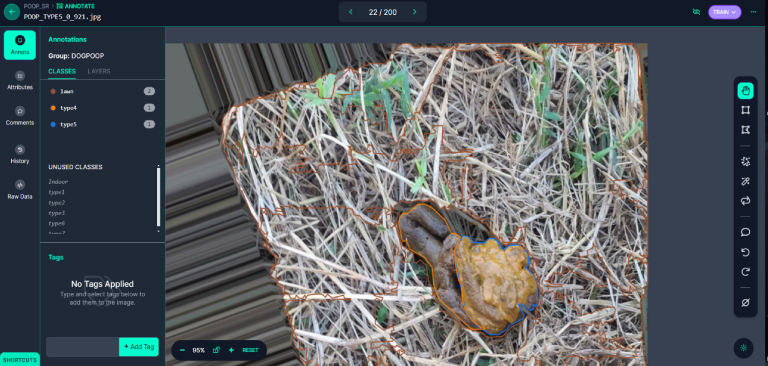
As pets now outnumber newborns in households, the demand for pet medical care and attention has surged. This has led to a significant burden for pet owners. To address this, our experiment utilizes image recognition technology to preliminarily assess the health condition of dogs, providing a rapid and economical health assessment method. By collaboration, we collected 2613 stool photos, which were enhanced to a total of 6079 images and analyzed using LabVIEW and the YOLOv8 segmentation model. The model performed excellently, achieving a precision of 86.805%, a recall rate of 74.672%, and an mAP50 of 83.354%. This proves its high recognition rate in determining the condition of dog stools. With the advancement of technology and the proliferation of mobile devices, the aim of this experiment is to develop an application that allows pet owners to assess their pets’ health anytime and manage it more conveniently. Additionally, the experiment aims to expand the database through cloud computing, optimize the model, and establish a global pet health interactive community. These developments not only propel innovation in the field of pet medical care but also provide practical health management tools for pet families, potentially offering substantial help to more pet owners in the future.
Kai-Chao Yao, Tao-Shuo Wang, "Implementing Instance Segmentation for Image Recognition Based on YOLOv8: A Case Study on Canine Fecal Matter" in Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, 2025, pp 1 - 16, https://doi.org/10.2352/J.ImagingSci.Technol.2025.69.6.060501
 Find this author on Google Scholar
Find this author on Google Scholar Find this author on PubMed
Find this author on PubMed