
Increasingly sophisticated algorithms, including trained artificial intelligence methods, are now widely employed to enhance image quality. Unfortunately, these algorithms often produce somewhat hallucinatory results, showing details that do not correspond to the actual scene content. It is not possible to avoid all hallucination, but by modeling pixel value error, it becomes feasible to recognize when a potential enhancement would generate image content that is statistically inconsistent with the image as captured. An image enhancement algorithm should never give a pixel a value that is outside of the error bounds for the value obtained from the sensor. More precisely, the repaired pixel values should have a high probability of accurately reflecting the true scene content. The current work investigates computation methods and properties of a class of pixel value error model that empirically maps a probability density function (PDF). The accuracy of maps created by various practical single-shot algorithms is compared to that obtained by analysis of many images captured under controlled circumstances. In addition to applications discussed in earlier work, the use of these PDFs to constrain AI-suggested modifications to an image is explored and evaluated.
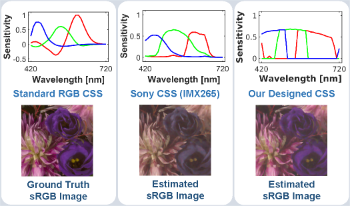
Camera spectral sensitivity (CSS) establishes the connection between scene radiance and device-captured RGB tristimulus values. Since the spectral sensitivity of most color imaging devices typically deviates from that of human vision or a standard color space and also noise is often introduced during the process of photoelectric signal conversion and transmission, the design of an efficient CSS with noise robustness and high color fidelity is of paramount importance. In this paper, we propose a CSS optimization method with noise consideration that designs theoretically an optimal CSS for each noise level. Additionally, taking practical considerations into account, we further extend the proposed method for a universally optimal CSS adaptable to diverse noise levels. Experimental results show that our optimized CSS is more robust to noise and has better imaging performance than existing optimization methods based on a fixed CSS. The source code is available at https://github.com/xyu12/Joint-Design-of-CSS-and-CCM-with-Noise-Consideration-EI2024.

A similarity search in images has become a typical operation in many applications. A presence of noise in images greatly affects the correctness of detection of similar image blocks, resulting in a reduction of efficiency of image processing methods, e.g., non-local denoising. In this paper, we study noise immunity of various distance measures (similarity metrics). Taking into account a wide variety of information content in real life images and variations of noise type and intensity. We propose a set of test data and obtain preliminary results for several typical cases of image and noise properties. The recommendations for metrics' and threshold selection are given. Fast implementation of the proposed benchmark is realized using CUDA technology.