
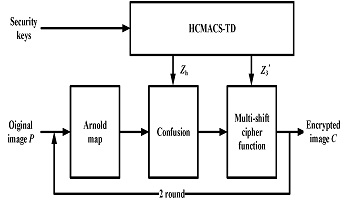
A novel image encryption algorithm based on delay induced hyper-chaos (hyper-chaotic multi-attractors Chen system with time delay, HCMACS-TD), Arnold map and Multi-shift cipher function is proposed. To prevent private images from being stolen or used by unauthorized accesses, protecting images is very important. HCMACS-TD generating by linear time delay feedback, which possesses more than one positive Lyapunov exponent, the infinite dimensional, multi-attractors, and a wider chaotic parameter range is used in image encryption algorithm. Arnold map is used to complete the shuffle of the image and the multi-shift cipher function is used to encrypt the shuffled and confused image. In addition, the shuffled image except the first pixel as the initial element of the confusion process, enhances the relationship between the encrypted image and the original image. The performances of the proposed image encryption algorithm are evaluated, and the results show that the proposed image encryption algorithm has considerable advantages over some existing algorithms.
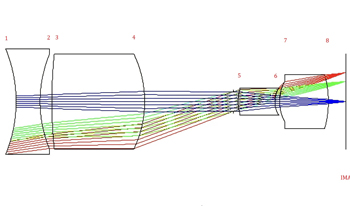
The optical fibre endoscope with cold light is still mainstream in the endoscope market, but the inherent structural characteristics of the optical fibre endoscope lead to its shortcomings, such as high price, inconvenient to carry, and easy distortion of image. The micro medical electronic endoscope can receive the front-end optical system image through the miniature CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and transmit the image to the display through the cable, which greatly solves the limitations of the optical fibre endoscope. In this paper, using ZEMAX software, an optical imaging system with 75∘ field of view is designed. The system consists of four lenses, and all of them are standard spherical lenses. The maximum aperture is 2.2 mm and can match the 1/10-inch CCD. The distortion of the edge field of view is less than 20%, the aberration is small, and the light convergence is good. The maximum spatial resolution is 175 lp/mm.

In order to promote the development of sports and improve the sports literacy of athletes, this paper discusses the video analysis of sports athletes and extends the application of deep learning (DL) algorithm in feature extraction, detection and estimation to improve the analysis effect of sports videos and promote the development of sports. This paper takes basketball players as the main research object to study the sports video analysis. Based on this, first, the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) are discussed. Then a DL video detection and segmentation method based on fusion clustering analysis is proposed by combining the advantages of both with clustering analysis. The designed model is F-C-VDS. Second, CNN is applied to the estimation of basketball players’ and individuals’ altitudes by introducing the idea of feature fusion. Finally, the F-C-VDS model is compared with several neural network models. Its effectiveness is tested based on three postures: moving, jumping and standing. The results show that the segmentation accuracy of F-C-VDS is 97.91% and the segmentation time is 1.01 s. Compared with traditional FCN, the segmentation efficiency is improved by 6.49 %, and the whole segmentation process is stable and more significant than CNN. The average pose estimation accuracy of CNN under feature fusion can reach 80.48%, of which 83.32 % corresponds to moving pose, 82.82 % corresponds to jumping pose and 75.31 % corresponds to standing pose. The proposed DL algorithm can effectively detect, segment and estimate athletes’ altitudes from video images and can be applied to various sports videos. This paper not only provides a reference for the development of DL technology, but also contributes to the development of sports.
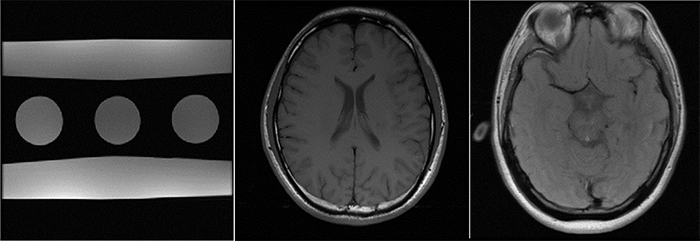
Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA) is a k-space-based magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstruction algorithm that obtains coefficients by acquiring k-space center data with the Nyquist frequency requirement, fitting these data as auto-calibration signal (ACS). The under-sampled k-space data are then filled using the linear correlation of the neighboring points of the k-space. At high reduction factors, images reconstructed by using GRAPPA have high levels of noise even when the number of ACS lines is significantly increased. NL-GRAPPA (Non-linear GRAPPA) can improve GRAPPA for a comparatively impressive image quality. However, it is extremely difficult to reduce the sampling time significantly because of the high number of ACS lines that must be sampled. In this paper, we proposed an undersampling parallel MRI (pMRI) reconstruction technique based on the ideology of normal distribution to improve the traditional GRAPPA and NL-GRAPPA methods. The proposed method mainly takes advantage of the fact that the data in the center of the k-space had a greater impact on the imaging quality than the data at the edges, and then samples the data based on the ideology of normal distribution, i.e., discarding part of the data at the edges of the k-space. The experimental results show that our proposed method can significantly reduce the number of sampled lines and have higher imaging quality with a lower number of ACS lines.
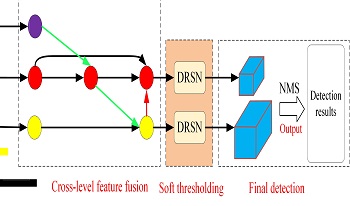
Detection of dim small ground targets in SAR remote sensing images suffers from deficient target information and significant irrelevant background noise. In order to solve this problem, we propose the CD-YOLO (Cross-DRSN YOLO) based on multi-level feature fusion. In CD-YOLO, the convolutional neural network is firstly used to extract features from the input SAR image step by step, thus the spatial pyramid of shallow and deep feature maps is obtained. Cross-level feature fusion is then performed on the spatial pyramid of feature maps, combined with the constructed soft thresholding module which adopts DRSN (Deep Residual Shrinkage Network), to enhance the spatial features of dim small targets and eliminate the noise-related features. Finally, end-to-end target detection is carried out on the two large parallel feature maps generated after soft thresholding. Detection results are output combined with multi-channel information. Due to lack of sufficient image data, a SAR dim small ground target dataset named SGDSTD (SAR Small Ground-based Dim Small Target Dataset) is constructed. Experimental results show that CD-YOLO achieves a real-time performance of 32.3 frames per second, and its AP0.5 and AP0.5: 0.95 on the SGDSTD dataset achieve 91.6% and 51.9%, respectively. Precision and recall of CD-YOLO on the SGDSTD dataset are 86.9% and 81.4%, respectively. The experiment results prove the effectiveness of the proposed method.
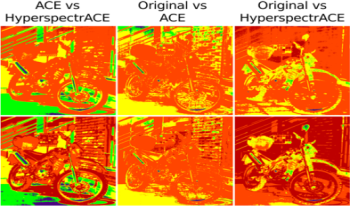
The automatic color equalization (ACE) algorithm, part of the Retinex-derived family of spatial color algorithms (SCAs), is an image enhancement algorithm that mimics the adjustment behavior of the human visual system (HVS). It is commonly used on a unique channel for black & white images or independently on the three channels for color images. In this work, we introduce a novel application of ACE on hyperspectral images, referred to as HyperspectrACE. Here the goal is not to introduce the most performing hyperspectral image enhancer in the field, but to discuss the performance of a qualitative model of human color sensation when applied on more than the standard RGB channels. For this reason, we present the test of the proposed approach compared with classic ACE and other classic methods, to assess the differences in image dynamic stretching and global and local filtering contrast adjustment.