


The measurement of the appearance of objects as perceived by individuals is necessary to meet industrial needs (quality control at the end of the production line, realistic reproduction of a 3D object, generation of new visual effects) and societal needs (development of virtual reality, creation of digital twins of cultural heritage objects). This need for measurement, initially addressed by colorimetry, has become more complex over the past 20 years with the arrival of new effects such as "sparkle" in the automotive industry, iridescence in cosmetics, and new demands such as measuring translucency for 3D printing or satin finish for natural-looking objects. To characterize these new effects, traditional measurement techniques have naturally evolved toward bidirectional quantities such as BRDF, BTDF, SVBRDF, or BSSRDF! Metrologists have developed instruments capable of measuring these new quantities. Today, there are solutions for acquiring them all, using rotation platforms, robotic arms, HDR imaging sensors, and very bright LED sources.

Nowadays, industrial gloss evaluation is mostly limited to the specular gloss meter, focusing on a single attribute of surface gloss. The correlation of such meters with the human gloss appraisal is thus rather weak. Although more advanced image-based gloss meters have become available, their application is typically restricted to niche industries due to the high cost and complexity. This paper extends a previous design of a comprehensive and affordable image-based gloss meter (iGM) for the determination of each of the five main attributes of surface gloss (specular gloss, DOI, haze, contrast and surface-uniformity gloss). Together with an extensive introduction on surface gloss and its evaluation, the iGM design is described and some of its capabilities and opportunities are illustrated.
The measurement of specular gloss using a glossmeter is normalized in the ISO 2813 Standard, which is widely used for many industrial applications. In practice, the principle of the measurement relies on using a primary standard that approximates a perfectly polished back glass surface and an optical design where rectangular diaphragms are used for the source and detection apertures. Any deviation in the refractive index or the polishing level of the standard artefact, or in the machining of the rectangular diaphragms ends in measurement uncertainties. To tackle these issues, we propose to calculate the specular gloss from the bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) measured using a goniospectrophotometer equipped with a conoscopic detection. With such an instrument, no calibration sample is needed anymore, and the geometry of measurement given in the standard can be applied with good accuracy. The method has been implemented and tested on samples of various gloss values.
Naturalness is a complex concept and a number of parameters might impact naturalness perception. In this work, we addressed how the combination of different elevation levels and size of prints impacts naturalness perception of 2.5D prints. The results of a subjective ranking experiment showed that observers perceived 2.5D prints as more natural at higher elevation with larger size of print. Moreover, we observed that elevation seems to be a more dominant parameter than size of the print for observers when evaluating naturalness.
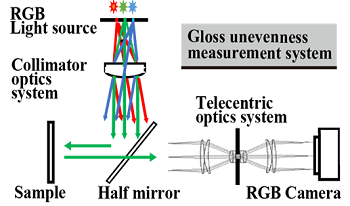
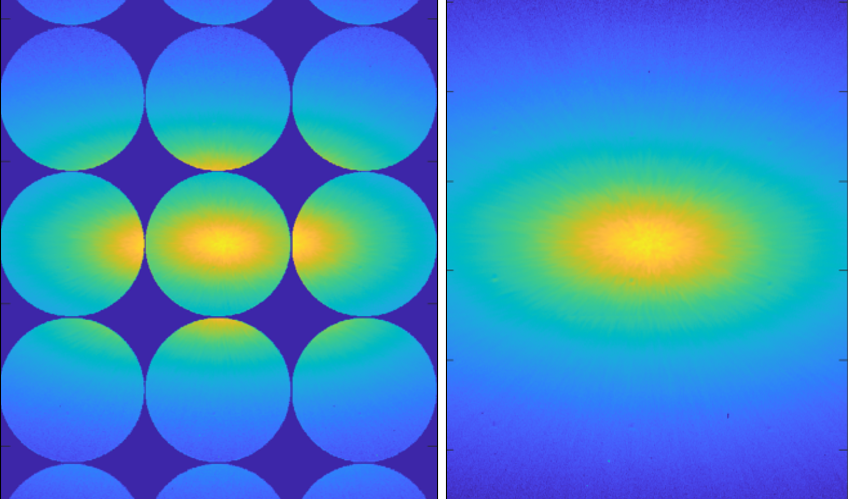
In this paper, we introduce the analysis for gloss unevenness by using developed multiple directional incident lights optics. Gloss unevenness is strongly related to recognition of material texture. However, it looks different depending on the angles, so it has been difficult to measure quantitatively. The gloss unevenness caused by surface roughness is able to analyze by the distribution of normal on the surface. We have developed the optical system that simultaneously illuminates with light from three different directions, angles, and captures images of gloss unevenness in one shot. We confirmed that the normal distribution of the surface can be estimated by analyzing the image. This proposed method can not only measure the gloss unevenness image, but also estimate the shape of the surface. As an application of this gloss unevenness observation technology, it is also possible to detect of scratches and coating unevenness in industrial quality control.
Accurate color reproduction is an essential parameter in many 3D printing applications. Although current technologies in full-color 3D printing have enabled the reproduction of thousands of colors, reproducing the precise target color is still challenging and requires tuning. In this paper, we integrate halftoning with a multi-layer printing approach, where ink is deposited at variable depths, to improve the reproduction of tones and fine details in poly-jet 3D printing. The proposed approach is implemented using a manually controlled ink placement add-on for a commercial 3D printer and is compared to the default software of that printer. Results demonstrate that the proposed multi-layer halftoning performs more accurately in reproducing the tones and details of the target appearance.
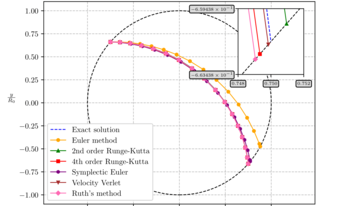
The primary objective of this paper is to demonstrate the utility of symplectic numerical techniques for ray tracing within gradient-index media. The relevant mathematics are explained in brief, deriving the optical Hamiltonian independently of the Lagrangian optical formalism before constructing a symplectic ray tracing algorithm. Numerical experiments with the Luneburg and Maxwell fish-eye lenses compare the effectiveness of symplectic methods with standard numerical integration techniques, challenging the idea that the increased accuracy of higher-order numerical methods justifies their elevated computational cost. Further uses for symplectic ray tracing are also discussed.