compared to combine the extracted features to perform classifications. The experimental results show the usefulness of the combination of extracted features in distinguishing between chromosomes and non-chromosome objects. The proposed method can effectively separate non-chromosome objects from chromosomes and could be used as the preprocessing procedure for chromosome image analysis.
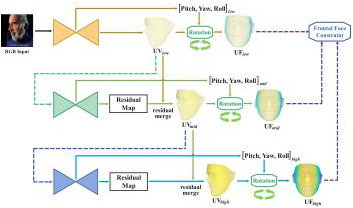
We propose an efficient multi-scale residual network that integrates 3D face alignment with head pose estimation from an RGB image. Existing methods excel in performing each task independently but often fail to acknowledge the interdependence between them. Additionally, these approaches lack a progressive fine-tuning process for 3D face alignment, which could otherwise require excessive computational resources and memory. To address these limitations, we introduce a hierarchical network that incorporates a frontal face constraint, significantly enhancing the accuracy of both tasks. Moreover, we implement a multi-scale residual merging process that allows for multi-stage refinement without compromising the efficiency of the model. Our experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our method compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
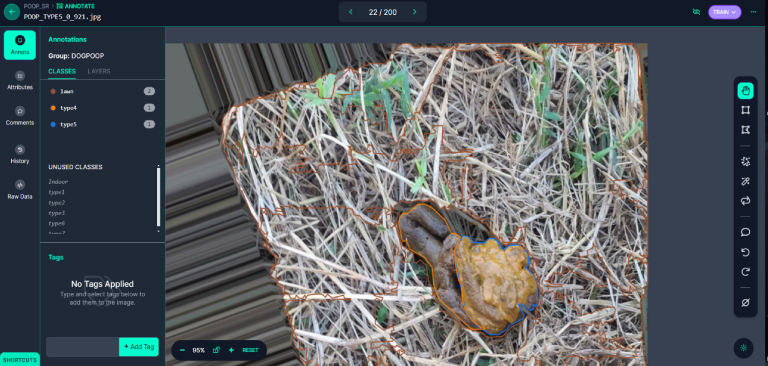
As pets now outnumber newborns in households, the demand for pet medical care and attention has surged. This has led to a significant burden for pet owners. To address this, our experiment utilizes image recognition technology to preliminarily assess the health condition of dogs, providing a rapid and economical health assessment method. By collaboration, we collected 2613 stool photos, which were enhanced to a total of 6079 images and analyzed using LabVIEW and the YOLOv8 segmentation model. The model performed excellently, achieving a precision of 86.805%, a recall rate of 74.672%, and an mAP50 of 83.354%. This proves its high recognition rate in determining the condition of dog stools. With the advancement of technology and the proliferation of mobile devices, the aim of this experiment is to develop an application that allows pet owners to assess their pets’ health anytime and manage it more conveniently. Additionally, the experiment aims to expand the database through cloud computing, optimize the model, and establish a global pet health interactive community. These developments not only propel innovation in the field of pet medical care but also provide practical health management tools for pet families, potentially offering substantial help to more pet owners in the future.