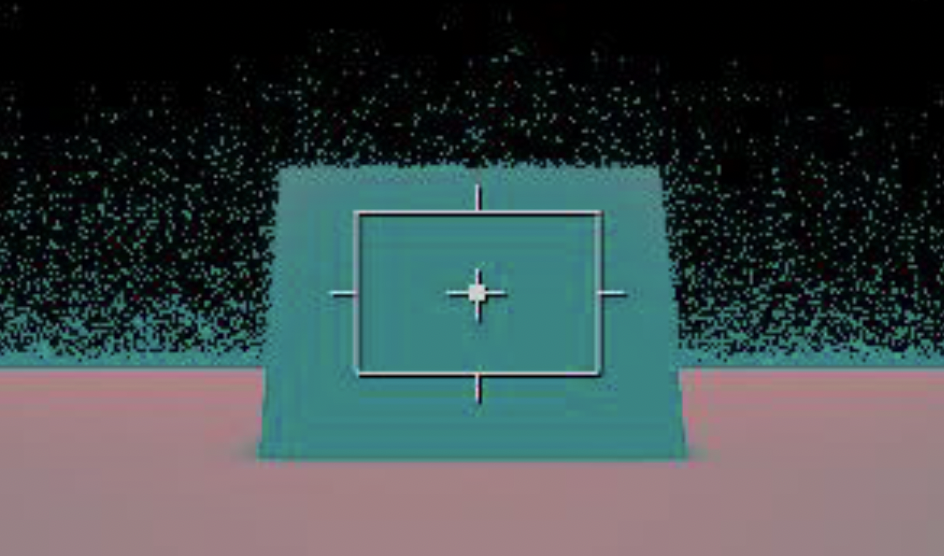
ACES is a standardized color management system widely used in the film and visual effects industry to ensure consistent and accurate color reproduction throughout the production pipeline. Integrating ACES into game engines like Unreal Engine could have significant benefits, especially for game developers who want to achieve high-quality, consistent color representation across different platforms and displays. Game developers can achieve heightened visual fidelity by leveraging ACES in Unreal Engine 5, especially concerning wide color gamuts and high dynamic range (HDR) content. The standardized color management system allows cross-platform development, guaranteeing consistent color reproduction on various devices and display technologies. Moreover, Unreal Engine 5's support for ACES facilitates seamless collaboration with other creative industries that utilize this industry-standard color pipeline. However, implementing ACES in a real-time engine presents unique challenges regarding performance optimization and ensuring compatibility with other game engines. Artists and developers may need to adapt their workflows to accommodate ACES color transforms, impacting the art pipeline and user-generated content. This paper uses ACES to investigate color input and output consistency to and from Epic Games Unreal 5 regarding Wide Color Gamut and High Dynamic Range imagery.
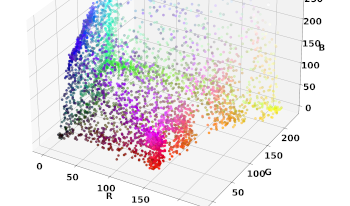
The JAB Code, a 2D barcode standardized in ISO/IEC 23634:2022, offers improved reliability and data capacity over traditional barcodes, but its color recognition poses challenges. These issues stem from the suboptimal utilization of the RGB color space in printing and the non-bijective RGB-to-CMYK conversion, prompting the need to select colors that ensure distinct segregation in the transformed color space for enhanced detection robustness. We propose an approach for calibrating the colors of the JAB Code, involving the creation of a test pattern, quantization of the color space, and the calibration of colors using a calibration target. This method aims to ensure optimal color representation within the barcode and can be integrated into JAB Code generation tools or web apps, simplifying the process for users and ultimately improving color accuracy and fidelity within the barcode. We conduct an experiment with different printers, utilizing a smartphone for image capture. The evaluation includes printing JAB Code test patterns, creating and calibrating standard and calibrated JAB Codes, and capturing images under various lighting conditions. We use the JAB Code detection algorithm to analyze color distances in the RGB space, revealing improvements in color distribution and lower error rates with printer color calibration, which can lead to faster reading processes and smaller JAB Code sizes with reduced area requirements. This work offers important insights that should be considered during the next revision of the ISO standard.
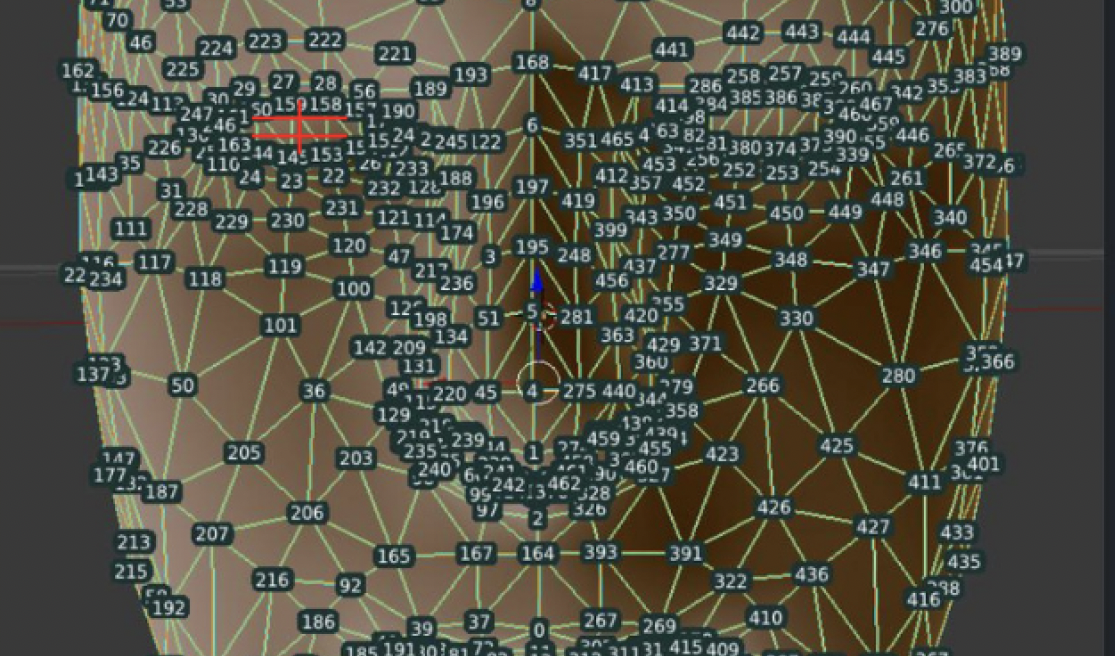
The Driver Monitoring System (DMS) presented in this work aims to enhance road safety by continuously monitoring a drivers behavior and emotional state during vehicle operation. The system utilizes computer vision and machine learning techniques to analyze the drivers face and actions, providing real-time alerts to mitigate potential hazards. The primary components of the DMS include gaze detection, emotion analysis, and phone usage detection. The system tracks the drivers eye movements to detect drowsiness and distraction through blink patterns and eye-closure durations. The DMS employs deep learning models to analyze the drivers facial expressions and extract dominant emotional states. In case of detected emotional distress, the system offers calming verbal prompts to maintain driver composure. Detected phone usage triggers visual and auditory alerts to discourage distracted driving. Integrating these features creates a comprehensive driver monitoring solution that assists in preventing accidents caused by drowsiness, distraction, and emotional instability. The systems effectiveness is demonstrated through real-time test scenarios, and its potential impact on road safety is discussed.
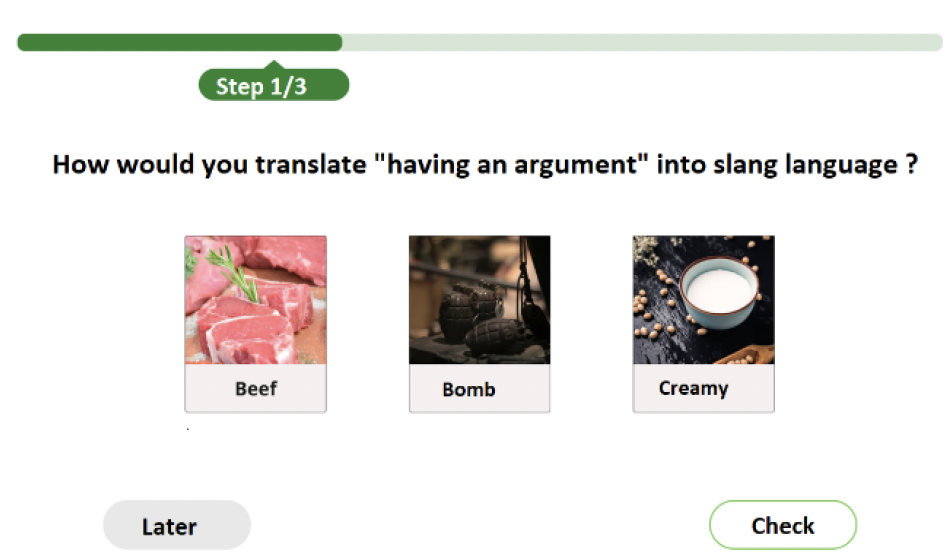
This paper presents a prototype that aims to make education accessible to all. The chosen learning topic focuses on youth language to overcome language barriers and create better access to society for those who are not fluent in German. The results are based on a systematic literature review and the development of a prototype tested using the BITV tests. The key findings are that accessibility should be a strategic goal set and repeatedly promoted by senior management. This way, it does not become less of a priority, which has often proven to be a weakness because the accessible elements of software are not necessarily needed for its core functions. With the insight of using an agile participation model, accessible applications can be completed in a shorter average time in the future. The project also demonstrates the importance of accessibility awareness in software development.
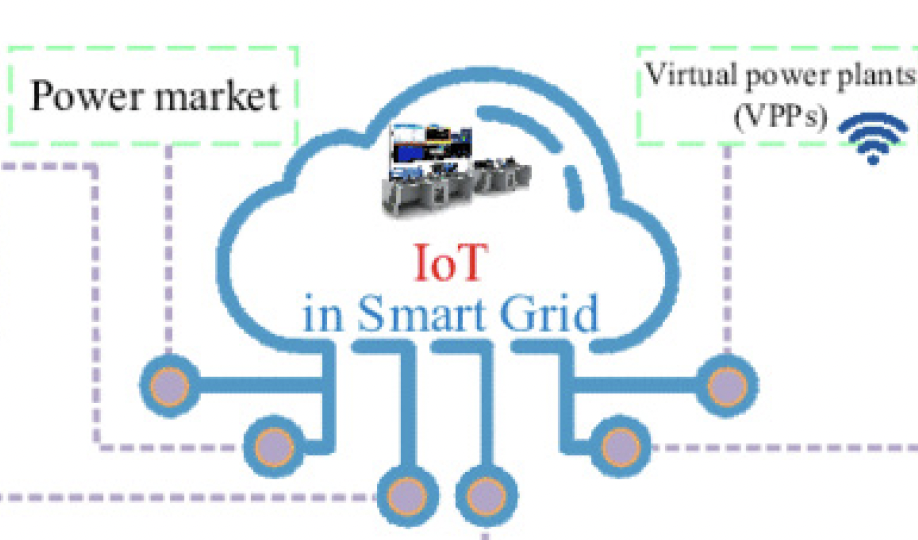
Critical infrastructure is the backbone of modern societies, and protecting this infrastructure is essential to ensure the stability of societies and economies. The electricity sector is one of the most critical infrastructures, and any disruption can have significant consequences. The threat landscape in this sector is constantly evolving. With the increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks and other threats, it has become essential to use innovative technologies to identify and mitigate them. Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) technologies have emerged and offer valuable tools for identifying and mitigating these threats. This article presents an in-depth overview of OSINT technologies and their applications in the protection of critical infrastructure, with an emphasis on the electricity sector. It discusses the vulnerabilities of the electricity sector, the types of OSINT technologies, and the benefits they provide. Case studies of successful applications of OSINT technologies in the electricity sector are presented to illustrate their effectiveness. This article also examines organizations challenges in implementing OSINT technologies, including technological, legal, and financial challenges. Finally, the article concludes by offering recommendations for successfully implementing OSINT technologies to protect critical infrastructure, particularly in the electricity sector. The insights offered in this article will be helpful for policymakers, security professionals, and anyone interested in protecting critical infrastructure.
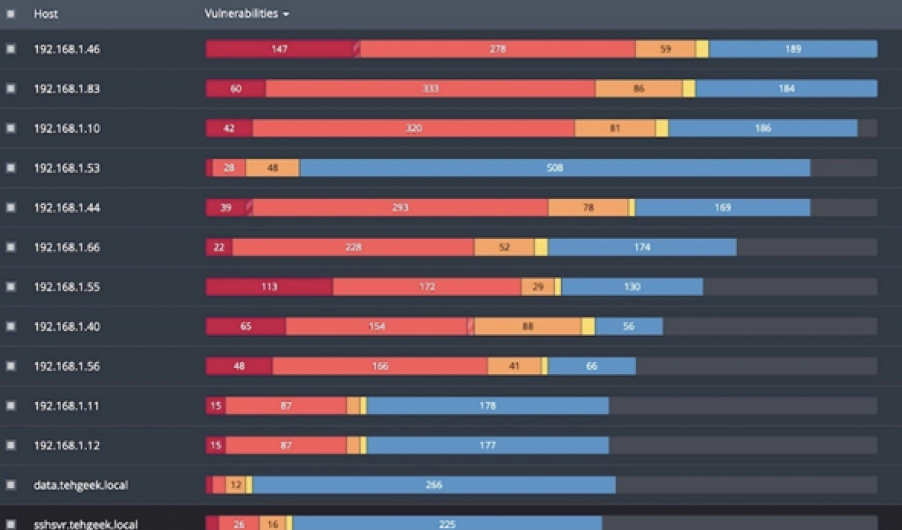
The fast growth of cloud computing technology has led to immense development in the public and private sectors. Cloud computing provides a high level of virtualization, massive scalability, multitenancy, and elasticity. This has enabled organizations, academia, government departments, and the public to advance with this technology. However, they cannot assuredly place their information in the cloud due to many security threats. Cloud security plays a vital role in establishing confidence between the cloud service providers, consumers, and multi-users to maintain the security levels of their data. Moreover, in the scope of cloud computing, the importance of security testing must be considered. Security testing involves evaluating the cloud infrastructure and applications for vulnerabilities, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected. This paper focused on the challenges, tools, techniques, and methodologies for cloud security testing. Furthermore, the paper introduces the tools offered by three significant CSPs for cloud security testing and the most critical cloud vulnerabilities. It explains some published vulnerabilities around these three major CSPs. Between these three significant CSPs, we focused on Azure offerings for securing their clouds and some known tools for security testing in the cloud. Lastly, we introduced and explained the most essential API vulnerabilities according to OWASP and a suggested way to mitigate them.

We introduce Model Surgery, a novel approach for optimizing Deep Neural Network (DNN) models for efficient inference on resource-constrained embedded processors. Model Surgery tackles the challenge of deploying complex DNN models on edge devices by selectively pruning or replacing computationally expensive layers with more efficient alternatives. We examined the removal or substitution of layers such as Squeeze-And-Excitation, SiLU, Swish, HSwish, GeLU, and Focus layer to create lightweight ``lite'' models. Subsequently, these lite models are trained using standard training scripts for optimal performance. The benefits of Model Surgery are showcased through the development of several lite models which demonstrate efficient execution on the hardware accelerators of commonly used embedded processors. To quantify the effectiveness of Model Surgery, we conducted a comparison of accuracy and inference time between the original and lite models via training and evaluating them on the Imagenet1K and COCO datasets. Our results suggest that Model Surgery can significantly enhance the applicability and efficiency of DNN models in edge-computing scenarios, paving the way for broader deployment on low-power devices. The source code for model surgery is also publically available as a part of model optimization toolkit at https://github.com/TexasInstruments/edgeai-modeloptimization/tree/main/torchmodelopt.
This paper introduces AI-based Cybersecurity Management Consulting (AI-CMC) as a disruptive technology to address the growing complexity of cybersecurity threats. AI-CMC combines advanced AI techniques with cybersecurity management, offering proactive and adaptive strategies through machine learning, natural language processing, and big data analytics. It enables real-time threat detection, predictive analytics, and intelligent decision-making. The paper explores AI-CMC's data-driven approach, learning models, and collaborative framework, demonstrating its potential to revolutionize cyber-security. It examines AI-CMC's benefits, challenges, and ethical considerations, emphasizing transparency and bias mitigation. A roadmap for transitioning to AI-CMC and its implications for industry standards, policies, and global strategies are discussed. Despite potential limitations and vulnerabilities, AI-CMC offers transformative solutions for enhancing threat resilience and safeguarding digital assets, calling for collaborative efforts and responsible use for a secure digital future.

In today's cybersecurity landscape, protecting information systems is crucial due to the rising threat of cyber-attacks. This research focuses on vulnerability management using open-source tools for domain and subdomain enumeration, vulnerability scanning, and remediation. Open-source software offers cost-effective and collaborative security solutions. Domain and subdomain enumeration tools play a vital role in mapping an organization's attack surface, providing insight into security posture. The analysis of vulnerability scanning tools highlights their effectiveness in identifying critical flaws in web applications and databases. Vulnerability remediation through patching, hardening, and exposure management processes closes security gaps. The research provides an empirical insight into using open-source tools for vulnerability management, listing their benefits and limitations empowering organizations to enhance their security posture. Recommendations for integrating these tools into existing security frameworks help combat cyber threats and protect valuable assets.
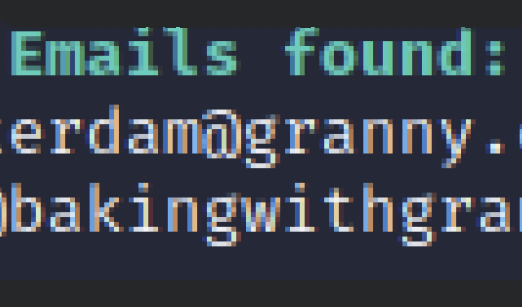
Open-source technologies (OSINT) and Social Media Intelligence (SOCMINT) are becoming increasingly popular with investigative and government agencies, intelligence services, media companies, and corporations - but also for cybercriminals in email phishing. The amount of public and private data available is rising rapidly. OSINT and SOCMINT technologies use sophisticated techniques and special tools to analyze the continually growing sources of information efficiently. This work aims to find descriptive information using the OSINT tools available online. The target will be achieved with the help of dummy accounts that would help understand the tools and evaluate further different tools. Also, find out what tools are commonly used and what improvements can be made to make them more descriptive for analysts.