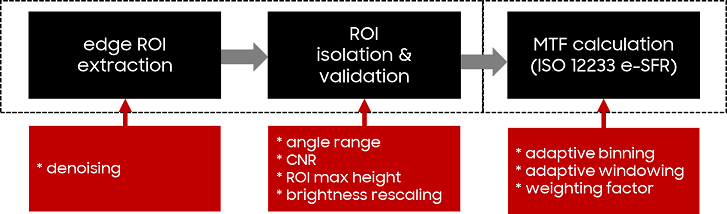
Evaluating spatial frequency response (SFR) in natural scenes is crucial for understanding camera system performance and its implications for image quality in various applications, including machine learning and automated recognition. Natural Scene derived Spatial Frequency Response (NS-SFR) represented a significant advancement by allowing for direct assessment of camera performance without the need for charts, which have been traditionally limited. However, the existing NS-SFR methods still face limitations related to restricted angular coverage and susceptibility to noise, undermining measurement accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel methodology that can enhance the NS-SFR by employing an adaptive oversampling rate (OSR) and phase shift (PS) to broaden angular coverage and by applying a newly developed adaptive window technique that effectively reduces the impact of noise, leading to more reliable results. Furthermore, by simulation and comparison with theoretical modulation transfer function (MTF) values, as well as in natural scenes, the proposed method demonstrated that our approach successfully addresses the challenges of the existing methods, offering a more accurate representation of camera performance in natural scenes.
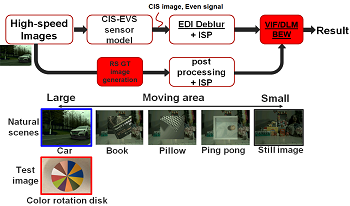
Event-based Vision Sensor (EVS) generates pixel-level and low-latency event data that is useful for reconstructing temporal components of images for deblurring. In this new application development, we need to know how EVS hardware parameters affect the natural motion scene image quality (IQ) to determine hardware specifications before starting design. To realize this approach, it is beneficial to build an End-to-End IQ simulation that runs from hardware simulations to natural motion scene IQ evaluation. Previously, we developed a Hybrid-EVS-CIS simulator to generate synthesized color rotation disk images and their event data fed into an image deblur block. Then image blurriness was evaluated by using the Blurred Edge Width metric (BEW). This paper proposes the extended IQ evaluation, which is an End-to-End IQ simulation for natural motion scenes. A simultaneous evaluation of blurriness and noise on images was verified by using Visual Information Fidelity and Detail Loss Metric. We also build a method to assess pixel-speed using BEW. Those IQ evaluation methods were the last pieces to realize End-to-End IQ simulation.

GPT-4, which is a multimodal large-scale language model, was released on March 14, 2023. GPT-4 is equipped with Transformer, a machine learning model for natural language processing, which trains a large neural network through unsupervised learning, followed by reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) based on human feedback. Although GPT-4 is one of the research achievements in the field of natural language processing (NLP), it is a technology that can be applied not only to natural language generation but also to image generation. However, specifications for GPT-4 have not been made public, therefore it is difficult to use for research purposes. In this study, we first generated an image database by adjusting parameters using Stable Diffusion, which is a deep learning model that is also used for image generation based on text input and images. And then, we carried out experiments to evaluate the 3D CG image quality from the generated database, and discussed the quality assessment of the image generation model.

This paper is the continuation of a previous work, which aimed to develop a color rendering model using ICtCp color space, to evaluate SDR and HDR-encoded content. However, the model was only tested on an SDR image dataset. The focus of this paper is to provide an analysis of a new HDR dataset of laboratory scenes images using our model and additional color rendering visualization tools. The new HDR dataset, captured with different devices and formats in controlled laboratory setups, allows the estimation of HDR performances, encompassing several key aspects including color accuracy, contrast, and displayed brightness level, in a variety of lighting scenarios. The study provides valuable insights into the color reproduction capabilities of modern imaging devices, highlighting the advantages of HDR imaging compared to SDR and the impact of different HDR formats on visual quality.

Printing display images normally proceeds well provided they comply with the SDR gamut supported by color management systems (CMS), like ICM used in Windows OS. Twilight vision, unfortunately, complicates this process, as it is quite difficult to convert images captured by UHDR systems given that their contrast ratios (CR) sometime exceeded 10^6:1 or so; SDR images have CR values of approx. 100:1. A typical example is the reproduction of lunar texture. Quite recently, we resolved this problem by employing just global tone mapping (GTM). Even with the use of GTM, emissive displays like LCD, not projection displays or printed matter, are strongly recommended to prevent image quality degradation. This study addresses the reasons why CMS fail to handle twilight vision material well and proposes enhanced GTM for printing emissive display images. The main point is the difference between the perception responses demonstrated in daytime and in twilight, even after the UHDR material is converted into SDR images. In other words, the key idea is to focus on the underutilized top and bottom margins of the reproduced SDR images. From another viewpoint, the most important result is the acquisition of super sensitivity. Our proposal enables high sensitivity even with the same sensor (increase is approx. 10 to 30 times).

This research explores the effect of various eyewear lenses, designed with varied transmittance properties, on human visual perception. These lenses are developed to enhance contrast for spatial-chromatic patterns like cyan-red (CR) and magenta-green (MG) compared to lenses with more uniform transmittance. The study evaluates participants’ accuracy and response times in identifying contrast patterns, aiming to understand how different eyewear configurations affect these visual metrics. Two experiments were conducted: the first adjusted spatial frequencies to determine visibility thresholds with different eyewear, while the second utilized a 4-alternative forced-choice (4-AFC) method to measure participants’ ability to identify contrast patterns. Results indicate that eyewear with varied transmittance enhances contrast sensitivity for these chromatic pairs more effectively than uniform transmittance lenses, offering valuable insights into optimizing color-enhancing eyewear for improving certain aspects of visual performance and providing broader applications in enhancing human visual perception across various visual tasks.

Portraits are one of the most common use cases in photography, especially in smartphone photography. However, evaluating portrait quality in real portraits is costly and difficult to reproduce. We propose a new method to evaluate a large range of detail preservation rendering on real portrait images. Our approach is based on 1) annotating a set of portrait images grouped by semantic content using pairwise comparison 2) taking advantage of the fact that we are focusing on portraits, using cross-content annotations to align the quality scales 3) training a machine learning model on the global quality scale. On top of providing a fine-grained wide range detail preservation quality output, numerical experiments show that the proposed method correlates highly with the perceptual evaluation of image quality experts.
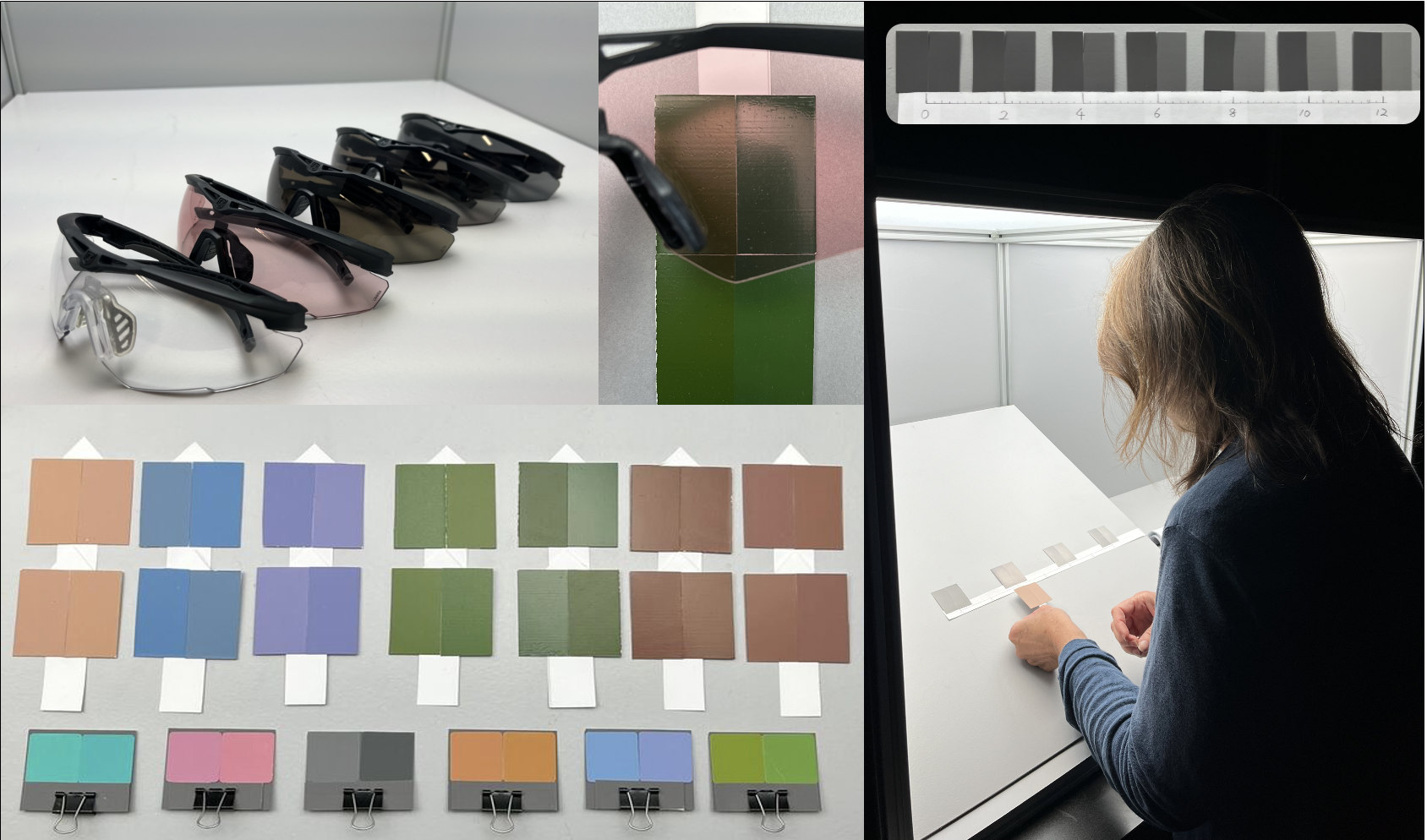

Tinted eyewear is increasingly utilized in outdoor environments to protect against ultraviolet radiation and manage luminance levels reaching the human visual system. While these protective functions are well-established, these modifications can also affect color perception. This research investigates how different tinted eyewear affects observers’ ability to distinguish small color differences in reflective samples, with implications for understanding how specific eyewear transmittance properties influence color discrimination ability in different environments. Two sets of stimuli are used: (1) six adjacent Munsell sample pairs varying only in hue, and (2) seven parameric pairs generated through Kubelka-Munk theory modeling of 16 pigments. Six eyewear with different transmittance properties were examined in this study under normalized lighting conditions. Color differences (ΔE2000) were predicted using spectral data and validated through psychophysical experiments with 27 observers using a scaling method. Results demonstrate that tinted eyewear can alter color discrimination ability compared to neutral eyewear, with effects varying based on the interaction between the eyewear’s spectral transmittance and the stimuli’s spectral reflectance. For example, one foliage pair showed a ΔE2000 of 2.37 under neutral eyewear that increased to 5.21 under a tinted eyewear, with corresponding mean observed visual differences of 2.79 and 5.51, respectively. Overall, the observed color difference evaluations aligned with predictions, with correlation coefficients (r) of 0.816. This research enhances the understanding of how tinted eyewear affects color perception and supports the development of eyewear optimized for specific outdoor environments.
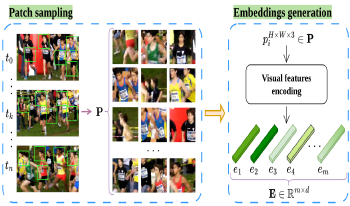
This paper proposes a novel frame selection technique based on embedding similarity to optimize video quality assessment (VQA). By leveraging high-dimensional feature embeddings extracted from deep neural networks (ResNet-50, VGG-16, and CLIP), we introduce a similarity-preserving approach that prioritizes perceptually relevant frames while reducing redundancy. The proposed method is evaluated on two datasets, CVD2014 and KonViD-1k, demonstrating robust performance across synthetic and real-world distortions. Results show that the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in handling diverse and in-the-wild video content, achieving robust performances on KonViD-1k. This work highlights the importance of embedding-driven frame selection in improving the accuracy and efficiency of VQA methods.
Members of several working groups within the ISO Technical Committee 42 (photography) have begun addressing the important topic of providing guidance for which skin tones to use for image quality testing in various photographic applications. For example, when color patches for skin tones are used in TC42 standards, they should be inclusive and represent a broad range of skin types. Skin tones are present in more than 60% of all captured photographs and therefore need to accurately be corrected in digital cameras, properly displayed and printed on various softcopy and hardcopy devices, and the permanence of the printed colors needs to be determined. During the 2023 plenary meeting of TC 42 in Japan, an ad hoc working group (AHG) was initiated to develop such guidance and report back during the upcoming 2025 plenary meeting in Berlin. The group has investigated existing skin tone studies, including Fitzpatrick, Von Luschan, L’Oreal, PERLA, Monk, Pantone ST, Massey NIS, Verkruysse, Holm and Wueller. It is currently drafting an ISO Technical Report that will document the work and result in recommendations regarding the selection of skin tone color patches and spectra to use for ISO related applications.