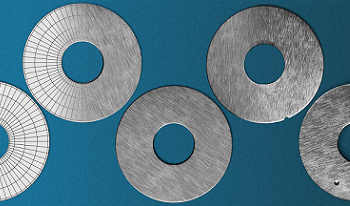
This paper presents a method for synthesizing 2D and 3D sensor data for various machine vision tasks. Depending on the task, different processing steps can be applied to a 3D model of an object. For object detection, segmentation and pose estimation, random object arrangements are generated automatically. In addition, objects can be virtually deformed in order to create realistic images of non-rigid objects. For automatic visual inspection, synthetic defects are introduced into the objects. Thus sensor-realistic datasets with typical object defects for quality control applications can be created, even in the absence of defective parts. The simulation of realistic images uses physically based rendering techniques. Material properties and different lighting situations are taken into account in the 3D models. The resulting tuples of 2D images and their ground truth annotations can be used to train a machine learning model, which is subsequently applied to real data. In order to minimize the reality gap, a random parameter set is selected for each image, resulting in images with high variety. Considering the use cases damage detection and object detection, it has been shown that a machine learning model trained only on synthetic data can also achieve very good results on real data.
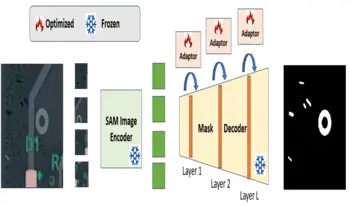
PCB defect segmentation aims to localize the defects in printed circuit boards (PCBs). While this problem has a great industrial impact, few datasets are publicly available. It is also challenging to predict the defects that appear during manufacturing. To address the former challenge, we curate a large dataset with various defective categories of imbalanced distribution, reflecting real-world conditions. The problem of unsupervised PCB anomaly segmentation (UAS), where no labeled defect data is available during training, is then investigated. We propose an efficient prompt tuning method to address PCB-UAS. Specifically, a pretrained large foundational segmentation model (SAM) is adapted to PCB-UAS by the introduction of a few learnable adapter layers. SAM is frozen during training and only the additional adapter parameters are learned. To overcome the lack of labeled defect images for training, we propose to create synthetic defect images that mimic the real ones. Experiments highlight that the proposed method can outperform baselines by 7 points with 16.6 times less learnable parameters.
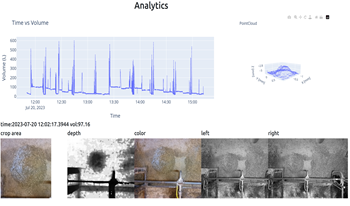
Accurate measurements of daily feed consumption for dairy cattle is an important metric for determining animal health and feed efficiency. Traditionally, manual measurements or average feed consumption for groups of animals have been employed which leads to human error and overall inconsistent measurements for the individual. Therefore, we developed a scalable non-invasive analytics system that leverages depth information derived from stereo cameras to consistently measure feed offered and report findings throughout the day. A top-down array of cameras faces the available feed, measures feed depth, projects depth to a 3-dimensional (3D) mesh, and finally estimates feed volume from the 3D projection. Our successful experiments at the Purdue University Dairy, that houses 230 cows, demonstrates its robustness and scalability for larger operations holding significant potential for optimizing feed management in dairy farms, thereby improving animal health and sustainability in the dairy industry.

The 3D mapping of Erdstall facilities presents unique challenges due to their underground and confined nature. This research explores the application of mobile mapping systems to overcome these challenges and acquire accurate spatial data within Erdstall passages. Using a handheld device that combines an RGB camera with depth sensor and motion tracking technology, we address the difficulties associated with limited access, uneven surfaces, low light conditions, and complex geometries inherent to Erdstalls. The research contributes to the understanding of Erdstall architectures, spatial relationships, and historical contexts. By evaluating the effectiveness of mobile mapping technologies in Erdstalls, this study contributes valuable insights to the broader field of archaeological mapping in challenging environments. The results demonstrate the potential of mobile 3D mapping as a powerful tool for documenting and preserving underground heritage sites while providing a foundation for further interdisciplinary studies and initiatives.