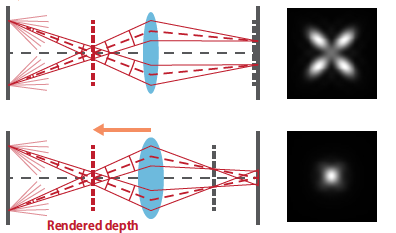
Light field (LF) displays are a promising 3D display technology to mitigate the vergence-accommodation conflict. Recently, we have proposed a simulation framework to model an LF display system. It has predicted that the in-focus optical resolution on the retina would drop as the relative depth of a rendered image to the display-specific optical reference depth grows. In this study, we examine the empirical optical resolution of a near-eye LF display prototype by capturing rendered test images and compare it to simulation results based on the previously developed computational model. We use an LF display prototype that employs a time-multiplexing technique and achieves a high angular resolution of 6-by-6 viewpoints in the eyebox. The test image is rendered at various depths ranging 0–3 diopters, and the optical resolution of the best-focus images is analyzed from images captured by a camera. Additionally, we compare the measurement results to the simulation results, discussing theoretical and practical limitations of LF displays.