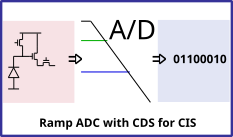
This article presents a novel architecture of a single slope single ramp column analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) for CMOS image sensors (CIS). The outlined ADC uses a global single slope ramp (SSR) with two comparators and two counters per column, one for the pixel reset level and one for the pixel signal level. A common reference level is used to start the conversion, while the reset and signal levels are used to terminate the respective conversion. With this architecture, the pixel reset, and signal levels are converted within a single conversion cycle. When the counter results are ready, a digital correlated double sampling (CDS) output is achieved by subtracting the reset counter value from the signal counter value with a digital subtractor. This architecture provides speed, offset compensation, and input swing adjustment through the reference level. Furthermore, the implementation is less vulnerable to temporal row noise, which is then suitable for low-noise applications. A 12-bit column ADC was designed and implemented in a 1920 x 1080 resolution CIS demonstrator, using a 0.18 m CIS process. With 200 MHz counter operation, the readout operation results in 25 frames per second.

Modern digital cameras capture images with a subsampling method via mosaic color filter array (CFA). Of particular interest is the CFA with Cyan-Magenta-Yellow (CMY) color filters. Despite the improvement of the sensitivity, images reconstructed from CMY CFA usually suffer from lower color fidelity compared to the conventional Red-Green-Blue (RGB) color filters. In this paper, we proposed a CMY CFA with novel spectral sensitivities (CMY2.0), which were carefully designed to overcome the shortcomings of previous CMY CFA (CMY1.0). A CMY CMOS image sensor (CIS) with such optimized spectral sensitivities is then realized in order to evaluate the color performance and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). As a result, the camera equipped with the CMY CFA with proposed spectral sensitivities (CMY2.0) features both an improved sensitivity and a high color fidelity, which is suitable for a wide range of applications, such as low-light photography, under-screen cameras and automotive cameras.

A Low-power and low-noise digital pixel sensor (DPS) is presented in this paper. To design and analyze the random noise (RN) of the developed DPS, especially, we utilize a novel simulationmethod called transient-based AC noise simulation (TBAS) which can effectively help to estimate the noise components of the lowpowered single-slope (SS) analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Based on this noise analysis, the high performance DPS has been successfully designed and demonstrated.

Nowadays, mobile phone set makers are implementing a full screen display by changing the mounting form factor of the front camera, which is superior in design. When it comes to smart phone front-facing cameras, the hole type front-facing camera degrade the industrial design, while pop-up style camera has also limitation in terms of waterproofness and durability. In the case of Under Display Camera(UDC) which is in its final form factor by design, where a camera is placed underneath the screen, the display panel on the light-receiving path degrades the camera optical sensitivity and causes decrease in image quality performance due to regular display panel pattern. In order to commercialize the UDC, improving image quality of the UDC and exact measurement are crucial. However, subjectively evaluating image taken through the display panel is challenging task measure the image quality performance. This paper introduces a numeric based UDC image quantitative measurement method as a more objective evaluation way.

Under Display Camera(UDC) technology is being developed to eliminate camera holes and place cameras behind display panels according to full display trend in mobile phone. However, these camera systems cause attenuation and diffraction as light passes through the panel, which is inevitable to deteriorate the camera image. In particular, the deterioration of image quality due to diffraction and flares is serious, in this regard, this paper discusses techniques for restoring it. The diffraction compensation algorithm in this paper is aimed at real-time processing through HW implementation in the sensor for preview and video mode, and we've been able to use effective techniques to reduce computation by about 40 percent.

Low optical-crosstalk color pixel scheme with wave-guiding structures is demonstrated in a high resolution CMOS image sensor with a 0.8um pixel pitch. The high and low refractive index configuration provides a good confinement of light waves in different color channels in a quad Bayer color filter array. The measurement result of this back-side illuminated (BSI) device exhibits a significant lower color crosstalk with enhanced SNR performance, while the better angular response and higher angular selectivity of phase detection pixels also show the suitability to a new generation of small pixels for CMOS image sensors.