
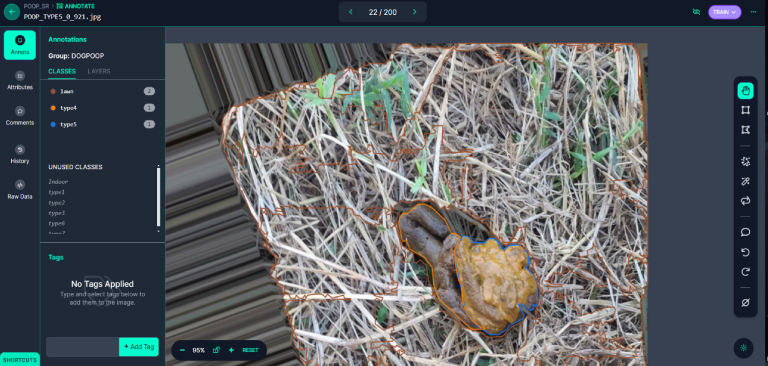
As pets now outnumber newborns in households, the demand for pet medical care and attention has surged. This has led to a significant burden for pet owners. To address this, our experiment utilizes image recognition technology to preliminarily assess the health condition of dogs, providing a rapid and economical health assessment method. By collaboration, we collected 2613 stool photos, which were enhanced to a total of 6079 images and analyzed using LabVIEW and the YOLOv8 segmentation model. The model performed excellently, achieving a precision of 86.805%, a recall rate of 74.672%, and an mAP50 of 83.354%. This proves its high recognition rate in determining the condition of dog stools. With the advancement of technology and the proliferation of mobile devices, the aim of this experiment is to develop an application that allows pet owners to assess their pets’ health anytime and manage it more conveniently. Additionally, the experiment aims to expand the database through cloud computing, optimize the model, and establish a global pet health interactive community. These developments not only propel innovation in the field of pet medical care but also provide practical health management tools for pet families, potentially offering substantial help to more pet owners in the future.
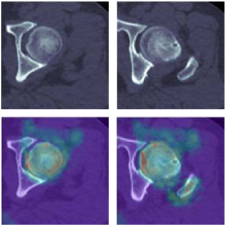
Accurate segmentation and recognition of retinal vessels is a very important medical image analysis technique, which enables clinicians to precisely locate and identify vessels and other tissues in fundus images. However, there are two problems with most existing U-net-based vessel segmentation models. The first is that retinal vessels have very low contrast with the image background, resulting in the loss of much detailed information. The second is that the complex curvature patterns of capillaries result in models that cannot accurately capture the continuity and coherence of the vessels. To solve these two problems, we propose a joint Transformer–Residual network based on a multiscale attention feature (MSAF) mechanism to effectively segment retinal vessels (MATR-Net). In MATR-Net, the convolutional layer in U-net is replaced with a Residual module and a dual encoder branch composed with Transformer to effectively capture the local information and global contextual information of retinal vessels. In addition, an MSAF module is proposed in the encoder part of this paper. By combining features of different scales to obtain more detailed pixels lost due to the pooling layer, the segmentation model effectively improves the feature extraction ability for capillaries with complex curvature patterns and accurately captures the continuity of vessels. To validate the effectiveness of MATR-Net, this study conducts comprehensive experiments on the DRIVE and STARE datasets and compares it with state-of-the-art deep learning models. The results show that MATR-Net exhibits excellent segmentation performance with Dice similarity coefficient and Precision of 84.57%, 80.78%, 84.18%, and 80.99% on DRIVE and STARE, respectively.
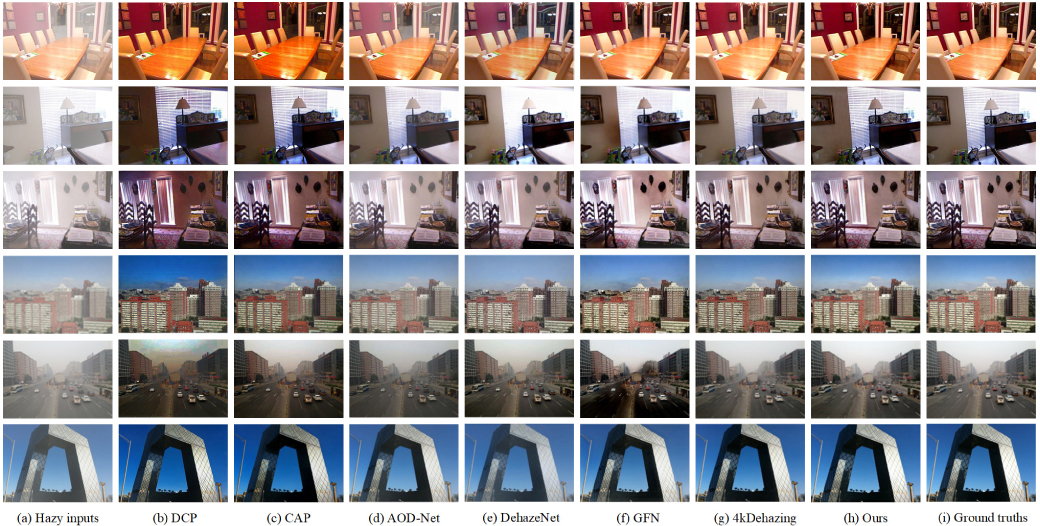

We propose a new convolutional neural network called Physics-guided Encoder–Decoder Network (PEDNet) designed for end-to-end single image dehazing. The network uses a reformulated atmospheric scattering model, which is embedded into the network for end-to-end learning. The overall structure is in the form of an encoder–decoder, which fully extracts and fuses contextual information from four different scales through skip connections. In addition, in view of the uneven spread of haze in the real world, we design a Res2FA module based on Res2Net, which introduces a Feature Attention block that is able to focus on important information at a finer granularity. The PEDNet is more adaptable when handling various hazy image types since it employs a physically driven dehazing model. The efficacy of every network module is demonstrated by ablation experiment results. Our suggested solution is superior to current state-of-the-art methods according to experimental results from both synthetic and real-world datasets.
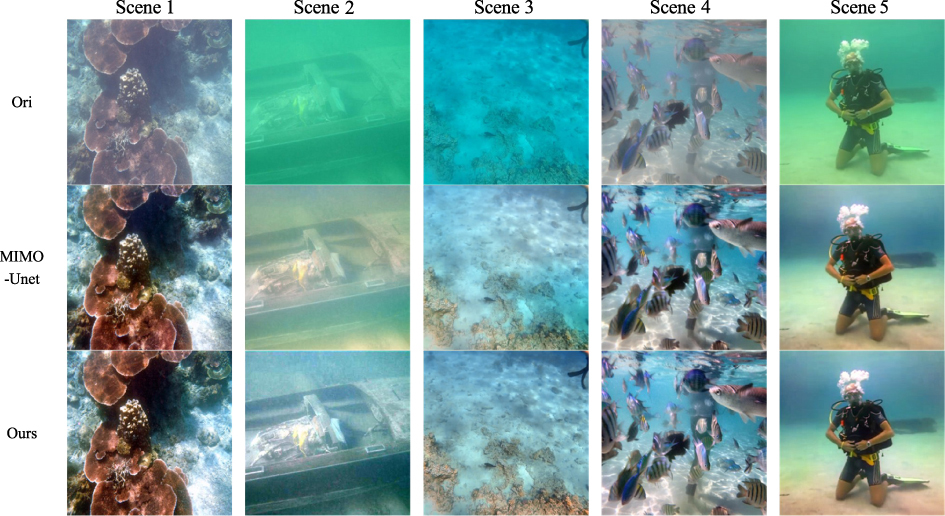

Underwater images are afflicted by dynamic blur, low illumination, poor contrast, and noise interference, hampering the accuracy of underwater robot proximity detection and its application in marine development. This study introduces a solution utilizing the MIMO-UNet network. The network integrates the Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling module between the encoder and the decoder to augment feature extraction and contextual information retrieval. Furthermore, the addition of a channel attention module in the decoder enhances detailed feature extraction. A novel technique combines multi-scale content loss, frequency loss, and mean squared error loss to optimize network weight updates, enhance high-frequency loss information, and ensure network convergence. The effectiveness of the method is assessed using the UIEB dataset. Ablation experiments confirm the efficacy and reasoning behind each module design while performance comparisons demonstrate the algorithm’s superiority over other underwater enhancement methods.
Digital watermarking is an important way to ensure the copyright protection of Thangka element images in Tibetan culture. These images exhibit rich foreground content and dense lines. However, existing digital watermarking methods often overlook these characteristics and employ a single watermark embedding strength that compromises performance. To address these issues, this paper proposes a robust Just Noticeable Distortion (JND) guided perceptually Thangka digital watermarking method. First, by considering the characteristics of texture distribution, it selectively identifies local regions of interest for large and small Thangka element images. Second, it constructs a visual perception JND to adaptively obtain the watermark embedding intensity. Finally, to enhance the robustness to JPEG compression and geometric attacks, it introduces a compression regulator factor and employs a Speeded-Up Robust Features feature matching algorithm. The experimental results show that the method achieves better performance compared with several classical methods in terms of imperceptibility and robustness.

Multichannel methods have attracted much attention in color image denoising. These are image denoising methods that combine the low-rankness of a matrix with the nonlocal self-similarity of a natural image. The methods apply to color images with noise of different intensities in each color channel. Denoising methods based on the low-rankness of tensors, and extensions of matrices, have also attracted attention in recent years. Many tensor-based methods have been proposed as extensions of matrix-based methods and have achieved higher denoising performance than matrix-based methods. Tensor-based methods perform denoising using an approximate function of the tensor rank. However, unlike multichannel methods, tensor-based methods do not assume different noise intensities for each channel. On the other hand, the tensor nuclear norm minus Frobenius norm (TNNFN) has been proposed in the domain of traffic data completion. The TNNFN is one of the tensor rank approximation functions and is known to have high performance in traffic data completion, but it has not been applied to image restoration. In this paper, we propose MC-TNNFN as a tensor-based multichannel method. It is a TNNFN-based multichannel method that uses TNNFN to remove noise from a tensor constructed from similar patches and then estimates the original image. Experimental results using natural images show that the proposed method outperforms existing methods objectively and subjectively.
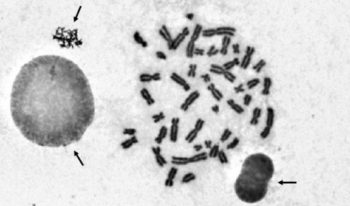
For the automated analysis of metaphase chromosome images, the chromosomes on the images need to be segmented first. However, the segmentation results often contain several non-chromosome objects. Elimination of non-chromosome objects is essential in automated chromosome image analysis. This study aims to exclude non-chromosome objects from segmented chromosome candidates for further analysis. A feature-based method was developed to eliminate non-chromosome objects from metaphase chromosome images. In a metaphase chromosome image, the chromosome candidates were segmented by a threshold first. After segmenting the chromosome candidates, four classes of features, namely, area, density-based features, roughness-based features, and widths, of the segmented candidates were extracted to discriminate between chromosomes and non-chromosome objects. Seven classifiers were used and compared to combine the extracted features to perform classifications. The experimental results show the usefulness of the combination of extracted features in distinguishing between chromosomes and non-chromosome objects. The proposed method can effectively separate non-chromosome objects from chromosomes and could be used as the preprocessing procedure for chromosome image analysis.
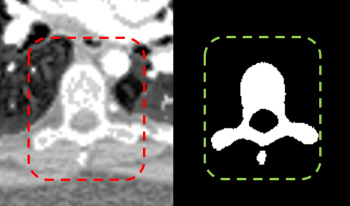
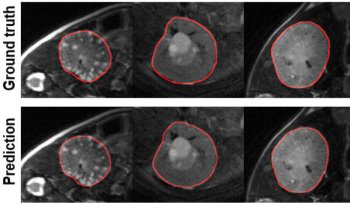
Spinal CT image segmentation is actively researched in the field of medical image processing. However, due to factors such as high variability among spinal CT slices and image artifacts, and so on, automatic and accurate spinal CT segmentation tasks are extremely challenging. To address these issues, we propose a cascaded U-shaped framework that combines multi-scale features and attention mechanisms (MA-WNet) for the automatic segmentation of spinal CT images. Specifically, our framework combines two U-shaped networks to achieve coarse and fine segmentation separately for spinal CT images. Within each U-shaped network, we add multi-scale feature extraction modules during both the encoding and decoding phases to address variations in spine shape across different slices. Additionally, various attention mechanisms are embedded to mitigate the effects of image artifacts and irrelevant information on segmentation outcomes. Experimental results show that our proposed method achieves average segmentation Dice similarity coefficients of 94.53% and 91.38% on the CSI 2014 and VerSe 2020 datasets, respectively, indicating highly accurate segmentation performance, which is valuable for potential clinical applications.
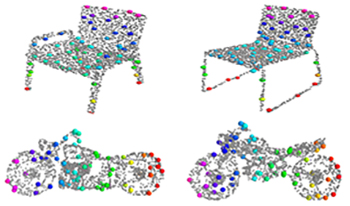
Sparse representation is the key part of shape registration, compression, and regeneration. Most existing models generate sparse representation by detecting salient points directly from input point clouds, but they are susceptible to noise, deformations, and outliers. The authors propose a novel alternative solution that combines global distribution probabilities and local contextual features to learn semantic structural consistency and adaptively generate sparse structural representation for arbitrary 3D point clouds. First, they construct a 3D variational auto-encoder network to learn an optimal latent space aligned with multiple anisotropic Gaussian mixture models (GMMs). Then, they combine GMM parameters with contextual properties to construct enhanced point features that effectively resist noise and geometric deformations, better revealing underlying semantic structural consistency. Second, they design a weight scoring unit that computes a contribution matrix to the semantic structure and adaptively generates sparse structural points. Finally, the authors enforce semantic correspondence and structural consistency to ensure that the generated structural points have stronger discriminative ability in both feature and distribution domains. Extensive experiments on shape benchmarks have shown that the proposed network outperforms state-of-the-art methods, with lower costs and more significant performance in shape segmentation and classification.