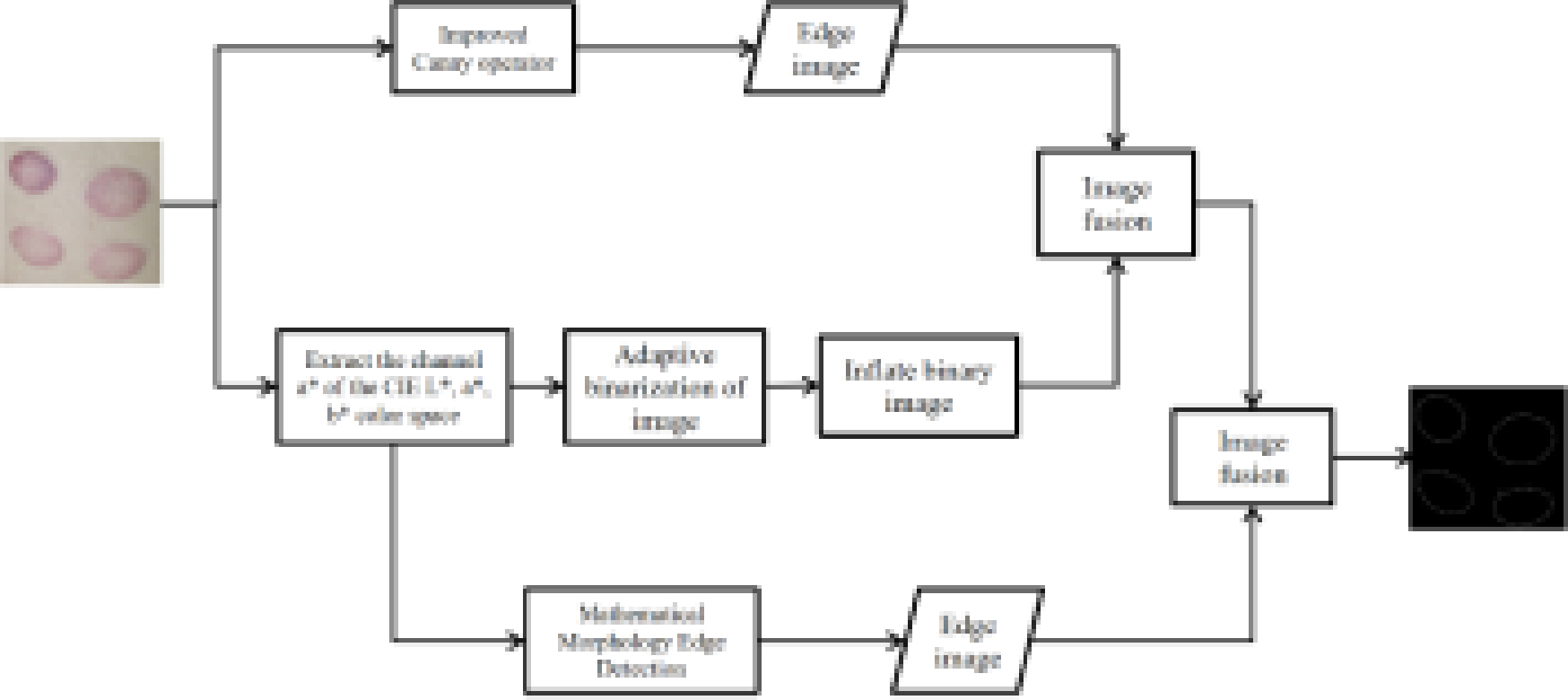
This paper presents an improved Canny algorithm for locating the edges of cupping spots with an aim toward solving the problem that these edges cannot be completely detected due to the presence of pores, texture, and other impurities on the skin surface. First, hybrid filtering, the four-direction Sobel operator, and the maximum inter-class variance (Otsu) algorithm are introduced to improve the original Canny algorithm, enhancing its adaptability and accuracy in edge localization. Second, the binary image in the CIE L∗a∗b∗ color space is used as a mask area to fuse with the obtained edge image. Finally, the edge images of the fused image and the channel a* image are merged to yield the final detection image. The experimental results demonstrate that compared to the traditional Canny algorithm, the improved algorithm can clearly detect the edge of cupping spots from cupping therapy in traditional Chinese medicine, fully demonstrating the feasibility and effectiveness of the algorithm.

Handwriting significantly contributes to the task of the writer identification and verification of modern and historical documents. This work developed a writer verification system for ancient Hebrew square-script manuscripts, mainly based on the edge-direction feature. Two configurations within the proposed system are carried out, i.e., character-based edge-direction feature extraction and extraction techniques of handwriting shape representation that may drive the system performance. A classification-based verification approach, utilizing Support Vector Machine (SVM) as the classifier, is employed to evaluate the performance of the two configurations. This study has confirmed that the skeleton-based shape representation technique outperforms the edge detection technique used in the predecessor approach. Furthermore, a character-based writer verification system provides the corresponding scholars and experts with an alphabetical investigation to identify the uniqueness of each writer’s handwriting.