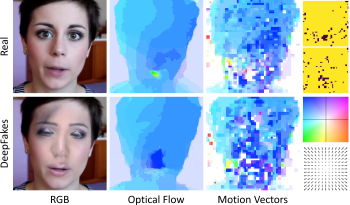
Video DeepFakes are fake media created with Deep Learning (DL) that manipulate a person’s expression or identity. Most current DeepFake detection methods analyze each frame independently, ignoring inconsistencies and unnatural movements between frames. Some newer methods employ optical flow models to capture this temporal aspect, but they are computationally expensive. In contrast, we propose using the related but often ignored Motion Vectors (MVs) and Information Masks (IMs) from the H.264 video codec, to detect temporal inconsistencies in DeepFakes. Our experiments show that this approach is effective and has minimal computational costs, compared with per-frame RGB-only methods. This could lead to new, real-time temporally-aware DeepFake detection methods for video calls and streaming.

In recent years, the number of forged videos circulating on the Internet has immensely increased. Software and services to create such forgeries have become more and more accessible to the public. In this regard, the risk of malicious use of forged videos has risen. This work proposes an approach based on the Ghost effect knwon from image forensics for detecting forgeries in videos that can replace faces in video sequences or change the mimic of a face. The experimental results show that the proposed approach is able to identify forgery in high-quality encoded video content.

Google started the WebM Project in 2010 to develop open source, royalty--free video codecs designed specifically for media on the Web. Subsequently, Google jointly founded a consortium of major tech companies called the Alliance for Open Media (AOM) to develop a new codec AV1, aiming at a next edition codec that achieves at least a generational improvement in coding efficiency over VP9. This paper proposes a new coding tool as one of the many efforts devoted to AOM/AV1. In particular, we propose a second ALTREF_FRAME in the AV1 syntax, which brings the total reference frames to seven on top of the work presented in [11]. ALTREF_FRAME is a constructed, no-show reference obtained through temporal filtering of a look-ahead frame. The use of twoALTREF_FRAMEs adds further flexibility to the multi-layer, multi-reference symmetric framework, and provides a great potential for the overall Rate- Distortion (RD) performance enhancement. The experimental results have been collected over several video test sets of various resolutions and characteristics both texture- and motion-wise, which demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves a consistent coding gain, compared against the AV1 baseline as well as against the results in [11]. For instance, using overall-PSNR as the distortion metric, an average bitrate saving of 5.880% in BDRate is obtained for the CIF-level resolution set, and 4.595% on average for the VGA-level resolution set.