
Archives are traditionally identified as holders of text-based information. However, they also possess audio and video materials, which are the focus of this paper. In archival institutions, the absence of transcriptions for audio and video materials presents significant challenges. These materials often hold historical, cultural, and research value, but without transcriptions, their accessibility and usability are limited. The lack of transcriptions makes it difficult to index and search the content, hindering effective utilization. While existing ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) technologies can assist, these may suffer from mediocre accuracy, especially with older or poor-quality materials. This work addresses the challenge by utilizing state of the art multilingual LLM (Large Language Model), simple to use UI (User Interface) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) ready containers to create a simple and effective multilingual transportable ASR module.

The National Museum of African American History and Culture’s Freedmen’s Bureau Project is a comprehensive initiative that has provided digital access to the Freedmen’s Bureau records. Previously, this important collection could only be accessed in person through the National Archives and Records Administration, with no way to search for specific people or topics. Smithsonian staff have worked with the public to index and transcribe the records to provide free full-text access to these invaluable records. To date over 600,000 pages of Freedmen’s Bureau records have been collaboratively transcribed by more than 60,000 individual volunteers. This data has been made available to the public for research in the Freedmen’s Bureau Search Portal. This groundbreaking search application is the result of more than a decade of data creation, processing, and cleaning; transcription; community engagement; and historical and genealogical research. The work of Smithsonian staff is ongoing and emerging technologies present exciting opportunities to expand access and continue to enable meaningful discoveries.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) contributes significantly to the development of autonomous vehicles in an unmatched way. This paper outlines techniques and algorithms for the implementation of Intelligent Autonomous vehicles (IAV) leveraging AI algorithms for traffic perception, decision-making and control in autonomous vehicles through merging traffic scenario detection, traffic lane detection, semantic segmentation, pedestrian detection, and traffic sign classification and detection. The modern computer vision and deep neural networks-based algorithms enable the real-time analysis of different vehicle data through artificial intelligence. The vehicle dynamics are constituted through AI in vehicle control systems for increased safety and efficiency to ensure that they are optimized with time. In addition, the paper will also discuss challenges and possible future directions, underscore how AI has the potential of driving autonomous vehicles towards safer and more reliable as well as intelligent transportation systems. This is the hope of the future whereby mobility is intelligent, sustainable, and accessible with the combination of AI with autonomous vehicles.
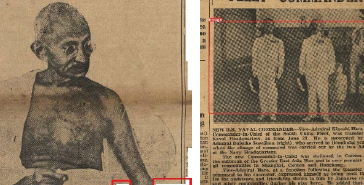
This paper presents the methodologies to extract the headline and illustrations from a historical newspaper for storytelling to support digital scholarship. It explored the ways in which new digital tools can facilitate the understanding of the newspaper content in the setting of time and space, "The Hongkong News" was selected from Hong Kong Early Tabloid Newspaper for the case study owing to its uniqueness in historical value towards the scholars. The proposed methodologies were evaluated in OCR (Optical Character Recognition) with scraping and Deep Learning Object Detection models. Two visualization products were developed to showcase the feasibility of our proposed methods to serve the storytelling purpose.

A software package and PoC to help usability in various cases like quality issues and metadata collecting after digitization is introduced. Here usability means the improvement of the process using AI based automation as much as possible and providing easy-to-use interfaces for the end user. This is done with the help of existing open source tools.

Monitoring Systems and the Internet of Things have become increasingly important, among others, in Renewable Energy applications. A combination of measuring sensors and actuators controlled and processed by an intelligent central system is necessary to reduce energy consumption automatically. This paper develops a modern concept for a Smart Energy House. The functionality and the hardware implementation are explained in detail based on a concrete simulation of the self-refilling water tank. The system comprises various separate located IoT modules integrated with a central host using TCP/IP network infrastructure, as well as communication technologies and protocols, such as WiFi and MQTT. Those sensors, also called clients, are wireless devices designed to measure different environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, in real-time. Changes in the current water level and battery charging progress are also being monitored. The host consists of three parts: storage service, web-based monitoring platform, and program logic for decision-making methods. Most of the processes, such as electrical control, data collection, information query, and analyzing functions, were implemented using Python libraries and self-written algorithms. An essential part of an intelligent home monitoring and automation system is secured remote accessibility and maintenance in any emergency. Therefore, the system supports both local and remote access. Data visualization and alarming routines are implemented within the web-based free software “Grafana” combined with the time-series database “InfluxDB”. Finally, the results demonstrated in this article show that the system has excellent application prospects due to its stability, low cost, high performance, user-friendly and customary configuration. The concept has been improved and prepared for the Smart Energy House test object located in Berlin.

Microgrids incorporating Renewable Energy (RE) sources are being used nowadays to overcome the lack of electric power supply or grid instabilities in rural areas. Microgrids are decentralized and performant solutions to distribute electric power and to supply the consumers of a community with energy. They can be used to provide stable electrical energy to hospitals, companies and residential areas and therefore, they can contribute significantly to rural development. Based on renewable sources, they are climate neutral as well. Very often, in regular operation, a Microgrid is connected with an utility national or another distributed grid. In case of an utility grid fault occurrence, the Microgrid can still provide power since it incorporates renewable sources. However, since renewable sources like photovoltaics or wind power are volatile in supply, grid instabilities, voltage and frequency fluctuations and harmonic distortions in the Microgrid can occur. This paper focuses on developing a Microgrid (M.G.) model using MATLAB Simulink and analyzing its issues at different operational modes assuming a photovoltaic generator and a coupling to an utility grid as power sources. In order to analyze and predict the behavior of the Microgrid, deep learning methods based on Auto Regressive Moving Average (ARIMA) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) will be applied. It is shown that these methods allow to optimize the operation modes of the Microgrid. For instance, a balance between power supply and demand at different times could be reached and lead to economic efficiency and feasibility.

Autonomous driving plays a crucial role to prevent accidents and modern vehicles are equipped with multimodal sensor systems and AI-driven perception and sensor fusion. These features are however not stable during a vehicle’s lifetime due to various means of degradation. This introduces an inherent, yet unaddressed risk: once vehicles are in the field, their individual exposure to environmental effects lead to unpredictable behavior. The goal of this paper is to raise awareness of automotive sensor degradation. Various effects exist, which in combination may have a severe impact on the AI-based processing and ultimately on the customer domain. Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) type approaches are used to structure a complete coverage of relevant automotive degradation effects. Sensors include cameras, RADARs, LiDARs and other modalities, both outside and in-cabin. Sensor robustness alone is a well-known topic which is addressed by DV/PV. However, this is not sufficient and various degradations will be looked at which go significantly beyond currently tested environmental stress scenarios. In addition, the combination of sensor degradation and its impact on AI processing is identified as a validation gap. An outlook to future analysis and ways to detect relevant sensor degradations is also presented.