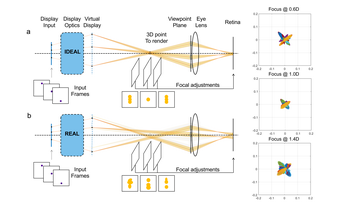
Aberrations in the optical system of a light field (LF) display can degrade its quality and affect the focusing effects in the retinal image, formed by the superposition of multiperspective LF views. To address this problem, we propose a method for calibrating and correcting aberrated LF displays. We employ an LF display optical model to subsequently derive the retinal image formation with a given LF input. This enables us to efficiently measure actual viewpoint locations and the deformation of each perspective image, by capturing focal-stack images during the calibration process. We then use the calibration coefficients to pre-warp the input images so that the aberrations are compensated. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on a simulated model of an aberrated near-eye LF display and show that it improves the display's optical quality and the accuracy of the focusing effects.

Interest in 3D viewing has been increasing significantly over the last few years, with the vast majority of focus being on Virtual Reality (VR), a single-user form of Stereo 3D (S3D) with positional tracking, and Augmented Reality (AR) devices. However, Volumetric 3D displays and Light Field Displays (LFD) are also generating interest in the areas of operational and scientific analysis due to the unique capabilities of this class of hardware. The amount of available 3D data is also growing exponentially including computational simulation results, medical data (e.g. computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), ultrasound), computer-aided design (CAD) data, plenoptic camera data, synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data, light detection and ranging (LiDAR) data, 3D data from global positioning system (GPS) satellite scans, and numerous other 3D data sources. Much of this 3D data is available in the cloud and often at long distances from the application or user. While significant progress has been made developing open standards for S3D devices, no standard has yet converged that would allow 3D data streaming for devices such as LFDs that display an assembly of simultaneous views for full parallax and multi-user support without the need for specialized eyewear. A 3D Streaming Standard is desired that will allow display of 3D scenes on any Streaming Media for Field of Light Displays (SMFoLD) compliant device including S3D, VR, AR, Volumetric 3D, and LFD devices. With support from the Air Force Research Laboratories, Third Dimension Technologies (TDT), in collaboration with Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and Insight Media, has initialized work on the development of an SMFoLD Open Standard.