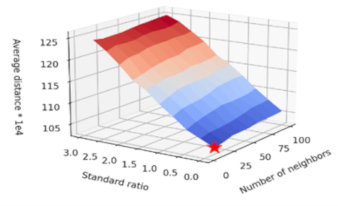
Point clouds generated from 3D scans of part surfaces consist of discrete 3D points, some of which may be incorrect, or outliers. Outlier points can be caused by the scanning method, part surface attributes, and data acquisition techniques. Filtering techniques to remove these outliers from point clouds frequently require a “guess and check” method to determine proper filter parameters. This paper presents two novel approaches to automatically determine proper filter parameters using the relationships among point cloud outlier removal, principal component variance, and the average nearest neighbor distance. Two post-processing workflows were developed that reduce outlier frequency in point clouds using these relationships. These post-processing workflows were applied to point clouds with artificially generated noise and outliers along with two real-world point clouds. Analysis of the results showed both approaches effectively reducing outlier frequency when used in suitable circumstances.
Michael Holm, Eliot Winer, "Two Automated Point Cloud Filtration Approaches using Principal Component Variance and Nearest Neighbor Distance" in Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, 2024, pp 1 - 18, https://doi.org/10.2352/J.ImagingSci.Technol.2024.68.6.060506
 Find this author on Google Scholar
Find this author on Google Scholar Find this author on PubMed
Find this author on PubMed

