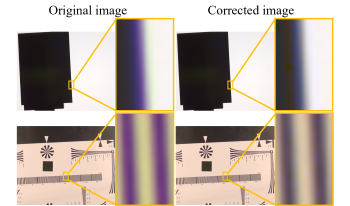
In digital cameras, the wavelength dependency of images captured through lenses and filters affects the spatial resolution characteristics of the images, which adversely impacts image quality. Previously, lens design and image processing techniques have been considered to address the aforementioned problem. Although aberrations could be improved, it was difficult to completely analyze the wavelength dependency of resolution characteristics. This study aims to reduce the wavelength dependency of the spatial resolution of digital cameras. Edge-based modulation transfer function (MTF) measurements using a 2D spectroradiometer were used to obtain wavelength-specific MTFs and quantitively reveal the wavelength dependency of the spatial resolution characteristics. Moreover, we experimentally confirmed that adjusting the MTFs of the CIEXYZ images obtained by combining spectral images to be closer reduces the difference in spatial resolution among color images while minimizing the color change before and after the adjustment.
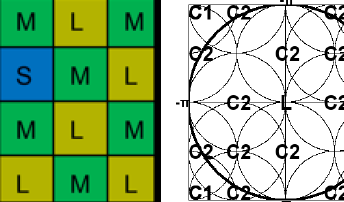
New, high-resolution CMOS image sensors for mobile phones have moved beyond the single-binnable Quad Bayer and RGBW-Kodak patterns to the double binnable Hexadeca Bayer pattern featuring 4x4 tiles of like-colored pixels. Pixel binning enables high-speed, low-power readout in low-resolution modes and, more importantly, a reduction of read noise via floating diffusion binning. In this paper, we present the non-intuitive result that Nona and Hexadeca Bayer can be superior to Quad Bayer in demosaicking quality due to degeneracies in the latters spectrum. However, Hexadeca Bayer suffers from the weakness of generating Quad Bayer after one round of binning. We introduce novel double binnable RGBW and LMS CFAs, composed of 2x2 tiles capable of 4:1 floating diffusion binning, that are free from spectral degeneracies and thus demosaic well in full resolution and both binned modes. RGBW offers a 6 dB low-light, read noise-limited, SNR advantage over Quad and Hexadeca Bayer in all resolution modes, while for LMS, the corresponding advantage is 4.2 dB.
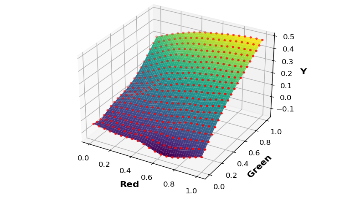
Color correction involves converting device-dependent RGB values into a device-independent color space, like XYZ or sRGB. This paper introduces a novel method for deriving a matrix-based transformation using tensor product B-splines, extending previous polynomial approaches. The proposed spline-based model offers enhanced adaptability in color correction, consistently surpassing traditional polynomial methods across various cameras. Splines, being piecewise polynomials, offer increased flexibility in modeling, adapting to different spectral characteristics of cameras. Performance comparison of the spline-based model against previous methods was conducted using simulated data of natural scenes on two different cameras in both training and testing phases.

Accurate color reproduction on a display requires an inverse display model, mapping colorimetric values (e.g. CIE XYZ) into RGB values driving the display. To create such a model, we collected a large dataset of display color measurements for a high refresh-rate 4-primary OLED display. We demonstrated that, unlike traditional LCD displays, multi-primary OLED display color responses are non-additive and non-linear for some colors. We tested the performances of different regression methods: polynomial regression, look-up tables, multi-layer perceptrons, and others. The best-performing models were additionally validated on newly measured (unseen) test colors. We found that the performances of several variations of 4th-degree polynomial models were comparable to the look-up table and machine-learning-based models while being less resource-intensive.

Variability in the encoding of unique hues within the color vision system results in significant diversity in hue appearances among individuals. This paper introduces a novel algorithm that equalizes hue appearance for individual observers by incorporating their unique hue perception and replacing the default NCS unique hue in a modern color appearance model with individualized selections. By customizing the color representation to match the observer's perception, the algorithm enhances the consistency and personalized rendering of hue appearance. The findings of this study contribute to advancing color perception research and have practical implications in various domains such as, graphic design, and visual color reproduction.

Consistency of color appearance (CCA) can be defined as an image attribute that gives a sense of identity among a set of images with different tones and colors, where the relationship between a group of colors in one embodiment is consistent with the relationship between the corresponding set of colors in another image. The consistency of color is a complex and important aspect of color reproduction. Maintaining color consistency is particularly crucial for printing and graphic communications, in general, where precise reproduction is required for scene identification, brand identity, and image quality. Characterizing consistency of color appearance in images is a challenging task because it is affected by differences in reproduction processes, viewing environments, and the output requirements. This research addressed the necessity for standardized approaches to assess and model CCA, a pivotal aspect in ensuring precise and uniform color replication across diverse media and platforms. In the experiment observers evaluated and compared the effects of gamut and gray balance variations on visual appearance of printed and displayed images and correlated the resulting CCA scale with image-based colorimetrical data. The study results showed that there is a close similarity between observed CCA for images presented under hard proofing (printed images) and soft proofing (display images) conditions. A high correlation between image-based CCA metrics for displayed and printed images when tested with observers' CCA responses, indicates the feasibility of using display images to study CCA for print production. The use of image data in the analysis offers a fruitful approach for modeling CCA.