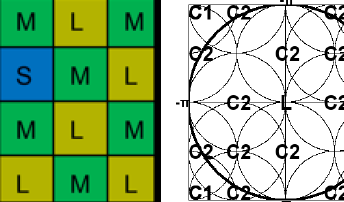
New, high-resolution CMOS image sensors for mobile phones have moved beyond the single-binnable Quad Bayer and RGBW-Kodak patterns to the double binnable Hexadeca Bayer pattern featuring 4x4 tiles of like-colored pixels. Pixel binning enables high-speed, low-power readout in low-resolution modes and, more importantly, a reduction of read noise via floating diffusion binning. In this paper, we present the non-intuitive result that Nona and Hexadeca Bayer can be superior to Quad Bayer in demosaicking quality due to degeneracies in the latters spectrum. However, Hexadeca Bayer suffers from the weakness of generating Quad Bayer after one round of binning. We introduce novel double binnable RGBW and LMS CFAs, composed of 2x2 tiles capable of 4:1 floating diffusion binning, that are free from spectral degeneracies and thus demosaic well in full resolution and both binned modes. RGBW offers a 6 dB low-light, read noise-limited, SNR advantage over Quad and Hexadeca Bayer in all resolution modes, while for LMS, the corresponding advantage is 4.2 dB.

Recently, many deep learning applications have been used on the mobile platform. To deploy them in the mobile platform, the networks should be quantized. The quantization of computer vision networks has been studied well but there have been few studies for the quantization of image restoration networks. In this paper, we studied the effect of the quantization of activations for deep learning network on image quality following previous study for weight quantization for deep learning network. This study is also about the quantization on raw RGBW image demosaicing for 10 bit image while fixing weight bit as 8 bit. Experimental results show that 11 bit activation quantization can sustain image quality at the similar level with floating-point network. Even though the activations bit-depth can be very small bit in the computer vision applications, but image restoration tasks like demosaicing require much more bits than those applications. 11 bit may not fit the general purpose hardware like NPU, GPU or CPU but for the custom hardware it is very important to reduce its hardware area and power as well as memory size.

Recently, a CFA sensor including a W channel has been developed. Since the W channel receives brightness information, it has a broad spectrum band compared to primary colors (Red, Green, Blue) and exhibits a high SNR. A camera using the CFA sensor obtains only certain type of color information for each pixel, so a color interpolation method is used to restore the full resolution image. In this paper, we propose a new color interpolation method for Sony-RGBW CFA. The proposed method is edge-adaptive and preferentially restores the W channel with a high sampling rate. In the next step, the R, G, and B channels are restored in the color difference domain using the W channel with the full resolution. Experimental results showed that the reconstructed image obtained by applying the proposed algorithm to the Sony-RGBW is superior to the image restored by conventional method in terms of SNR and visual confirmation.