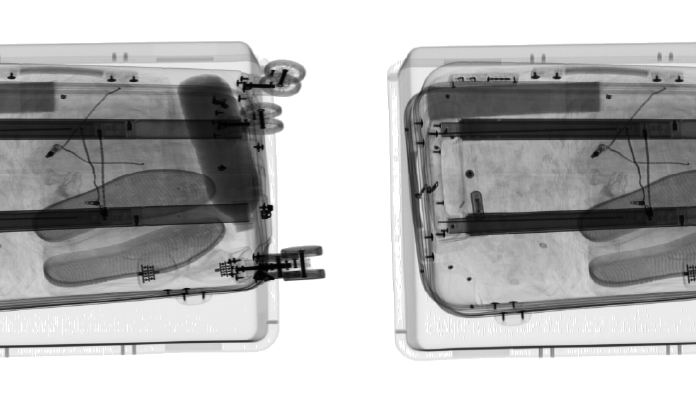
The utilization of dual-energy X-ray detection technology in security inspection plays a crucial role in ensuring public safety and preventing crimes. However, the X-ray images generated in such security checks often suffer from substantial noise due to the capture process. The noise significantly degrades the quality of the displayed image and affects the performance of the automatic threat detection pipeline. While deep learning-based image denoising methods have shown remarkable progress, most existing approaches rely on large training datasets and clean reference images, which are not readily available in security inspection scenarios. This limitation hampers the widespread application of these methods in the field of security inspection. In this paper, we addressed a denoising problem designed for X-ray images, where the noise model follows a Poisson-Gaussian distribution. Importantly, our method does not require clean reference images for training. Our denoising approach is built upon the Blindspot neural network, which effectively addresses the challenges associated with noise removal. To evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed approach, we conducted experiments on a real X-ray image dataset. The results indicate that our method achieves favorable BRISQUE scores across different baggage scenes.
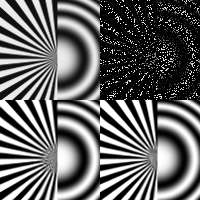
In this paper, we investigate the challenge of image restoration from severely incomplete data, encompassing compressive sensing image restoration and image inpainting. We propose a versatile implementation framework of plug-and-play ADMM image reconstruction, leveraging readily several available denoisers including model-based nonlocal denoisers and deep learning-based denoisers. We conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis against state-of-the-art methods, showcasing superior performance in both qualitative and quantitative aspects, including image quality and implementation complexity.

Facial video inpainting plays a crucial role in a wide range of applications, including but not limited to the removal of obstructions in video conferencing and telemedicine, enhancement of facial expression analysis, privacy protection, integration of graphical overlays, and virtual makeup. This domain presents serious challenges due to the intricate nature of facial features and the inherent human familiarity with faces, heightening the need for accurate and persuasive completions. In addressing challenges specifically related to occlusion removal in this context, our focus is on the progressive task of generating complete images from facial data covered by masks, ensuring both spatial and temporal coherence. Our study introduces a network designed for expression-based video inpainting, employing generative adversarial networks (GANs) to handle static and moving occlusions across all frames. By utilizing facial landmarks and an occlusion-free reference image, our model maintains the users identity consistently across frames. We further enhance emotional preservation through a customized facial expression recognition (FER) loss function, ensuring detailed inpainted outputs. Our proposed framework exhibits proficiency in eliminating occlusions from facial videos in an adaptive form, whether appearing static or dynamic on the frames, while providing realistic and coherent results.
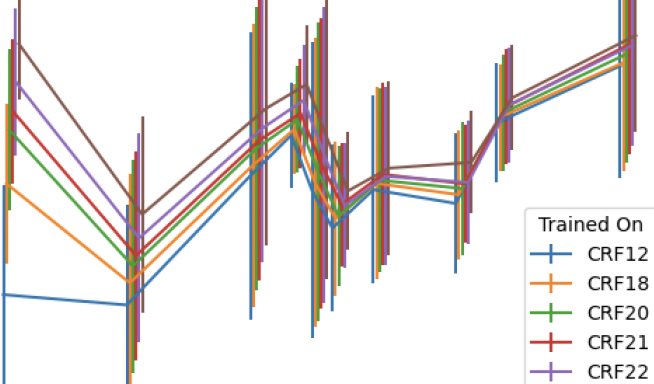
Remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) is a camera based technique used to estimate a subject's heart rate from video. It exploits the difference in light reflection between blood-dense tissue and other tissue by detecting small variations in the color of RGB pixels on skin. While often undetectable to the human eye, these subtle changes are easily detectable from high-quality video. Working with high-quality video presents many challenges due to the amount of storage space required to house it, computing power needed to analyze it, and time required to transport it. These problems can be potentially mitigated through the use of compression algorithms, but modern compression algorithms are unconcerned with maintaining the small pixel intensity variations within or between frames that are needed for the rPPG algorithms to function. When provided with compressed videos, rPPG algorithms are therefore left with less information and may predict heart rates less accurately. We examine the effects of compression on deep learning rPPG with multiple commonly used and popular compression codecs (H.264, H.265, and VP9). This is done at a variety of rate factors and frame rates to determine a threshold for which compressed video still returns a valid heart rate. These compression techniques are applied against multiple public rPPG datasets (DDPM and PURE). We find that rPPG trained on lossless data effectively fails when evaluated on data compressed at compression constant rate factors (CRFs) of 22 and higher for both H.264 and H.265, and at a constant-quality mode of CRF above 37 for VP9. We find that training on compressed data yielded less accurate results than training on loss-less or less compressed data. We did not find any specific benefit to training and testing on data compressed at identical compression levels.
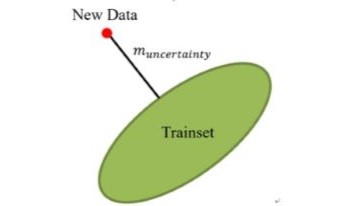
Although CNN-based classifiers have been successfully applied to object recognition, their performance is not consistent. In particular, when a CNN-based classifier is applied to a new dataset, the performance can substantially deteriorate. Furthermore, classification accuracy for certain classes can be very low. In many cases, the poor performance of ill-performing classes is due to biased training samples, which fail to represent the general coverage of the ill-performing classes. In this paper, we explore how to enhance the training samples of such ill-performing classes based on coverage optimization measures. Experimental results show some promising results.
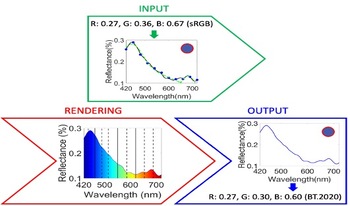
Spectral rendering encompasses methods aimed at generating synthetic imagery with realistic color expression by simulating the interaction of light with different materials and wavelengths. Unlike conventional rendering methods that use tristimulus RGB values as input, spectral rendering uses the full spectrum of light as input, which allows for more accurate color reproduction and more realistic visual effects. Spectral rendering poses many new challenges in terms of input data acquisition, memory use, and efficiency. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive survey of the recent advances and open problems in spectral rendering, covering the main stages of the rendering pipeline such as spectrum sampling and reconstruction, RGB to spectrum upsampling, and selection of paths and wavelengths at rendering. We also discuss the applications that benefit from spectral rendering. Our goal is to provide an elaborate overview of the current state-of-the-art and to identify future research directions and opportunities in this exciting field.

There are many electronic documents salient to read for each given topic; however, finding a suitable reading order for pedagogical purposes has been underserved historically by the text analytics community. In this research, we propose an automatic reading order generation technique that can suggest a suitable and optimal reading order for curriculum generation quantitatively. It is necessary to read the relevant documents in some logical order to understand the topics clearly. There are many learning pedagogies advanced, so for our purposes we use the author-supplied reading orders of salient content sets for ground truth. Our method suggests the best reading order automatically by checking the relevant topics, document distances, and semantic structure of the given documents. The system will generate a suitable and efficient reading sequence by analyzing the information, similarity, overlap of contents, and distances using word frequency, and topic sets. We measure the similarity, relevance, distance, and overlap of different documents using cosine similarity, entropy relevance, Euclidean distances, and Jaccard similarities respectively. We propose an algorithm that will generate the best possible reading order for a set of given documents. We evaluated the performance of our system against the ground truth reading order using different kinds of textbooks and generalized the finding for any given set of documents.
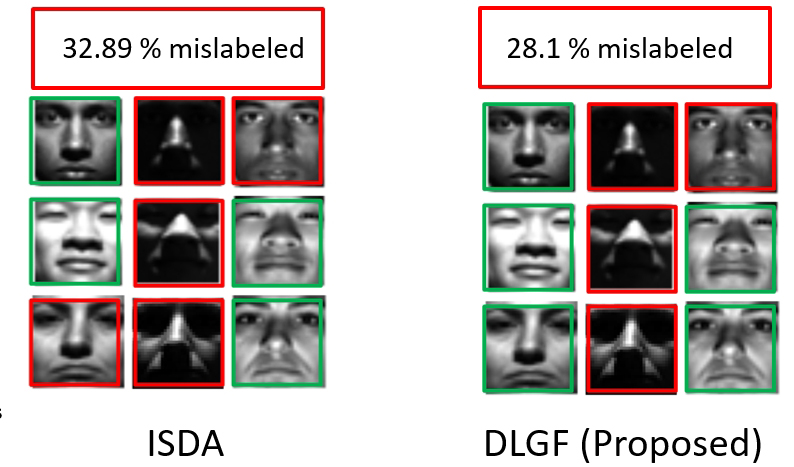

In this paper, a novel framework for semi-supervised learning based on graphs is introduced. We present an innovative approach for concurrently estimating label inference and performing a linear transformation. This specific linear transformation is directed towards achieving a discriminant subspace, which effectively reduces the dimensionality of the data. To enhance the semisupervised learning process, our framework places a strong emphasis on leveraging the inherent data structure and incorporating the information provided by soft labels from the available unlabeled samples. The method we propose ultimately results in an improved discriminative linear transformation. The effectiveness of our approach is verified through a series of experiments conducted on real image datasets. These experiments not only confirm the efficacy of our proposed method but also demonstrate its superior performance when compared to semi-supervised methods that simultaneously incorporate integration and label inference.

In the dynamic realm of image processing, coordinate-based neural networks have made significant strides, especially in tasks such as 3D reconstruction, pose estimation, and traditional image/video processing. However, these Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) models often grapple with computational and memory challenges. Addressing these, this study introduces an innovative approach using Tensor-Product B-Spline (TPB), offering a promising solution to lessen computational demands without sacrificing accuracy. The central objective was to harness TPB’s potential for image denoising and super-resolution, aiming to sidestep computational burdens of neural fields. This was achieved by replacing iterative processes with deterministic TPB solutions, ensuring enhanced performance and reduced load. The developed framework adeptly manages both super-resolution and denoising, utilizing implicit TPB functions layered to optimize image reconstruction. Evaluation on the Set14 and Kodak datasets showed the TPB-based approach to be comparable to established methods, producing high-quality results in both quantitative metrics and visual evaluations. This pioneering methodology, emphasizing its novelty, offers a refreshed perspective in image processing, setting a promising trajectory for future advancements in the domain.

Deep learning has enabled rapid advancements in the field of image processing. Learning based approaches have achieved stunning success over their traditional signal processing-based counterparts for a variety of applications such as object detection, semantic segmentation etc. This has resulted in the parallel development of hardware architectures capable of optimizing the inferencing of deep learning algorithms in real time. Embedded devices tend to have hard constraints on internal memory space and must rely on larger (but relatively very slow) DDR memory to store vast data generated while processing the deep learning algorithms. Thus, associated systems have to be evolved to make use of the optimized hardware balancing compute times with data operations. We propose such a generalized framework that can, given a set of compute elements and memory arrangement, devise an efficient method for processing of multidimensional data to optimize inference time of deep learning algorithms for vision applications.