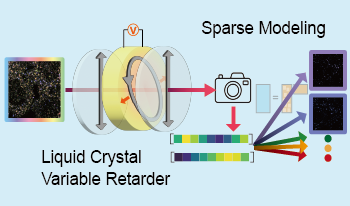
In spatial transcriptomics, which allows the analysis of gene expression while preserving its location in tissues, RNA molecules are hybridized with a fluorescent-labeled DNA probe for detection. In this study, we aim to improve the efficiency of spatial transcriptomics by simultaneously using multiple fluorescent dyes with overlapping spectra. We propose a method to quantify each fluorescent dyes using a liquid crystal variable retarder as a spectral modulator, which can control the spectral transmittance by changing the voltage. The spectrum of light passing through the modulator is integrated by the image sensor and observed as intensity. We quantify the fluorescent dyes at each pixel using intensities of various spectral transmittances as a spectral code and applying sparse modeling using a dictionary created by simulating observations for the fluorescent dyes used in hybridization. We verified the principle of the proposed method and demonstrated its feasibility through simulation experiments.