
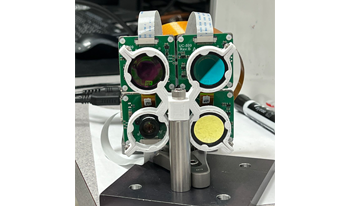
We demonstrate a physics-aware transformer for feature-based data fusion from cameras with diverse resolution, color spaces, focal planes, focal lengths, and exposure. We also demonstrate a scalable solution for synthetic training data generation for the transformer using open-source computer graphics software. We demonstrate image synthesis on arrays with diverse spectral responses, instantaneous field of view and frame rate.
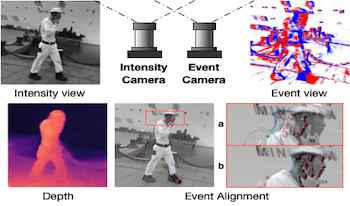
Event cameras are novel bio-inspired vision sensors that output pixel-level intensity changes in microsecond accuracy with high dynamic range and low power consumption. Despite these advantages, event cameras cannot be directly applied to computational imaging tasks due to the inability to obtain high-quality intensity and events simultaneously. This paper aims to connect a standalone event camera and a modern intensity camera so that applications can take advantage of both sensors. We establish this connection through a multi-modal stereo matching task. We first convert events to a reconstructed image and extend the existing stereo networks to this multi-modality condition. We propose a self-supervised method to train the multi-modal stereo network without using ground truth disparity data. The structure loss calculated on image gradients is used to enable self-supervised learning on such multi-modal data. Exploiting the internal stereo constraint between views with different modalities, we introduce general stereo loss functions, including disparity cross-consistency loss and internal disparity loss, leading to improved performance and robustness compared to existing approaches. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, especially the proposed general stereo loss functions, on both synthetic and real datasets. Finally, we shed light on employing the aligned events and intensity images in downstream tasks, e.g., video interpolation application.
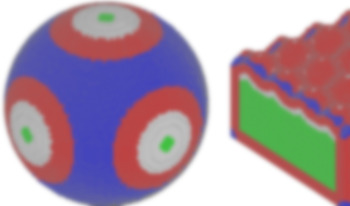
Two-and-a-half and 3D printing are becoming increasingly popular, and consequently the demand for high quality surface reproduction is also increasing. Halftoning plays an important role in the quality of the surface reproduction. Three dimensional halftoning methods, that adapt the halftone structures to the geometrical structure of 3D surfaces or to the viewing direction, could further improve surface reproduction quality. In this paper, a 3D adaptive halftoning method is proposed, that incorporates different halftone structures on the same 3D surface. The halftone structures are firstly adapted to the 3D geometrical structure of the surface. Secondly, the halftone structures are adapted based on the normal vector to the surface at a specific voxel. Two simple approaches to approximate the normal vector are also proposed. The problem of edge artefacts that might occur in the previously proposed 3D Iterative Method Controlling the Dot Placement (IMCDP) halftoning method is discussed and a solution to reduce these artefacts is given. The results show that the proposed adaptive halftoning can combine different halftone structures on the same 3D surface with no transition artefacts between different halftone structures. It is also shown that using second-order frequency modulation (FM) halftone, in comparison to first-order FM, can result in more homogeneous appearance of 3D surfaces with undesirable structures on them.

Structure-aware halftoning algorithms aim at improving their non-structure-aware version by preserving high-frequency details, structures, and tones and by employing additional information from the input image content. The recently proposed achromatic structure-aware Iterative Method Controlling the Dot Placement (IMCDP) halftoning algorithm uses the angle of the dominant line in each pixel’s neighborhood as supplementary information to align halftone structures with the dominant orientation in each region and results in sharper halftones, gives a more three-dimensional impression, and improves the structural similarity and tone preservation. However, this method is developed only for monochrome halftoning, the degree of sharpness enhancement is constant for the entire image, and the algorithm is prohibitively expensive for large images. In this paper, we present a faster and more flexible approach for representing the image structure using a Gabor-based orientation extraction technique which improves the computational performance of the structure-aware IMCDP by an order of magnitude while improving the visual qualities. In addition, we extended the method to color halftoning and studied the impact of orientation information in different color channels on improving sharpness enhancement, preserving structural similarity, and decreasing color reproduction error. Furthermore, we propose a dynamic sharpness enhancement approach, which adaptively varies the local sharpness of the halftone image based on different textures across the image. Our contributions in the present work enable the algorithm to adaptively work on large images with multiple regions and different textures.
Automation of driving leads to decrease in driver agency, and there are concerns about motion sickness in automated vehicles. The automated driving agencies are closely related to virtual reality technology, which has been confirmed in relation to simulator sickness. Such motion sickness has a similar mechanism as sensory conflict. In this study, we investigated the use of deep learning for predicting motion. We conducted experiments using an actual vehicle and a stereoscopic image simulation. For each experiment, we predicted the occurrences of motion sickness by comparing the data from the stereoscopic simulation to an experiment with actual vehicles. Based on the results of the motion sickness prediction, we were able to extend the data on a stereoscopic simulation in improving the accuracy of predicting motion sickness in an actual vehicle. Through the performance of stereoscopic visual simulation, it is considered possible to utilize the data in deep learning.

Light field cameras have been used for 3-dimensional geometrical measurement or refocusing of captured photo. In this paper, we propose the light field acquiring method using a spherical mirror array. By employing a mirror array and two cameras, a virtual camera array that captures an object from around it can be generated. Since large number of virtual cameras can be constructed from two real cameras, an affordable high-density camera array can be achieved using this method. Furthermore, the spherical mirrors enable the capturing of large objects as compared to the previous methods. We conducted simulations to capture the light field, and synthesized arbitrary viewpoint images of the object with observation from 360 degrees around it. The ability of this system to refocus assuming a large aperture is also confirmed. We have also built a prototype which approximates the proposal to conduct a capturing experiment in order to ensure the system’s feasibility.

With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, facial manipulation technology has also evolved remarkably. This has led to the problem of malicious misuse of technology in a society and also developed the research topic of facial forgery detection. In practice, substantial videos are processed by unknown compression and low-quality methods, which makes the detection of facial forgery extremely challenging. We find that deep neural networks trained for specific forged features have better robustness in the presence of unknown compression and low quality. For this reason, we propose an approach to improve facial forgery detection by implementing a divide-and-conquer idea based on the mixture of experts (MoE) framework. (1) Based on the characteristics of the forgery method itself, the facial forgery detection problem is divided into face-swapping detection and expression-swapping detection. (2) Based on the special similarities and differences between expert models, we design an effective lightweight combination method. (3) We propose the focal loss with adaptive decay (FAD) loss function, which effectively alleviates the problem of over-focusing on noisy samples of the focal loss function and further improves the similarity and difference between expert models. Numerous experiments have demonstrated the effectiveness and superiority of our framework on FaceForensics++ (FF++) datasets and benchmarks.
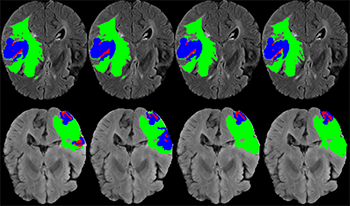
Brain tumor segmentation is an important topic in medical image processing. Three-dimensional (3D) convolutional neural networks (CNN) make full use of feature information and have better segmentation performance. However, conventional 3D CNNs involve a significant number of parameters and has high hardware requirements, which is not conducive to clinical application. To solve these issues, this study proposes a lightweight highly-efficient 3D CNN for brain tumor magnetic resonance imaging segmentation. We first replaced the conventional CNN with improved depth-wise CNN to save computational resources. Next, we employed a multi-channel convolution approach using convolution kernels of different sizes to aggregate features from different receptive fields. Finally, we used a squeeze-and-excitation unit to automatically extract useful feature information in the network. Application of the proposed model to the BraTS2019 validation set resulted in mean Dice scores of 0.9053, 0.8373, and 0.7847, with regard to whole tumor, tumor core, and enhanced tumor, respectively. This was achieved with 2.01 M parameters and 24.68 G floating point operations, and data training used 2.75 GB of video memory. The differences between our Dice scores and those derived using the network developed by the winner of the BraTS2019 challenge were only 0.0041, 0.0174, and 0.0274. Furthermore, the number of parameters and floating point operations were 2.3 times and 8.1 times lower and data training used 4 times lower video memory than the winning network. This indicates that the proposed network offers a higher precision for brain tumor segmentation while reducing computational requirements and effectively lowering hardware requirements for clinical applications.

According to the error sources and their error amounts obtained by the remote sensing imaging coupled typical error sources inversion method, we can improve the imaging quality of optical systems and make high-quality remote sensing images more useful in military and civilian fields. Based on the distorted remote sensing images, this paper proposes a remote sensing imaging coupled typical error sources inversion method, which can accurately invert the typical error sources of remote sensing imaging and their error amounts. Firstly, a set of coupled typical error decoupled equations are constructed according to the modulation transfer function model of typical error sources and the decoupled principle of the coupled error sources. The initial values of coupled typical error sources are subsequently determined based on the Deep Residual Shrinkage Network (DRSN). Finally, the Levenberg Marquardt-Particle Swarm Optimization (LM-PSO) hybrid optimization algorithm is used to solve the system of coupled typical error decoupled equations to invert the typical error sources and their error amounts of the remote sensing imaging system. The experimental results show that the relative error between the inverse value and the real value of the coupled typical error sources of the distorted remote sensing images by the method in this paper does not exceed 20% at most, and most of them are below 10%, which has excellent inversion performance.