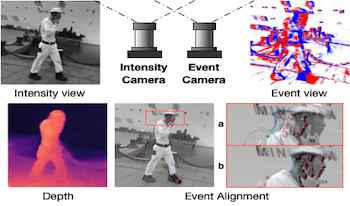
Event cameras are novel bio-inspired vision sensors that output pixel-level intensity changes in microsecond accuracy with high dynamic range and low power consumption. Despite these advantages, event cameras cannot be directly applied to computational imaging tasks due to the inability to obtain high-quality intensity and events simultaneously. This paper aims to connect a standalone event camera and a modern intensity camera so that applications can take advantage of both sensors. We establish this connection through a multi-modal stereo matching task. We first convert events to a reconstructed image and extend the existing stereo networks to this multi-modality condition. We propose a self-supervised method to train the multi-modal stereo network without using ground truth disparity data. The structure loss calculated on image gradients is used to enable self-supervised learning on such multi-modal data. Exploiting the internal stereo constraint between views with different modalities, we introduce general stereo loss functions, including disparity cross-consistency loss and internal disparity loss, leading to improved performance and robustness compared to existing approaches. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, especially the proposed general stereo loss functions, on both synthetic and real datasets. Finally, we shed light on employing the aligned events and intensity images in downstream tasks, e.g., video interpolation application.

Event cameras are novel bio-inspired vision sensors that output pixel-level intensity changes in microsecond accuracy with high dynamic range and low power consumption. Despite these advantages, event cameras cannot be directly applied to computational imaging tasks due to the inability to obtain high-quality intensity and events simultaneously. This paper aims to connect a standalone event camera and a modern intensity camera so that applications can take advantage of both sensors. We establish this connection through a multi-modal stereo matching task. We first convert events to a reconstructed image and extend the existing stereo networks to this multi-modality condition. We propose a self-supervised method to train the multi-modal stereo network without using ground truth disparity data. The structure loss calculated on image gradients is used to enable self-supervised learning on such multi-modal data. Exploiting the internal stereo constraint between views with different modalities, we introduce general stereo loss functions, including disparity cross-consistency loss and internal disparity loss, leading to improved performance and robustness compared to existing approaches. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, especially the proposed general stereo loss functions, on both synthetic and real datasets. Finally, we shed light on employing the aligned events and intensity images in downstream tasks, e.g., video interpolation application.