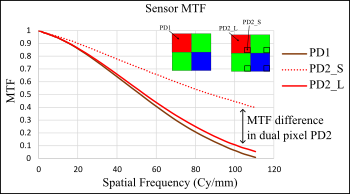
High dynamic range (HDR) image sensors have become increasingly important for automobile applications, particularly for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) in recent years. The traditional single photodiode and split photodiode pixels are the two most commonly used technologies to build HDR image sensors in the industry. This study used a monochrome CMOS image sensor to model single and split photodiode pixel images to examine image quality. Slanted edge images were used to calculate the spatial frequency response (SFR), and the results showed a significant difference in modulation transfer function (MTF) from the split photodiode. MTF of the large photodiode in the split photodiode pixel at half Nyquist was lower than MTF of the small photodiode, as expected. However, the sampling area and the spatial separation of the small photodiode in the split pixel caused edge artifacts in the image. The traditional single photodiode pixel does not experience a change in MTF with light level and edge artifacts were not observed.