
One major innovation in improving organizations’ security measures is the adoption of AI-based vulnerability scanners within the cybersecurity space. The paper analyzes crosssectional survey research identifying factors that influence the acceptance and use of such advanced tools among cybersecurity professionals. The primary method of gathering data was a structured survey questionnaire that used Likert-scale questions to quantify the participants’ opinions objectively. It contained 20 questions based on established models, including TAM, UTAUT, and IDT. In this research, the total number of people who responded to the survey was 49, comprising cybersecurity professionals working in various industry domains. This instrument has measured perceived usefulness, ease of use, performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, facilitating conditions, and the stages of adoption, including awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, and adoption. Our results provide insight into factors that drive or hinder the adoption of AI-based vulnerability scanners, focusing on the significant role of perceived benefits and organizational support. The present paper offers valuable implications for practitioners and researchers who aim to foster AI-driven security solutions within organizational contexts.

Open-source technologies (OSINT) and Social Media Intelligence (SOCMINT) are becoming increasingly popular with investigative and government agencies, intelligence services, media companies, and corporations. These OSINT and SOCMINT technologies use sophisticated techniques and special tools to efficiently analyze the continually growing sources of information. There is a great need for training and further education in the OSINT field worldwide. This report describes the importance of open source or social media intelligence for evaluating disaster management. It also gives an overview of the government work in Australia, Haiti, and Japan for disaster management using various OSINT tools and platforms. Thus, decision support for using OSINT and SOCMINT tools is given, and the necessary training needs for investigators can be better estimated.

Open-source intelligence is gaining popularity due to the rapid development of social networks. There is more and more information in the public domain. One of the most popular social networks is Twitter. It was chosen to analyze the dependence of changes in the number of likes, reposts, quotes and retweets on the aggressiveness of the post text for a separate profile, as this information can be important not only for the owner of the channel in the social network, but also for other studies that in some way influence user accounts and their behavior in the social network. Furthermore, this work includes a detailed analysis and evaluation of the Tweety library capabilities and situations in which it can be effectively applied. Lastly, this work includes the creation and description of a compiled neural network whose purpose is to predict changes in the number of likes, reposts, quotes, and retweets from the aggressiveness of the post text for a separate profile.

This paper presents a practical Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) use case for user similarity measurements with the use of open profile data from the Reddit social network. This PoC work combines the open data from Reddit and the part of the state-of-the-art BERT model. Using the PRAW Python library, the project fetches comments and posts of users. Then these texts are converted into a feature vector - representation of all user posts and comments. The main idea here is to create a comparable user's pair similarity score based on their comments and posts. For example, if we fix one user and calculate scores of all mutual pairs with other users, we will produce a total order on the set of all mutual pairs with that user. This total order can be described as a degree of written similarity with this chosen user. A set of "similar" users for one particular user can be used to recommend to the user interesting for him people. The similarity score also has a "transitive property": if $user_1$ is "similar" to $user_2$ and $user_2$ is similar to $user_3$ then inner properties of our model guarantees that $user_1$ and $user_3$ are pretty "similar" too. In this way, this score can be used to cluster a set of users into sets of "similar" users. It could be used in some recommendation algorithms or tune already existing algorithms to consider a cluster's peculiarities. Also, we can extend our model and calculate feature vectors for subreddits. In that way, we can find similar to the user's subreddits and recommend them to him.

Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) has come a long way, and it is still developing ideas, and lots of investigations are yet to happen in the near future. The main essential requirement for all the OSINT investigations is the information that is valuable data from a good source. This paper discusses various tools and methodologies related to Facebook data collection and analyzes part of the collected data. At the end of the paper, the reader will get a deep and clear insight into the available techniques, tools, and descriptions about tools that are present to scrape the data out of the Facebook platform and the types of investigations and analyses that the gathered data can do.
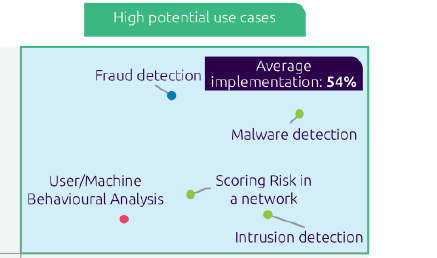
Companies are increasingly facing the challenges of a persistent cyber threat landscape. By means of AI, cyber attacks can be efficiently conducted more successful through offensive AI. As for cyber defense, AI can be also utilized against cyber threats (defensive AI). Due to limited resources, especially in small and medium-sized companies (SMEs), there is a need to deploy more effective defensive cyber security solutions. Precisely, the adaptation of AI-based resilient defenses must be driven forward. Therefore, the aim of this paper is to identify and evaluate AI-related use cases with a high impact potential on the cyber security level, while being applicable to SMEs at the same time. In order to reach the research goal, an extensive literature review of several online catalogs, surveys and online platforms was conducted. In conclusion, seven crucial AI-based security features were outlined that are providing a high impact potential to the security level for SMEs. Afterwards, the results are discussed and set into a broader context. Even though AI-based security solutions are providing a large range of advantages, certain challenges and barriers using AI-related security applications are addressed in the paper as well. A high need for usable state of the art AI based cyber security solution for SMEs was identified.

Industrial control systems are essential for producing goods, electricity generation, infrastructure maintenance, and the transport of energy, water, and gas. They form the core of the critical infrastructure of modern industrial nations and are therefore of particular interest. Through the increased inter-connectivity of formerly isolated ICS process environments and standard IT technologies such as Ethernet, processes can be optimized and synergies leveraged. However, ICS/SCADA also becomes the target of the same cyber-attacks as conventional IT systems. Therefore, it is necessary to combine IT security has accumulated knowledge and experience with the classic Safety-First-mentality of ICS/SCADA environments to avoid significant problems in the foreseeable future. The new course was created for precisely this purpose. The investigation of the security of systems and organizations in Red and Blue Teams has long proven it is worth and is used worldwide. The first part of the Red Team side exercise deals specifically with finding and exploiting security vulnerabilities. Red Teaming refers to an independent group that acts as a counterpart to an organization to improve its operational effectiveness and enhance its security. It is the declared goal of the Red Team to detect security vulnerabilities. This work is intended to convey this interfacing knowledge; in the practical exercises for Red Teaming, these hybrid infrastructures and systems’ weak points are identified and exploited. Students will participate in numerous hands-on exercises throughout the course using the tools and techniques that form the basis for attacks on infrastructure, such as industrial control systems. A detailed accompanying theory precedes the exercises, and the course is structured as follows:Introduction <list list-type="bullet"> <list-item>ICS Cyber Kill Chain</list-item> <list-item>Types of information gathering</list-item> </list>Red Team Tools <list list-type="bullet"> <list-item>Nmap</list-item> <list-item>Maltego</list-item> <list-item>Shodan</list-item> <list-item>Google hacking</list-item> <list-item>The Harvester</list-item> <list-item>Wireshark</list-item> <list-item>GrassMarlin</list-item> <list-item>Metasploit Framework (MSF)</list-item> <list-item>John the Ripper</list-item> </list>Exercise 1 - Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) <list list-type="bullet"> <list-item>Gathering information with Maltego</list-item> <list-item>Find Remote Access with Google and Shodan</list-item> </list>Exercise 2 - Analysis of network recordings <list list-type="bullet"> <list-item>Analysis of ICS network recordings with Wireshark</list-item> <list-item>Analysis of ICS network recordings with GrassMarlin</list-item> </list>

Industrial control systems are essential for producing goods, generating electricity, maintaining infrastructure, and transporting energy, water, and gas. They form the core of the critical infrastructure of modern industrial nations and are therefore of particular interest. Through the increased interconnectivity of formerly isolated ICS process environments and the use of standard IT technologies such as Ethernet, processes can be optimized and synergies leveraged.However, ICS/SCADA also becomes the target of the same cyber-attacks as conventional IT systems. It is, therefore, necessary to combine the accumulated knowledge and experience of IT security with the classic Safety-First-mentality of ICS/SCADA-environments in order to avoid significant problems in the foreseeable future.The new course was created for precisely this purpose. The approach of investigating the security of systems and organizations in Red and Blue Teams has long proven it is worth and is used worldwide.This second part of the exercises describes the Blue Team action in case of an attack and beyond.As opposed to Red Teaming, Blue Teaming is an independent group that develops defenses against Red Team activities to improve an organization’s effectiveness and security and tests and improves them during a Red Team attack.The present work aims to impart the interfacing knowledge; in the practical exercises of Blue Teaming, weaknesses of these hybrid infrastructures and systems are identified, and decisions are discussed on how to counteract possible attacks or even prevent them in advance. Throughout the course, students will participate in numerous practical exercises using the tools and techniques that form the basis of decision-making to prevent attacks on infrastructures, such as industrial control systems. A detailed accompanying theory precedes the exercises, and the course is structured as follows:Introduction <list list-type="bullet"> <list-item>ICS Cyber Kill Chain</list-item> <list-item>Types of information gathering</list-item> </list>Blue Team Tools <list list-type="bullet"> <list-item>VirusTotal</list-item> <list-item>Dynamic malware analysis with any.run</list-item> <list-item>Checksum generation with Linux commands</list-item> </list>Incident-Response Complex exercise: Part 1 <list list-type="bullet"> <list-item>Preparation</list-item> <list-item>Detection & Analyses</list-item> <list-item>Containment</list-item> </list>Incident-Response Complex exercise: Part 2 <list list-type="bullet"> <list-item>Eradication</list-item> <list-item>Recovery</list-item> <list-item>Post Incident Activity</list-item> </list>

TP-Link Technologies Co, Ltd. is a Chinese manufacturer of networking products and has a 42% share of the consumer WLAN market, making it the market leader. The company sells about 150 million devices per year. Many people worldwide use the Internet every day and are connected to the Internet with their computers. In the world of smart homes, even coffee machines, refrigerators, smart sockets, and light bulbs have found their way to the Internet, not to mention the many smartphones, which are, of course, also connected to the Internet. Since many different dangers come from a heater or printer and the many other smart devices directly connected to the Internet, there is a safe haven: the local area network. To connect to the Internet, one needs a modem, which is built into a router in many cases. Routers route network packets back and forth between several computer networks. They are used to connect to the Internet, and they are the bridge between the home network and the Internet in almost every household connected to the Internet. Because of their nature as a bridge between local and global networks, they are also the largest attack vector. [19] This paper examines how up-to-date the firmware of standard home network routers is and how secure the firmware is. In order to obtain a representative result, the examined routers were selected according to fixed rules. Each router had to be a product of the manufacturer TP-Link, the routers had to be in the low-budged range (less than 20 Euro) and be available from Amazon. Also, two different types of investigations were identified for the selected devices. Firstly, the devices were examined in the form of physically existing hardware, and secondly, an attempt was made to access the firmware via the manufacturer’s website. It was found that even the fixing of current vulnerabilities and recently released update files are no guarantee that older vulnerabilities have been fixed. Secrets such as private keys and certificates are hard-coded in the firmware and can be extracted from update files. Moreover, devices are deliberately built to make it impossible to install the latest alternative firmware.

Like many other industries, small and medium IT enterprises (IT SMEs) find themselves challenged by globalization and digital transformation. This paper highlights the implications and challenges for IT SMEs in the area of IT security, compliance, and data governance. It describes the secure and compliant integration of IT products and services of IT SMEs in order to enhance their relative competitive position against global players of the IT industry. The paper presents an approach that entails competence areas for IT security, compliance, and data governance and shows a web-based tool for surveying and measuring areas in order to derive actual readiness of IT SMEs in these areas. The paper concludes with an outlook on the expected findings and planned further developments of the approach and tool.