
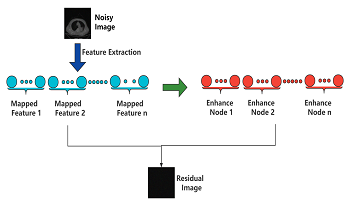
Image denoising plays an important role in CT sampling. Although good results have been achieved by filter-based, model-based and deep learning-based denoising methods, there are still many demanding constraints in real applications. In order to improve accuracy and efficiency, a residual learning network based on broad learning system (ReBLS) is proposed. First, features are extracted from the noisy images to generate a feature node layer. Subsequently, through a random matrix after orthogonal normalization, the feature nodes are reinforced into an enhanced node layer. Finally, the noise will be removed by the residual network. Compared with commonly used deep learning scheme, the broad learning replaces depth with expansion in breadth, the training and process time of broad learning is much shorter. Meanwhile, the learning of residuals can simplify the learning process and enhance the feature extraction. Experiments on the open dataset fully prove the accuracy and efficiency by comparing with five state-of-the-art denoising methods.
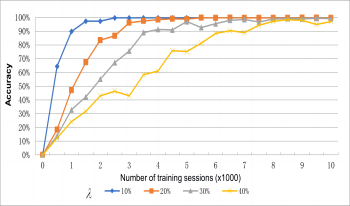
Nowadays, feature based 3D reconstruction and tracking technology have been widely used in the medical field. Feature matching is the most important step in feature-based 3D reconstruction process, as the accuracy of feature matching directly affects the accuracy of subsequent 3D point cloud coordinates. However, the matching performance of traditional feature matching methods is poor. To overcome this limitation, a method of matching based on convolutional neural network is presented. The convolutional neural network is trained by collecting a training set on the video sequence of a certain length from starting frame. The matched feature points in different endoscopic video frames are treated as the same category. The feature points in subsequent frames are matched by network classification. The proposed method is validated using the silicone simulation heart video and the endoscope video of the vivo beating heart obtained by Da Vinci’s surgical robot. Compared with SURF and ORB algorithms, as well as other methods, the experimental results show that the feature matching algorithm based on convolutional neural network is effective in the feature matching effect, rotation invariance, and scale invariance. For the first 200 frames of the video, the matching accuracy reached 90%.
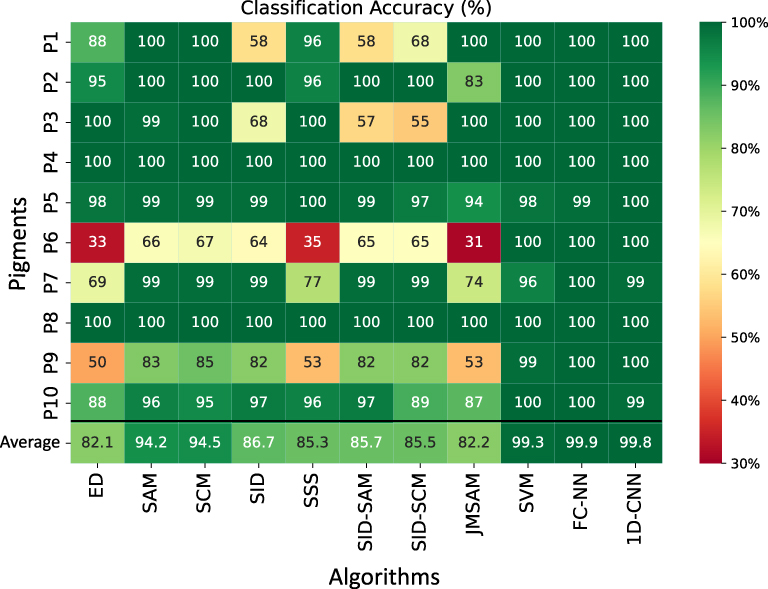
Hyperspectral imaging techniques are widely used in cultural heritage for documentation and material analysis. Pigment classification of an artwork is an essential task. Several algorithms have been used for hyperspectral data classification, and the effectiveness of each algorithm depends on the application domain. However, very few have been applied for pigment classification tasks in the cultural heritage domain. Most of these algorithms work effectively for spectral shape differences and might not perform well for spectra with differences in magnitude or for spectra that are nearly similar in shape but might belong to two different pigments. In this work, we evaluate the performance of different supervised-based algorithms and few machine learning models for the pigment classification of a mockup using hyperspectral imaging. The result obtained shows the importance of choosing appropriate algorithms for pigment classification.

Recent advances in pigment production resulted in the possibility to print with RGBW primaries instead of CMYK and performing additive color mixing in printing. The RGBW pigments studied in this work have the properties of structural colors, as the primary colors are a result of interference in a thin film coating of mica pigments. In this work, we investigate the angle-dependent gamut of RGBW primaries. We have elucidated optimal angles of illumination and observation for each primary ink and found the optimal angle of observation under diffuse illumination. We investigated dot off dot halftoned screen printing with RGBW inks on black paper and in terms of angle-dependent dot gain. Based on our observations, optimal viewing condition for the given RGBW inks is in a direction of around 30∘ to the surface normal. Here, the appearance of the resulting halftoned prints can be estimated well by Neugebauer formula (weighted averaging of the individual reflected spectra). Despite the negative physical dot gain during the dot off dot printing, we observe angularly dependent positive optical dot gain for halftoned prints. Application of interference RGBW pigments in 2.5D and 3D printing is not fully explored due to the technological limitations. In this work, we provide colorimetric data for efficient application of the angle-dependent properties of such pigments in practical applications.
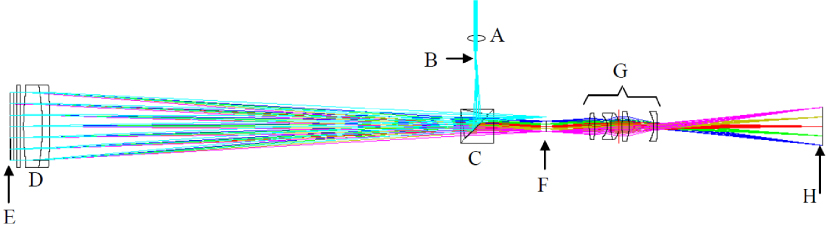
In a computer-generated holographic projection system, the image is reconstructed via the diffraction of light from a spatial light modulator. In this process, several factors could contribute to non-linearities between the reconstructed and the target image. This paper evaluates the non-linearity of the overall holographic projection system experimentally, using binary phase holograms computed using the one-step phase retrieval (OSPR) algorithm, and then applies a digital pre-distortion (DPD) method to correct for the non-linearity. Both a notable increase in reconstruction quality and a significant reduction in mean squared error were observed, proving the effectiveness of the proposed DPD-OSPR algorithm.
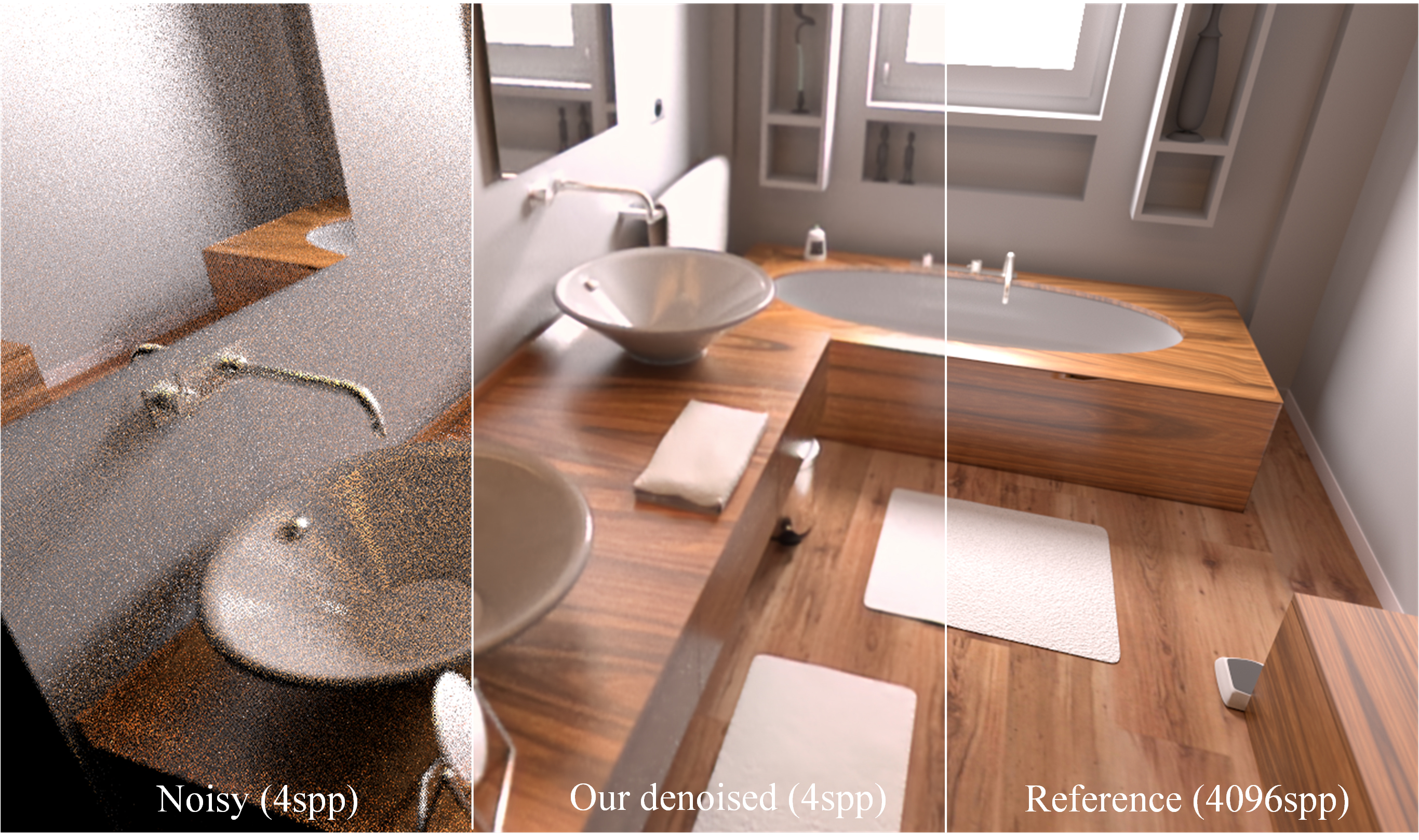

Monte Carlo (MC) rendering has attracted unprecedented attention for denoising and creating high-quality images, while deep learning-based MC denoisers also aim to improve rendering quality. Recently, there has been rapid development in using MC rendering synthesis along with deep learning, and significant progress has been reported on denoising using models trained on convolutional neural networks. Such usage and recent novel ideas have contributed to generating denoising rendering results, and sufficient details for image reconstruction from sparse MC samples or basic geometric auxiliary features. In this paper, we present a fast method for denoising Monte Carlo Rendering with a few samples per pixel. The basic idea is to use Dual Deep AutoEncoder Networks (DDAE) with a skip connection, for end-to-end inference from noisy rendered images to reconstructed realistic images. The first autoencoder accepts the noisy image together with the auxiliary buffers and outputs a sampling map. The second autoencoder accepts the noisy image together with the sampling map and outputs the final image. Consequently, our approach is less time-consuming and keeps the high-frequency details features lossless. In addition, we compare our DDAE results against state-of-the-art results by using the mean squared error (MSE) values with the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) values, and our approach reported better performance effects.

In recent years, behavioral biometrics authentication, which uses the habit of behavioral characteristics for personal authentication, has attracted attention as an authentication method with higher security since behavioral biometrics cannot mimic fingerprint and face authentications. In behavioral biometrics, extensive research has been done on voiceprints and gait. However, there are few authentication technologies that utilize the habits of hand and finger movements during hand gestures. Only color images or depth images are used for hand gesture authentication in conventional methods.
In this research, therefore, we propose to find individual habits from RGB-D images of finger movements and create a personal authentication system. 3D CNN, which is deep learning-based network, is used to extract individual habits. F-measure of 0.97 is achieved when rock-paper-scissors are used as the authentication operation. F-measure of 0.97 is achieved when the disinfection operation is used. These results show the effectiveness of using RGB-D video for personal authentication.
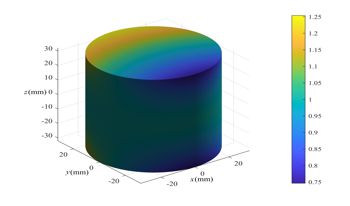
Circular cone-beam computed tomography (CT) is a popular configuration in industrial non-destructive testing. Corresponding to the circular cone-beam CT, the Feldkamp, Davis, and Kress (FDK) algorithm is the most popular reconstruction method. However, in the case of large cone angle scanning, the slice artifacts of the reconstruction using the FDK algorithm are visible because the data collected with the circular orbit scan mode do not satisfy the completeness conditions for exact reconstruction. To solve the problem, this study proposed a hybrid FDK (H-FDK) algorithm using a method that combines variable filtering and conjugate rays. First, the shape and curvature of the detector were changed for the filtering paths to be variable. Then, the conjugate weighting function for backprojection was constructed. Subsequently, optimization experiments were conducted to find optimal parameters for the detector and conjugate weighting function. Finally, the comparative experimental results demonstrated that the slices reconstructed by the H-FDK algorithm produced a discernible quality improvement.