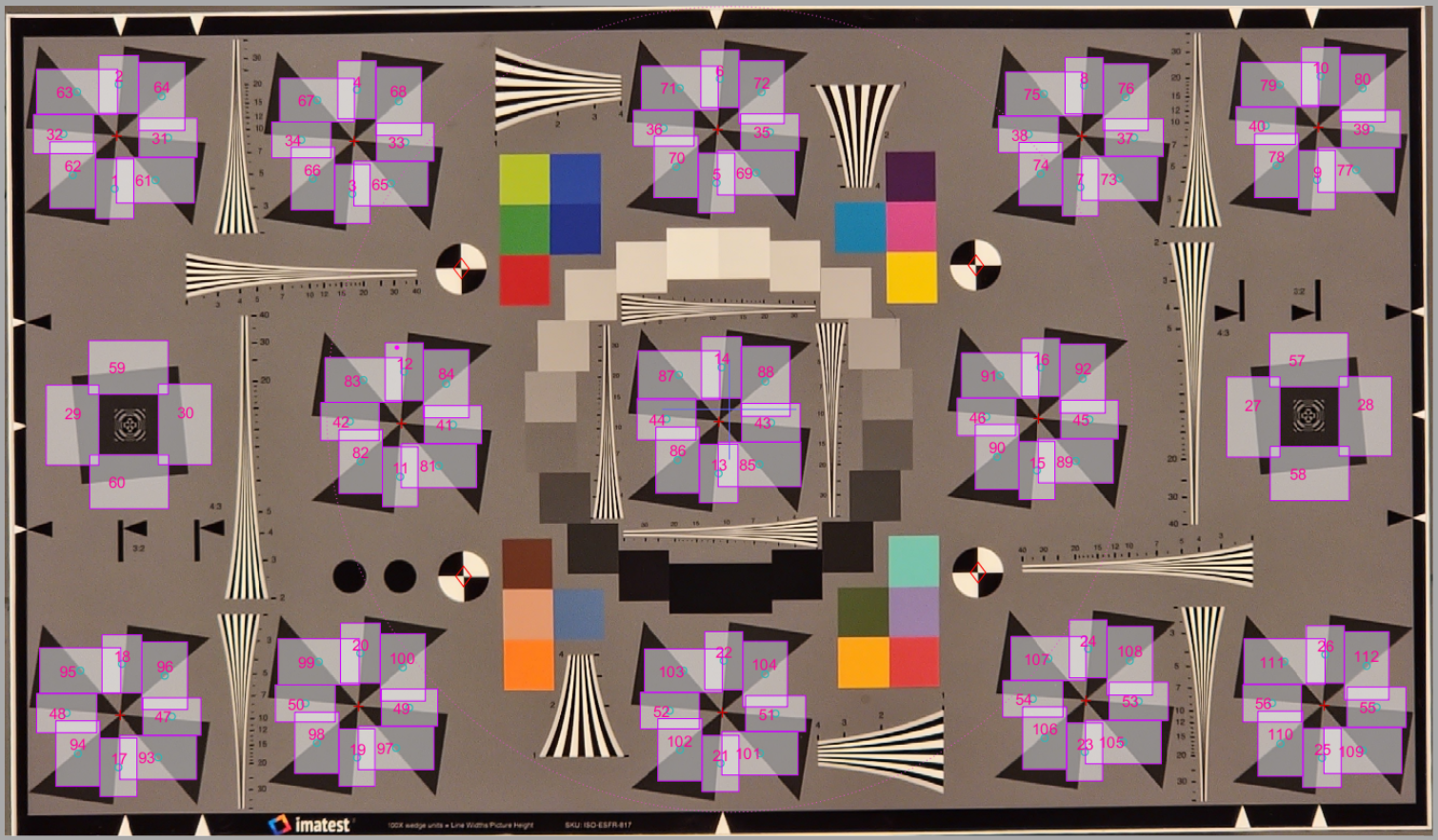
The introduction of the new edge-based spatial frequency response (e-SFR) feature, known as the slanted star, in ISO 12233:2023 marks a significant change to the standard. This feature offers four additional edge orientations compared to the previously used slanted square, enabling measurement of sagittal and tangential spatial frequency response (SFR) in addition to SFR derived from vertical and horizontal edges. However, the expanded utility provided by these additional edges presents challenges in reliably automating the placement of appropriate regions of interest (ROIs) for e-SFR analysis, thereby complicating the accurate comparison of resolution across various orientations. This paper addresses these challenges by providing recommendations for the efficient and precise detection and analysis of the ISO 12233 slanted star feature. Our recommendations are based on thorough simulations and experimentally validated results obtained under diverse and challenging conditions.