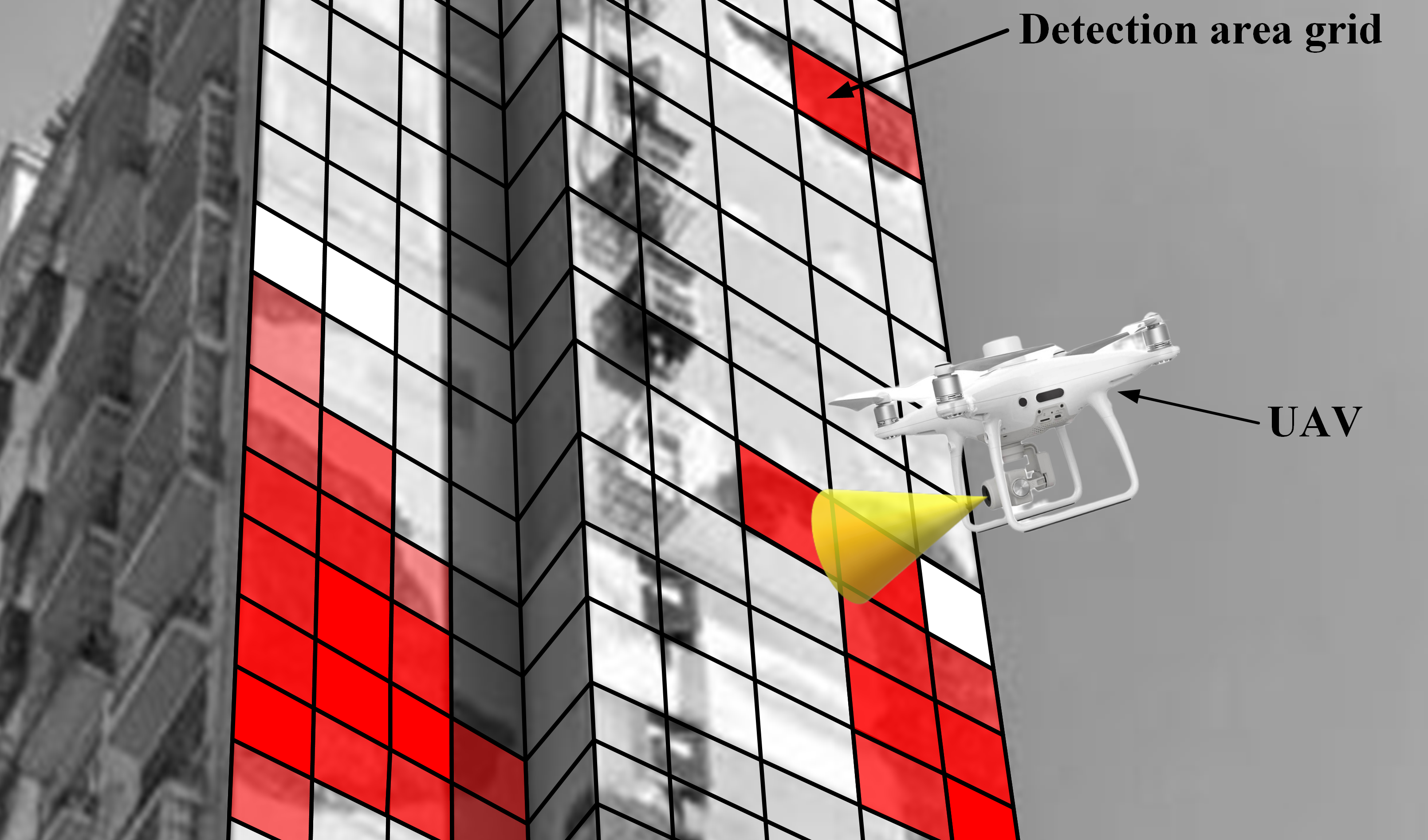
Considering the rapid acquisition and detection task of building enclosure damage information and the natural environment characteristics of building enclosure, a new unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) track planning framework considering image detection and UAV dynamic characteristics is proposed. Firstly, considering the position of UAV in the task space for track planning, combined with the characteristics of the sensor detection equipment carried by UAV, and the task requirements of extracting and identifying the damage edge features and texture features on the shell of the building; the detection efficiency and detection safety of UAV are improved to the maximum extent. Secondly, the Improved Circle Chaos Initialization Strategy, Adaptive Weight Strategy and Elite Perturbation Mechanism are introduced to solve the problem that the traditional honey badger algorithm (HBA) is easy to fall into local optimal solution and to ensure that the designed algorithm is more in line with the inspection planning requirements of the outer surface of the building. Furthermore, improved honey badger algorithm (IHBA) is compared with particle swarm optimization (PSO), whale optimization algorithm (WOA) and traditional badger algorithm in multi-dimensional horizontal through design simulation experiments, which shows that the design algorithm in this paper is efficient in solving the damage information collection of building enclosure.
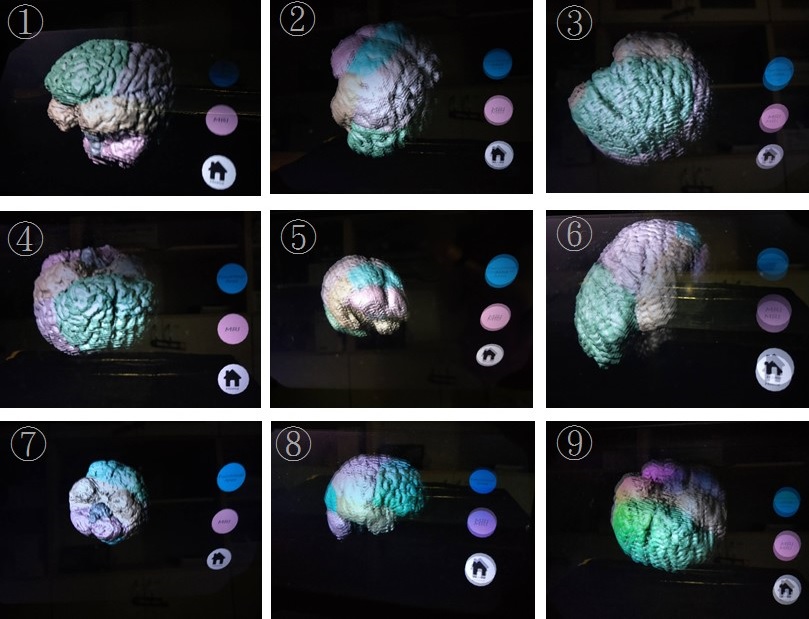
Two dimensional projections of three dimensional (3D) objects are used to teach anatomy. These projections are relatively unrealistic, and medical students cannot easily and accurately grasp the position and shape of each anatomical structure. As a remedy, 3D holographic projections allow for 3D anatomical structures to be projected in space without the use of worn contraptions. This study designed a method for optimizing 3D holographic projections with respect to the quality characteristics of 3D imaging definition and stereoscopic quality. The Taguchi method was used to determine the factors that most greatly influenced these quality characteristics, and the Delphi method and fuzzy theory were used to quantify image quality. Among three main factors of material of the projection panel, thickness of the projection panel, and angle made by the projection panel with the horizontal plane, thickness was the most influential. The optimal combination of factors was acrylic material, a thickness of 1 mm, and an angle of 45∘. This paper’s method aids medical pedagogy and can be used by the holographic projection manufacturing industry to optimize 3D imaging definition and stereoscopic quality.
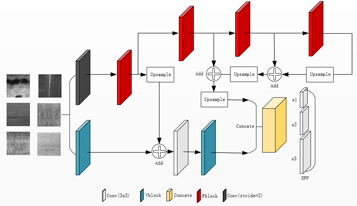
Defect detection is an imperative step in ensuring the quality of steel products. To overcome the problem of low accuracy and poor detection of subtle features in current detection methods, a revised neural network model structure has been proposed. VFSN’s main convolutional layer structure is VGG with residuals, where two convolutional blocks are designed. It’s connected to a spatial pyramid pool (SPP) after reducing the aliasing effects and detecting defect features at various scales by constructing multibranch inputs and multilevel feature overlays and fusions. Research on the open-source data set NEU-DET has shown high-accuracy recognition, with the recognition accuracy rate reaching 75.1% and an average accuracy rate improving by 2.7%. The F1 score improved by 1.3%. There’s a significant improvement in detecting small defects using the proposed network structure.
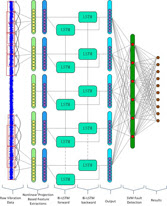
Machinery failure prediction and equipment health management is the key to reduce even prevent the occurrence of significant failures. In recent years, deep learning based intelligent fault diagnosis methods have become a hot topic of research in the field of machinery and equipment health management, especially the evaluation of the equipment health indicators and failure mode identification issues in complex environments. In this paper, a fused bidirectional long and short term memory (BiLSTM) and support vector machine (SVM) recurrent neural network deep learning algorithm is proposed to solve the problem of fast fault diagnosis of mechanical bearing vibration in complex environments. The algorithm uses a BiLSTM memory network as a feature extractor to capture fault features in the raw one dimensional (1-D) time series data, and then a SVM is used at the end of the network instead of the traditional softmax function as a classifier discriminator to further improve the accuracy of diagnosis. The experimental results indicate that the proposed algorithm model has higher diagnostic accuracy and faster diagnosis speed, and more suitable for fast diagnosis and real time detection of faults in complex environments.

To explore the characteristics of distance and speed perception of drivers in a tunnel environment, this paper investigates the difference and accuracy of driver’s distance perception inside and outside the tunnel by field test method and analyzes the influence of driver’s age on distance perception. In addition, the impact on tunnel contour mark height and spacing on speed perception is also studied based on the field test. The results show that: (1) whether inside or outside the tunnel, the perceived distance from the driver is generally larger when the speed is between [55,75] km/h, while the perceived distance is generally smaller than the true value when the speed is between [75,85] km/h. (2) The accuracy of distance perception is directly proportional to the driver’s age. (3) The vehicle type has a certain impact on speed perception under the same tunnel contour mark height, and the recommended height is 0.6–1.2 m. (4) For different vehicles, tunnel contour mark spacing of 15 m is the most conducive to driving safety, and it is recommended to be 10–20 m. At last, based on the distance and speed perception characteristics of drivers in the tunnel, a series of safety facilities optimization suggestions are put forward to ensure driving safety.
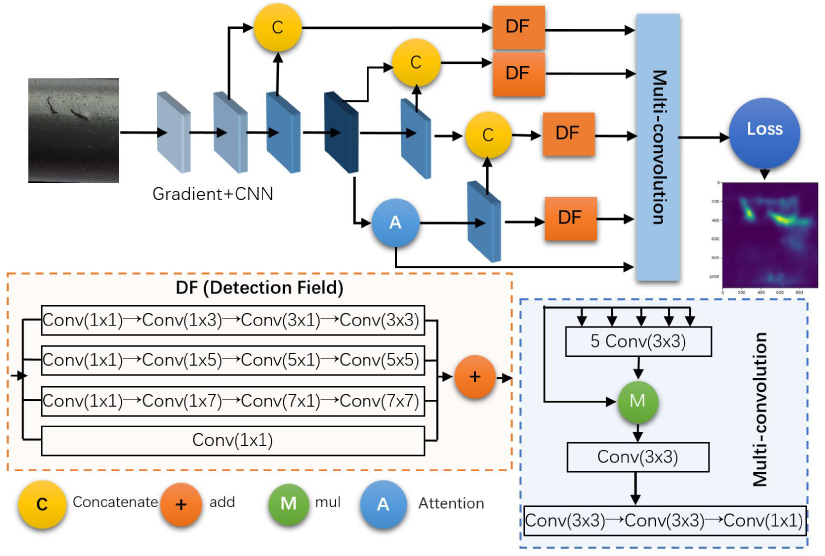
We propose a method for identifying the flaws on the product surface using a deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), making them more efficient and effective. Our approach – Gradient-weighted Flaw Detecting (GWFD), uses the gradients of the significant layers (identify the flaws in a CNN) to produce a localization map identifying the flaw areas on the product surface in the image for detecting industrial products. The problem with manual inspection is that it requires human and material resources, and accuracy cannot be guaranteed. The crux of identifying the flaws on the product surface is that the method can extract the features of the flaws and achieve a precise location. Unlike previous surface detection methods, GWFD combines an attention mechanism with edge detection to precisely focus on the flaw area of the product surface. At the same time, simple heuristic fine-tuning and reinforcement learning are applied during the training stage. Experiments show that GWFD achieves the precise location and detection of the flaws compared with other methods such as SIFT, KAZE, SSD MobileNet (V3), and SINet. GWFD helps users successfully inspect the flawed area of auto parts and has always been an industry pioneer for identifying flawed areas on the product surface. We hope that our work will promote and complete the practical application in more production lines.
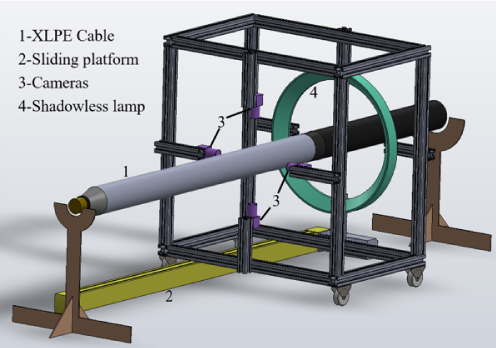
This study is aimed at the problems of inadequate accuracy and robustness of defect detection or subtle and insignificant defects located in 110 kV cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) cable joints. A two-stage CNN-based workmanship defect detection network (WDDCJNet) for XLPE cable joint is proposed. First, an improved attention mechanism called Parallel Convolutional Block Attention Module (PA_CBAM) incorporates parallel connections between the spatial attention and channel attention to enlarge the receptive field of the spatial attention mechanism. PA_CBAM further combined with ResNet50 and Feature Pyramid (FPN) to create an enhanced feature extraction network named PM_Resnet50_FPN, which is specifically designed to emphasize defect features and enhance the capability to extract subtle defects. Then, ROI Align is adopted to solve the problem of the offset of the mapping location area caused by the rounding operation to make anchor frame size more consistent with the defect scale. The K-means algorithm is also used to cluster the cable joint surface defect anchor frame. The proposed method is compared with the other state-of-art CNN algorithms on self-collected cable joints dataset. The experimental results prove that WDDCJNet can greatly improve the detection accuracy of five types of defects and meets the detection requirements of practical applications for cable joint workmanship defects.

In the area of reversible data hiding (RDH), multiple-histograms modification (MHM) has been widely recognized as one of the most high-performance techniques. With MHM, the correlation between the prediction-error (PE) and the local complexity (LC) can be well exploited for pixel sorting based data embedding, which is very important in MHM-based RDH algorithms for the obtained high image quality and the well-preserved embedding capacity. However, since PE and LC are usually obtained using different algorithms, their correlation may not be strong enough. In this paper, a novel correlation measurement is proposed by exploring the relationship of neighboring PEs to improve the performance of pixel sorting. In the proposed work, we first divide a cover image into non-overlapping cells of two pixels, and segment the pixel cells into two layers for layer-wise data embedding. Then, in the process of prediction, pixels in one layer are estimated from pixels in the other layer using a convolutional neural network (CNN), the loss function of which is designed to minimize not only the PE itself, but also the difference of PEs within the same pixel cell. Finally, both the difference of PEs and the LC are employed for pixel sorting to minimize the embedding distortion introduced by MHM. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
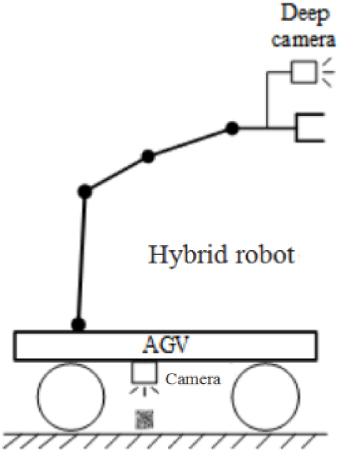
A hybrid robot fully integrates the merits of automated guided vehicle (AGV) and industrial manipulator. With the aid of computer vision algorithms, the camera on the AGV works like the eyes of the robot, making the robot highly intelligent. To promote the industrial application of the hybrid robot, it is necessary to enhance the navigation accuracy of the AGV and its ability to automatically handle materials in any pose. Therefore, this paper presents a fully automatic high-precision grasping system for the hybrid robot, which integrates the functions of high-precision visual positioning and automatic grasping. Both two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) features were employed to recognize the target. Specifically, the local features of the target were matched with those of the point cloud segment of the scene, and the pose transform matrix was obtained between the point cloud segment of the scene and the target, completing the recognition and positioning of the target. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieved a recognition rate of 97.6% in simple scenes, and 87.2% in complex, occluded scenes, and reduced the recognition time to merely 402.3 ms. The research results promote the application of the hybrid robot in industrial operations like automatic grasping, spraying, and stacking.
