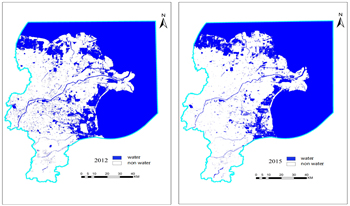
Currently, there is a relative insufficiency of research on the feature extraction of braided rivers and the river-scale water system evolution pattern under long time series in China. Therefore, continuous monitoring of surface water and analysis of its evolution process for the Yellow River Delta region have great application value to supplement and improve related knowledge and realize sustainable water resource management. The satellite remote sensing image is an important medium for obtaining surface water change data. Since free high-quality, long time-series high-resolution images are difficult to obtain, this paper selects the Landsat series of image data, which has a longer time span and better consistency, as the data source for the relevant research. In recent years, deep learning models have been gradually applied to the task of extracting surface water bodies from remote sensing images. However, deep learning methods usually have problems such as difficulty in capturing the fine contours of water bodies and poor extraction ability for fine water bodies. Based on this problem, this study proposes an Efficient Local Strip Convolutional Attention model for water system extraction and evolution analysis in the Yellow River Delta region. The experimental results show that the proposed model not only performs best in terms of overall accuracy but also obtains smoother water body boundaries and more complete extraction of small and medium-sized rivers, compared with the water body index methods MNDWI and AWEIsh, the machine learning method SVM, and the semantic segmentation models U-Net, SR-SegNet v2, and FWENet.
Yuyang Ye, Zhijiang Li, "Extraction and Spatiotemporal Evolution Analysis of Water System in the Yellow River Delta based on ELSCA Model" in Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, 2025, pp 1 - 15, https://doi.org/10.2352/J.ImagingSci.Technol.2025.69.3.030406
 Find this author on Google Scholar
Find this author on Google Scholar Find this author on PubMed
Find this author on PubMed