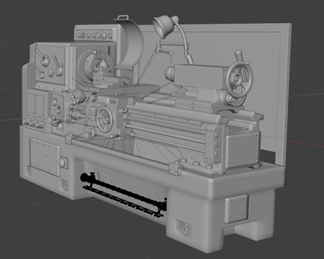
Utilizing a Value Engineering (VE) approach towards solving educational student throughput bottlenecks caused by equipment and space capacity issues in university machine shop learning, Virtual Reality (VR) presents an opportunity to provide scalable, customizable, and cost-effective means of easing these constraints. An experimental method is proposed to demonstrate applying VR towards increasing the output of the value function of an educational system. This method seeks to yield a high Transfer-Effectiveness-Ratio (TER) such that traditional educational strategies are supplemented by VR sufficiently so that further growth in classroom enrollment is enabled.
Myles Cupp, Marie Vans, "Virtual Reality as a Value Engineering Method in Machine Shop Learning" in Electronic Imaging, 2025, pp 164-1 - 164-6, https://doi.org/10.2352/EI.2025.37.13.ERVR-164
 Find this author on Google Scholar
Find this author on Google Scholar Find this author on PubMed
Find this author on PubMed