
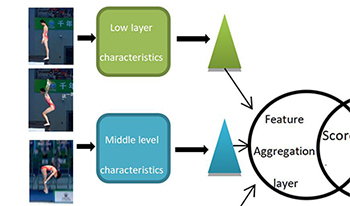
With the advent of the era of the media, the number of sports videos on the Internet is on the order of the magnitude of geometric growth. However, in the face of mass and form, diversity of sports videos, how users find interesting events and videos influences this growth. Classifying sports videos, games organization and management is required to effectively improve the video retrieval speed, as artificial classification and semantic annotations are highly susceptible to subjective consciousness and the influence of the cultural level of participants, resulting in low classification and labeling efficiency. Therefore, a digital video automatic classification technology has become a research hotspot in the field. Especially for sports videos, accurate automatic classification and semantic tagging can make the coach quickly find relevant video data, targeted guidance and training for athletes and users quickly find and promote interesting sports video program or fragment. Therefore, automatic classification of sports video technology has become an important branch in the field of digital video research. Extensive literature review is presented in this paper with an in-depth discussion and summary of sports videos based on automatic classification. This paper focuses on video classification based on deep learning and puts forward a multi-level multiple granularity based on cascade SRU airspace feature extraction method. First, convolution neural network is used to extract videos of high, medium and low levels of frame characteristics. Second, each layer of the frame uses characteristics such as build time domain pyramid, cascade SRL learning video time dependence and the characteristic of hierarchical structure in time domain. Finally, the three levels of pyramid time domain features are aggregated into multi-level multi-granularity global characteristics of the video. Experiments show that the feature extraction has good representation ability and robustness.
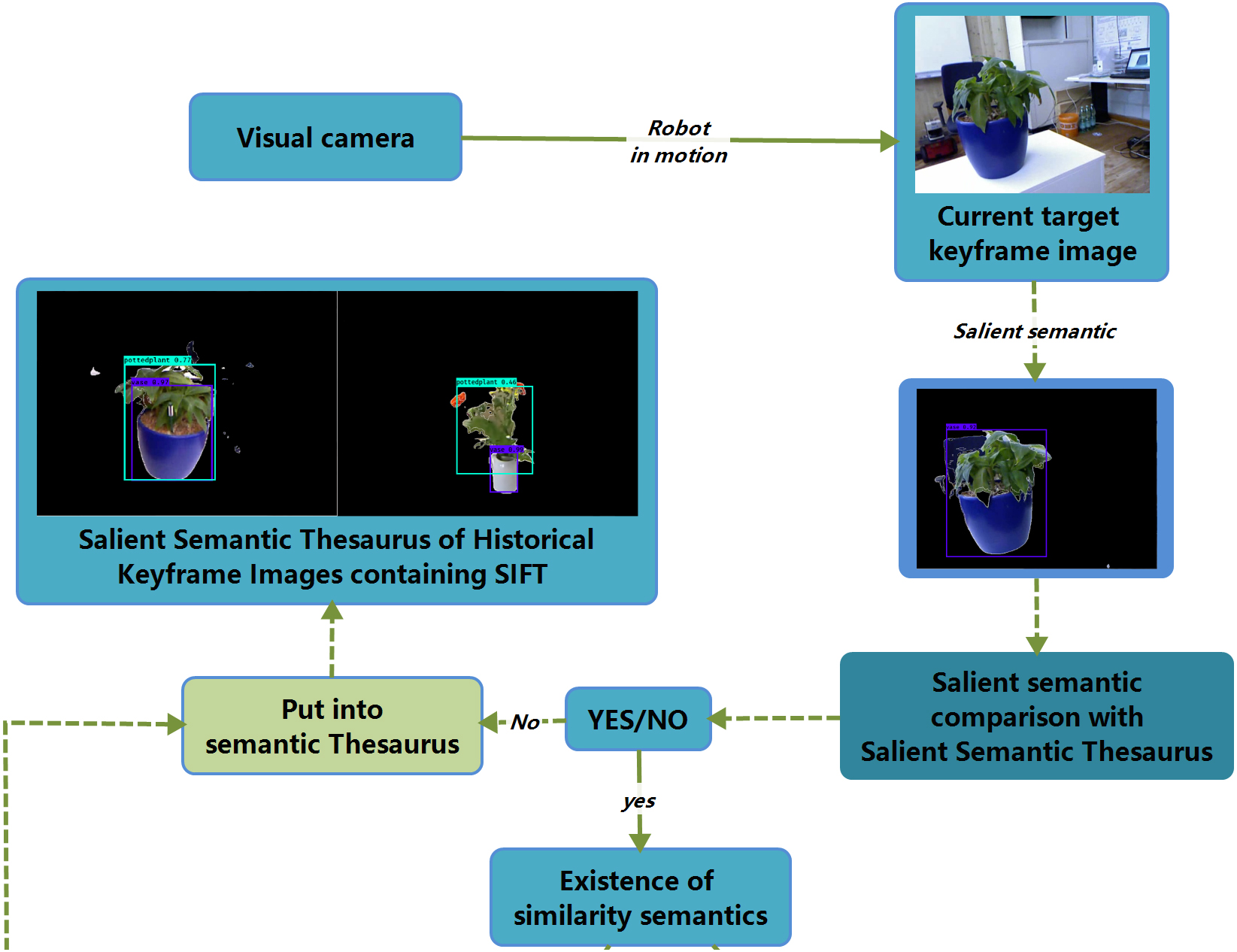
Vision-based closed-loop detection can effectively eliminate the cumulative error of the robot’s visual odometer. The main closed-loop detection BOVW and Semantic research Route faces some bottlenecks. We propose a salient Semantic-SIFT research idea for improving this task, including (1) the salient detection neural network filters excessive scene background information. (2) the neural network labels the semantics of salient objects. (3) comparing the tested salient semantics with the thesaurus to get the potential closed-loop scene. (4) the similarity is calculated based on SIFT features for similarity verification. Our algorithm is based on semantic and SIFT features for complementary advantages. Compared with the panoramic semantic and BOVW way, our algorithm saves computation effort by comparing only the scene’s salient semantics, simplifying semantic word bag construction and map description, as well as simplifying the SIFT similarity comparison of every pair of images. Experiments show that the proposed algorithm performs well in evaluation indicators and excellently in real time for closed-loop detection compared with some recent widely concerned works. The proposed semantic plus SIFT feature fusion from coarse to fine is a new research way for closed-loop detection.

The automatic detection and identification of fish food processing factory images are of great significance for fishery products. However, due to the small size of fish food processing, target detection has considerable challenges and complex issues. In the last decade, numerous target detection methods for food have been proposed, such as methods based on infrared light, spatial-temporal joint processing models and human visual attention, but the detection of small food targets for food processing has not been fully investigated. In this regard, based on the characteristics of small fish food processing factories, a novel detection pattern based on improved You Only Look Once v5 (YOLOv5) is proposed to focus on the essential features of small fish food processing targets in this study. Compared with YOLOv5 anchor frames, YOLOv5 Small Target Detection (YOLOv5-STD) has an extra set of small selection boxes, which is sensitive to small food objects in fish processing factory images. By incorporating the optimization path aggregation network (PANet) function, the solution method of YOLOv5-STD is proposed, and its head neck architecture is optimized. A series of experimental results show that the proposed method can be used to detect small fish food processing targets more accurately and reliably than state-of-the art methods.
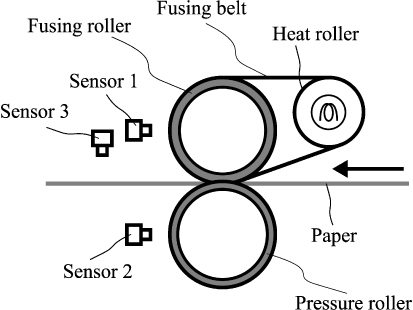
Since the fusing process in electrophotography has a significant impact not only on printing quality but also on machine internal temperature and toner blocking on outlet tray, accurate paper temperature prediction for various types of papers is essential, especially in the production printing. To develop the thermophysical model of fusing process to predict the paper temperature after the fusing process, thermal properties such as thermal conductivity, specific heat, and thermal contact resistance of several types of papers are necessary. However, paper is composed of complex fiber, surface coating, filler, and moisture, making it difficult to measure thermophysical properties of paper accurately. This work developed a machine learning (ML) model that can predict the thermophysical properties of paper based on a conventionally used 1D thermal network model of the fusing process and experiment results. The thermophysical properties of each paper obtained by ML and the thermophysical properties obtained by the conventional method were input to the thermal network model to predict the paper temperature after the fusing process and compared with the measured paper temperatures of the experiment. The results showed that the paper temperature was predicted with higher accuracy by using thermophysical properties obtained by ML than that by the conventional method. Although the method for predicting paper temperature by using only ML had been proposed, it had the disadvantage of requiring a large number of training experiments. In contrast, this method trained under the conditions of one fusing temperature and two printing speeds, and was able to predict under five fusing temperatures and four printing speeds.
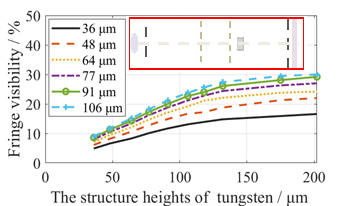
The X-ray Talbot–Lau interferometer is a sensitive method for probing wavefront phase distribution and high-energy-density plasmas. In this study, we have quantitatively calculated the fringe visibility obtained using an X-ray cascaded Talbot–Lau interferometer (CTLI) with W-absorption gratings of different structural heights. A cascaded configuration with different W-absorption gratings was built experimentally to verify the validity of the calculation results. The relationship between the sensitivity of the interferometers and the duty ratio of the gratings is also discussed. The analytical results presented in this study will be useful for optimizing the design and fabrication of W-absorption gratings to improve the sensitivity of X-ray CTLI.
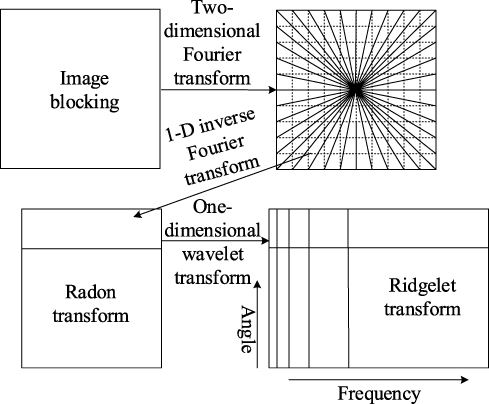
In order to encrypt and watermark the pixel flipped text image, a digital watermarking algorithm for pixel flipped text image based on calculus operator is proposed. The original image is evenly divided into blocks, and subsequently then the sub block is subjected to the fundamental wave transformation of the calculus operator. The embedding position is determined by combining the characteristics of the human visual system (HVS) and the parity quantization algorithm. The watermark information is embedded into the sub block, and the differential operator is used to perform the inverse ridgelet transformation on the sub block to obtain the watermark image. The sum of the absolute differences of adjacent pixels is used to calculate the correlation, and the pixel fluctuation function is designed to improve the accuracy of image restoration and the embedding capacity and expand the key space. The mean value of histogram is used as the calibration point to avoid the possibility of synchronization attack through synchronous embedding and detection process. The watermark information is added to the low frequency part of the image to enhance the robustness of the watermark. The watermark information is added to the low frequency part of the three-level lifting wavelet decomposition of the image, and the three-level lifting wavelet inverse transform is performed according to the wavelet coefficients after embedding the watermark information, so as to obtain the color image fraction containing the watermark, and achieve the digital watermark acquisition of pixel flipped text image. The simulation results show that the proposed method is robust for extracting digital watermark from pixel flipped text images, achieves blind inspection of watermark images with high security. The quality of watermarked images with different embedding capacities is good, and the watermark information can be completely extracted. Compared with other methods, better watermark embedding rate, extraction accuracy and robustness is seen with the proposed method.
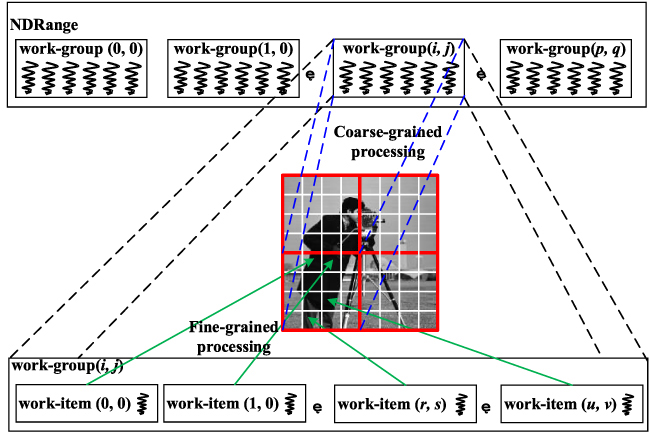
Edge detection algorithms are widely used in image segmentation, image fusion, computer vision, and other fields. The traditional LoG edge extraction algorithm has limitations, such as slow computing speed, occupying host resources, and so on. In order to overcome these limitations, a parallel algorithm of LoG edge extraction based on OpenCL is designed and implemented. First, the Gaussian filtering and Laplacian differential operation in the LoG algorithm are parallelized, and the parallelism of the LoG algorithm is improved from the algorithm structure. At the same time, the GPU’s many-core architecture is used to process each sub-image block in parallel, and each work-item is responsible for one pixel so that the processing objects can be processed in parallel. In addition, strategies such as memory access vectorization, local memory optimization, and resource optimization are adopted to further improve the performance of the kernel. The experimental results show that the parallel optimized LoG algorithm has achieved 21.9 times, 4 times, and 1.09 times speedup compared with the CPU serial algorithm, OpenMP parallel algorithm, and CUDA parallel algorithm, respectively. The feasibility, effectiveness, and portability of the algorithm are verified, and it has good prospects in engineering applications.