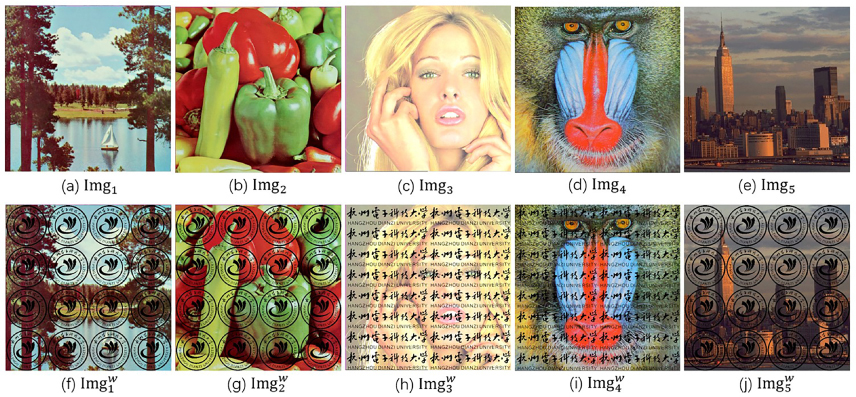
Digital watermarking is an important way to ensure the copyright protection of Thangka element images in Tibetan culture. These images exhibit rich foreground content and dense lines. However, existing digital watermarking methods often overlook these characteristics and employ a single watermark embedding strength that compromises performance. To address these issues, this paper proposes a robust Just Noticeable Distortion (JND) guided perceptually Thangka digital watermarking method. First, by considering the characteristics of texture distribution, it selectively identifies local regions of interest for large and small Thangka element images. Second, it constructs a visual perception JND to adaptively obtain the watermark embedding intensity. Finally, to enhance the robustness to JPEG compression and geometric attacks, it introduces a compression regulator factor and employs a Speeded-Up Robust Features feature matching algorithm. The experimental results show that the method achieves better performance compared with several classical methods in terms of imperceptibility and robustness.
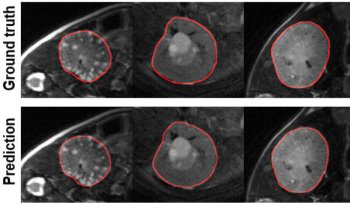
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence and image processing technologies, images are susceptible to accidental or deliberate tampering attacks. This paper presents a watermark tampering detection method to address the challenges of marking and identifying image sources in specialized fields such as medicine and justice. A quaternary encoding matrix is proposed to map the geometric information of any arbitrary watermark onto the carrier image, bridging the watermark and the magic matrix that performs steganographic modifications. The specific magic matrix serves as the key to retrieving and visualizing the steganographically embedded watermark. In comparative experiments, our method shows a significant improvement over the existing method, with the peak signal-to-noise ratio of stego images being 24.58 dB higher and the Intersection over Union increasing by 20.30%. This demonstrates that our method effectively maintains the authentication and integrity of carrier images while producing high-quality images after steganography.

In this paper, an algorithm that embed watermarking into color QR code based on image normalization and contourlet transform is proposed, which is based on image normalization and invariant centroid theory. For the purpose of enhancing the invisibility and resistance to geometric attack of watermarking, we first encrypt the watermarking with chaotic method before information embedding, and then eliminate the effect of geometric change by utilizing image normalization. Based on the matrix singular value decomposition in contourlet domain, suggests an adaptive watermarking scheme that watermarks are embedded into the above resulted images. Corresponding, we perform inverse transform to the QR code which is attacked by geometric transformation and non geometric transformation including blurring, JPEG compression, noise addition, sharpening, scaling, rotation, and cropping before extracting the watermarking. Thus, we can prove the truth of the attacked QR code by the extracted watermarking which is recognizable.