
It is time-consuming and labor-intensive to detect rice diseases manually. The purpose of this research is to develop a convolutional neural networks (CNNs)-based system to automatically detect the diseased rice leaf infected with rice leaf blast, helminthosporium leaf blight, and bacterial leaf blight. The sizes of rice leaf spots vary with the severity of disease infection. A single model based CNN cannot effectively classify images, especially for images with objects of small size as well as multiple object scales, and complicated image background. In this research, a multiscale serial convolution neural network (MSSCNN) and a multiscale parallel convolution neural network (MSPCNN) are proposed to identify diseased rice leaf spots based on multi-modal fusion to extract different perception features and combine them to improve the performances obtained by using only one modality. Experimental results delineate that MSSCNN and MSPCNN can get better performance in identifying the diseased rice leaves. In MSPCNN, the features of tiny spots on diseased rice leaves can be completely preserved. MSPCNN can hence offer better performances than MSSCNN. Additionally, MSPCNN architecture is suitable for parallel computing environment.
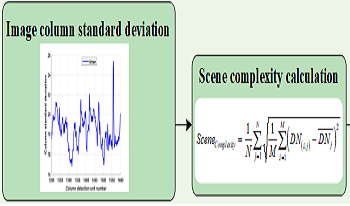
To improve the quality of optical remote sensing images, this paper proposes an adaptive moving window moment matching method for non-uniformity correction of remote sensing images. First, the scene complexity of the remote sensing image to be corrected is calculated, and the range of the width of the moving window is determined accordingly; Subsequently, the local scene complexity of the image in the window centered on the column to be corrected is calculated, and the width of the moving window is controlled adaptively; the correction gain and offset values of the column to be corrected of the image in the moving window are then calculated, and the correction of the columns to be corrected is performed accordingly; finally, the whole remote sensing image is traversed, and moment matching correction is performed column by column, and the correction of the non-uniformity of the whole remote sensing image is completed. The experimental results show that the non-uniformity correction effect of this algorithm is better than other competing algorithms, and the mean value of non-uniformity coefficient of the corrected image is reduced by more than 0.1802% compared with the minimum value in other comparison algorithms, which effectively eliminates the streak and stripe noise in the image, and better preserves the detailed information of the image.

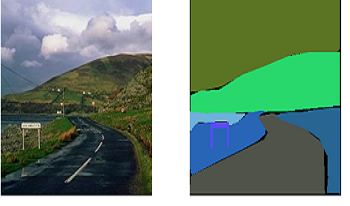
Recent advances in convolutional neural networks and vision transformers have brought about a revolution in the area of computer vision. Studies have shown that the performance of deep learning-based models is sensitive to image quality. The human visual system is trained to infer semantic information from poor quality images, but deep learning algorithms may find it challenging to perform this task. In this paper, we study the effect of image quality and color parameters on deep learning models trained for the task of semantic segmentation. One of the major challenges in benchmarking robust deep learning-based computer vision models is lack of challenging data covering different quality and colour parameters. In this paper, we have generated data using the subset of the standard benchmark semantic segmentation dataset (ADE20K) with the goal of studying the effect of different quality and colour parameters for the semantic segmentation task. To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the first attempts to benchmark semantic segmentation algorithms under different colour and quality parameters, and this study will motivate further research in this direction.
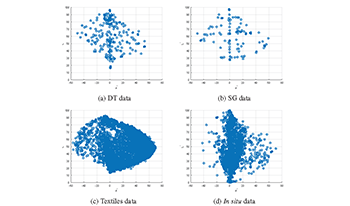
We investigate the relationship between goodness measures of spectral sensitivities to actual ΔE performance in the presence of signal dependent noise. We show that the Vora value does not perform as well as Sharma’s figure of merit (FOM). In addition, we show that Sharma’s FOM has issues when the spectral samples include lower luminance data. We introduce an FOM that accounts for signal dependent noise and has a linear relationship to ΔE performance. The improvement introduced by including signal dependent noise in the FOM results in closer relationships of the FOM to colorimetric accuracy in all cases but is especially important when the ensemble under investigation has a wide range of luminance values.

Objects in nature have diverse appearances, and appearance is one of the elements constituting the unique visual aspect of an object. However, previous studies have shown that when an object is represented as a digital image, its appearance can change compared to the real object depending on the material. In this study, the focus was on the “bumpiness” of the object surface, whereby a method was proposed to edit the bumpiness of the object in the image. First, the statistics obtained from images were analyzed in relation to the sensibility value of the bumpiness perceived by humans. Since the statistics on the original image could not fully explain the perception of bumpiness, analyses were conducted on multiscale images. The results suggested that the mean, standard deviation, and top, defined as the average of the luminance values within the top 10 [percentile], were highly influential as cues for bumpiness perception. The results also indicated that the components in the range of 5–65 [cycles per image-width] were highly influential. Based on these analysis results, a method is proposed to edit bumpiness perception by modulating components in the low and medium frequency bands. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated by image modulation experiments on objects of various materials.
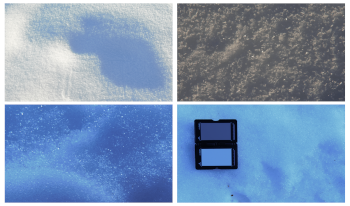
Sparkle from snow is a common phenomenon in Nature but not well studied in the literature. We perform a statistical study on digital snow images captured in-situ to analyze sparkle events by using contrast and density of sparkle spots descriptors. The method for measuring sparkles by Ferrero et al. is adapted, tested, and verified to the case of snow. The dataset is divided into three categories representing the type of snow acquired: dense snow, fresh snow, and old snow. Our analysis highlights the link between the sparkle of snow, the nature of snow and its grain structure. Sparkle could thus be a feature used for snow classification.
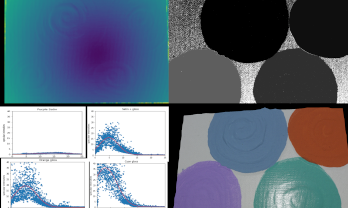
Spatially varying bidirectional reflectance distribution functions (SVBRDFs) play an important role in appearance modeling of real-world surfaces. Automatic capture of these surface properties is highly desirable, but many techniques only partially capture these properties or use complicated setups to do so. Micro surface roughness variations are especially difficult to capture using image-based methods. In this paper, we propose a novel approach towards estimating the complete SVBRDFs of surfaces using a portable projector-camera system made of standard consumer-grade components. Our approach uses insights about the relations between the illumination and viewing geometry and captured image statistics to estimate surface reflectance properties. Our technique should be of great value to practitioners seeking to model and render the geometric and reflectance properties of complex real-world surfaces.
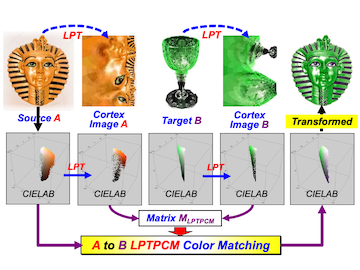
MA (Material Appearance) is a perceptual phenomenon that our brain deciphers from the retinal image. What features of retinal image are most closely related to the stimulus inside the visual cortex of V1 ∼ V5? The function of V1 is the most well-studied. V1 has the function of seeing fine in the fovea and rough in the periphery, and is mathematically described by LPT (Log-Polar Transform).
Since LPT samples the retinal image at a higher rate in the fovea but at lower rate peripherally, the color information tends to gather in center of V1. Paying attention to this LPT features in V1, we reported a novel method to transfer MA from one to another scenes. After LPT, PCM (Principal Component Matching) is applied to match the color distribution between source and target scenes. By just showing the target scene as an example, our previously reported LPT-PCM model can transfer the MA of target to that of source without any a priori information. However, this model had drawbacks such as changes in appearance depending on the background margins and unpredictable results for the scenes consisting of multiple color clusters.
This article explores measures to overcome such drawbacks and discusses the applicability of proposed LPT-PCM. Finally we propose a new numerical index to evaluate the similarity between the target and the transferred with the examined samples.