
Traditional gun archiving methods are mostly carried out through bullets’ physics or photography, which are inefficient and difficult to trace, and cannot meet the needs of large-scale archiving. Aiming at such problems, a rapid archival technology of bullets based on graph convolutional neural network has been studied and developed. First, the spot laser is used to take the circle points of the bullet rifling traces. The obtained data is filtered and noise-reduced to make the corresponding line graph, and then the dynamic time warping (DTW) algorithm convolutional neural network model is used to perform the processing on the processed data. Not only is similarity matched, the rapid matching of the rifling of the bullet is also accomplished. Comparison of experimental results shows that this technology has the advantages of rapid archiving and high accuracy. Furthermore, it can be carried out in large numbers at the same time, and is more suitable for practical promotion and application.

In various social activities, people usually focus on the other person’s facial expression, which is an important element in interpersonal communication. The facial expression typically reflects a person’s current mood and conveys emotional information. Perceiving the facial expressions of people in images through cameras has always been a popular research topic. Previous studies have classified facial expressions into different categories, such as happy, sad, fear, angry, calm, disgust and surprise, and have identified them using image processing methods. However, traditional image processing methods have a low detection efficiency and low recognition accuracy due to variation of perspectives. As a result, most of them can only be applied to the front face and short distance situations. In this paper, we propose a lightweight deep learning framework for facial expression recognition using Octave convolutional neural network (FerOctNet). FerOctNet including multi-scale convolutional processing and residual learning is able to obtain multi-scale features with enriched representation ability by integrating the deep level features with rich semantic information with shallow details of the features. Compared with other deep learning networks, not only does the proposed method have a good recognition rate, but also contains fewer parameters in the network.
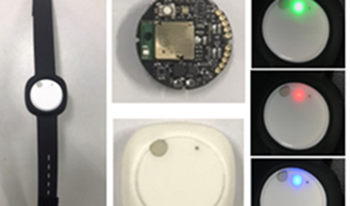
The inertial measurement unit (IMU) is a popular sensor device, which is mainly employed to acquire body or hand gesture action information for performing specific recognition tasks. We present a dual-channel artificial neural network (ANN) recognition decision hybridization scheme incorporated with deep leaning of IMU-based spectrogram images for cognition of several common hand gesture intention categorization actions focused on the 6-axis IMU sensing data (containing 3-axis accelerometer and 3-axis gyroscope information) and the 6-axis IMU derived spectrogram images. In this hand gesture intention cognition approach, both symmetric and asymmetric ANN structures are considered for intention action classifications. The proposed dual-channel ANN decision fusion framework contains one ANN recognition channel with inputs of “6-axis IMU raw data” and the other ANN recognition channel with inputs of “IMU spectrogram image derived-critical deep learning features”. Recognition decisions estimated from either of these two ANN recognition channels form the fusion framework. Three fusion schemes on dual-channel ANN recognition decisions are presented in this study, channel output layer accumulation, same channel candidate output and same-or-dual channel candidate output. In this study, the well-known deep learning neural network, visual geometry group- convolution neural network (VGG-CNN), is employed to carry out deep learning computations on IMU-based spectrogram images, from which, the critical deep learning feature of each spectrogram image can then be extracted and used as an input for the dual-channel ANN. For recognition performance comparisons, hand gesture intention recognition by the traditional VGG-CNN deep neural network approach (i.e. recognition of IMU spectrogram images using typical deep learning of the CNN model) is also performed. Experiments on classifications of six hand gesture intention actions show that the presented dual-channel ANN decision fusion incorporated with deep learning of IMU spectrum images has competitive performances, reaching better recognition accuracy than traditional CNN deep learning.
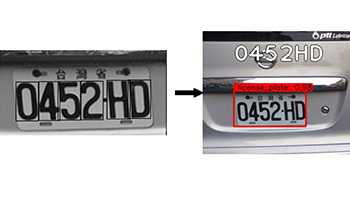
Deep learning is a research field with great application potential. However, training a deep learning model requires a large amount of paired data, which is time-consuming and expensive for real-world applications. In light of this problem, researchers have conducted methods to overcome the lack of training data, including data augmentation, data enhancement, transfer learning, and semi-supervised learning (SSL). Based on this concept, in this study, we conduct a self-training method to fine-tune a YOLOv4 license plate detection framework that requires only a limited amount of training datasets. The framework requires only a small amount of labeled data to complete the training process. Furthermore, this study utilizes Tesseract optical character recognition (OCR) on the detected license plates to achieve better performance. We propose a high-performance license plate recognition system for detecting different tilting angles and complex backgrounds.

The continuing development of remote sensing has resulted in a rapidly increasing number of remote sensing applications. High-resolution remote sensing images are used in various fields in the military. We propose methods for object detection based on remote sensing images. We develop a signal processing method for normalizing remote sensing images to eliminate noise such as fog, haze, and poor lighting. This method further improves detection accuracy and reduces error rates. We develop YOLOv4-faster, an accelerated neural network model based on the YOLO (You-Only-Look-Once) object detection method. YOLOv4-faster outperforms existing networks in terms of execution time and detection performance. We conduct a series of experiments on two public datasets (TGRS-HRRSD and NWPU VHR-10) as well as a dataset containing six military target classes provided by IMINT & Analysis and collected from Google Earth. YOLOv4-faster improves efficiency by utilizing multi-scale operations for the accurate detection of objects of various sizes, especially small objects. The experimental results show improved mAP (mean average precision) performance of the proposed method for object detection in remote sensing images. We thus propose a novel system for automatic object detection for high-resolution remote sensing images.
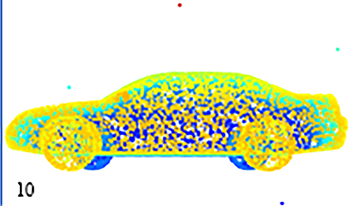
Nowadays, point clouds are frequently gathered by 3D scanners such as Lidar and Kinect, which produces thousands of point cloud models. Point cloud processing is vital to 3D vision, especially 3D object recognition, positioning, and navigation technology. Addressing uneven data density caused by coordinate frame transformations and the inherent problem of insufficient context connection in point clouds, the DiM-PCNet (Multi-scale and Multi-level Point Clouds Classification Network, and the Di is a prefix to represent double M in Multi-scale and Multi-level) is proposed in this paper. DiM-PCNet is provided for object classification with multi-scale and multi-level features. We encode the point cloud in multi-scale and fully fuse the features with the raw point cloud for keeping the context relationship. In DiM-PCNet, we sample the point clouds from eight parts for multi-scales feature extraction. The multi-scales features are fully fused by multi-level pyramid models. The multi-scale and multi-level strategies are applied in DiM-PCNet, in which the abundant and important features of point clouds are extracted and utilized in the 3D object classification. It is worth noting that the DiM-PCNet feature block can be embedded into the segmentation net, where the accuracy achieved is 87.1%. We conducted experiments on ShapeNet and ModelNet40 and the experimental results show that DiM-PCNet achieves state-of-the-art performance in 3D object classification. The experiment shows competitive performance on robustness and segmentation tasks.

The challenges of the aging population is becoming more and more prominent worldwide. Among them, in the face of the elderly fall phenomenon, human fall detection technology research and development has practical application value. Because of a large number of network parameters in the field of fall detection and the limited computing power of embedded devices, which makes it difficult to run on the embedded platform, this paper proposes an OT-YOLOV3 (OpenCV+Tiny-YOLOV3) fall detection method. In this method, Gaussian processing and other operations are used to preprocess the fallen image to avoid the influence of the angle change of the image on the recognition result. Then, the feature extraction network in Tiny-YOLOV3 was replaced by the MobileNet network to increase the number of network layers and reduce the number of parameters and calculations in the model. At the same time, the multi-scale prediction method was used to improve detection accuracy. Experimental results show that the accuracy of the proposed model is 10% higher than that of the YOLOV3 (You Only Look Once Version three) model, 4% higher than that of the Tiny-YOLOV3 model, 3% higher than that of the YOLOV3 model, 3% higher than that of Tiny-YOLOV3 model, and the model size is only 45% of that of YOLOV3 model and 65% of Tiny-YOLOV3. Compared with YOLOV3 and Tiny-YOLOV3 processing methods, the drop recognition effect is significantly improved and the model memory is reduced, which meets the requirements of real-time and efficient detection for embedded devices.
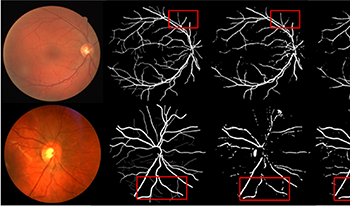
Fundus blood vessel segmentation is important to obtain the early diagnosis of ophthalmic- related diseases. A great number of approaches have been published, yet micro-vessel segmentation is still not able to deliver the desired results. In this paper, an improved retinal segmentation algorithm incorporating an effective channel attention (ECA) module is presented. Firstly, the ECA module is imported into the downsampling stage of a U-shape neural network (U-Net) to capture the cross-channel interaction information. Secondly, a dilated convolutional module is added to expand the receptive field of the retina, so that more micro-vessel features can be extracted. Experiments were performed on two publicly available datasets, namely DRIVE and CHASE_DB1. Finally, the improved U-Net was used to validate the results. The proposed method achieves high accuracy in terms of the dice coefficient, mean pixel accuracy (mPA) metric and the mean intersection over union (mIoU) metric. The advantages of the algorithm include low complexity and having to use fewer parameters.
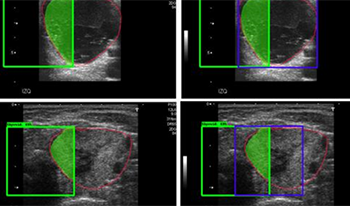
Thyroid nodules classification in ultrasound images is actively researched in the field of medical image processing. However, due to the low quality of ultrasound images, severe speckle noise, the complexity and diversity of nodules, etc., the classification and diagnosis of thyroid nodules are extremely challenging. At present, deep learning has been widely used in the field of medical image processing, and has achieved good results. However, there are still many problems to be solved. To address these issues, we propose a mask-guided hierarchical deep learning (MHDL) framework for the thyroid nodules classification. Specifically, we first develop a Mask RCNN network to locate thyroid nodules as the region of interest (ROI) for each image, to remove confounding information from input ultrasound images and extract texture, shape and radiology features as the low dimensional features. We then design a residual attention network to extract depth feature map of ROI, and combine the above low dimensional features to form a mixed feature space via dimension alignment technology. Finally, we present an AttentionDrop-based convolutional neural network to implement the classification of benign and malignant thyroid nodules in the mixed feature space. The experimental results show that our proposed method can obtain accurate nodule classification results, and hierarchical deep learning network can further improve the classification performance, which has immense clinical application value.