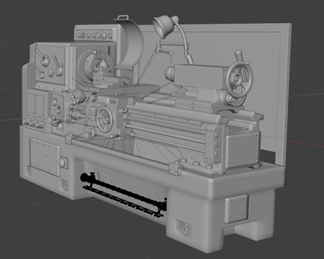
Utilizing a Value Engineering (VE) approach towards solving educational student throughput bottlenecks caused by equipment and space capacity issues in university machine shop learning, Virtual Reality (VR) presents an opportunity to provide scalable, customizable, and cost-effective means of easing these constraints. An experimental method is proposed to demonstrate applying VR towards increasing the output of the value function of an educational system. This method seeks to yield a high Transfer-Effectiveness-Ratio (TER) such that traditional educational strategies are supplemented by VR sufficiently so that further growth in classroom enrollment is enabled.

Design education has special requirements on using virtual studio setups. The Zoom fatigue during the world-wide COVID pandemic let our institution to test new tools which can help improve digital design education by supporting features like idea sharing, collaborative making, serendipitous discussion and group forming. For this purpose, we tested different tools during our Master program Innovation Design Engineering and collected student feedback. We found that immersion is a key factor impacting the effectiveness of group work in distance learning. This paper presents our applications and analysis of different platforms and contributes insights on how to build a virtual studio environment for an interdisciplinary master programme in design engineering. In this work, we will focus on our studies on Gather.town, Meta Horizon Workrooms and Spatial.

Since 2016 the RCA Grand Challenge is an interdisciplinary event that runs each year across the entire School of Design at the Royal College of Art. Around 400 Master and PhD students with design background participate in this event, focusing on tackling key global challenges through collaboration. In 2022, the Grand Challenge was focusing on elaborating topics in the context of Ocean-driven activities. In this context, a VR workshop was conducted with around 40 students with mostly no background in using VR platforms. In the end – after a 4-week design sprint – 10 UNREAL engine-based projects were presented of which we will discuss a selection here. One of the projects managed to be among the overall winning teams of the Grand Challenge 2022.

We present the results of the Quality of Experience (QoE) evaluation of 360 degree immersive video in university education. Fourth-year Veterinary Medicine students virtually attended some practical lessons which had been recorded in immersive 360 video format, covering topics of Surgical Pathology and Surgery related to horses. One hundred students participated in the experience. They evaluated it through an extensive questionnaire covering several QoE factors, including presence, audiovisual quality, satisfaction or cybersickness: 79% evaluated the experience as excellent or good, and they acknowledged an improvement of the learning process by the implementation of VR as didactic tool, and 91% reported that they would recommend it to other students. Female students consistently gave slightly better average scores than their male counterparts, although mostly within confidence intervals. Strongest inter-gender differences appeared in active social presence dimensions, according to the Temple Presence Inventory. The study also evaluates the suitability of synthetic measurement protocols, such as the Distributed Reality Experience Questionnaire (DREQ) and Net Promoter Score (NPS). We show that NPS is a valid tool for QoE analysis, but that its clustering boundary values must be adapted to the specificities of the experiment population.