Digital watermarks for texts come in numerous forms. The text itself, but also its appearance, i.e. font, letter spacing or line spacing, can be modified. Here, we present an approach that marks the text itself by introducing changes to the written words. For this, numerous methods are known, such as change from active to passive, modulation of sentence lengths or replacements with synonyms. We use ChatGPT to supplement existing texts with suggestions for synonymous formulations. We also look at evaluating the transparency of the marked texts with the help of ChatGPT.
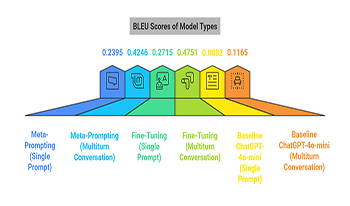
With the exponential growth of large language models (LLMs), enhancing model adaptability for diverse real-world applications has become crucial. This study critically examines domain-specific fine-tuning of ChatGPT and explores the potential of In-Context Learning (ICL) as a complementary strategy, highlighting the delicate balance between generalizability and specificity in health promotion communication. Employing two distinct fine-tuning strategies—single-prompt interactions and multi-turn conversation models—the research advances current methodologies for tailoring LLMs to specialized domains. By incorporating approaches such as data augmentation, transfer learning, and adaptive fine-tuning, alongside structured Meta-Prompting, the study systematically evaluates ChatGPT’s adaptability in handling health-specific dialogues, comparing model performance across varied interaction types. Case studies and targeted customization strategies underscore the practical utility and significant impact of these adaptations in applied health communication contexts, demonstrating the enhanced contextual understanding in multi-turn interactions. Results indicate the superior efficacy of the multi-turn approach in managing nuanced, contextually rich dialogues, underscoring the capacity of the model for sustained engagement in health-related discourse. ICL with Meta-Prompting, on the other hand, demonstrates notable flexibility and resource efficiency. These findings have significant implications for advancing AI in health communication, suggesting a developmental trajectory that integrates technological sophistication with a focus on empathetic user engagement.