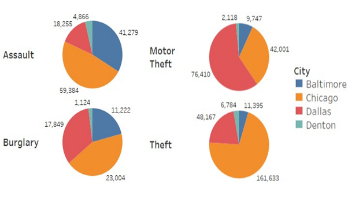
The rise in crime rates over the past few years is a major issue and is a huge source of worry for police departments and law enforcement organizations. Crime severely harms the lives of victims and the communities they live in many places throughout the world. It is an issue of public disturbance, and large cities often see criminal activity. Many studies, media, and websites include statistics on crime and it is contributing elements, such as population, unemployment, and poverty rate. This paper compares and visualizes the crime data for four different cities in the USA, namely Chicago, Baltimore, Dallas, and Denton. We assess areas that are significantly affected based on zip codes and variations in crime categories. As the crime rates have significantly changed both upward and downward throughout time, these changes are compared to their external causes such as population, unemployment, and poverty. The results show crime frequency and distribution across four different cities and supply valuable information about the complex relationship between social factors and criminal behavior. These results and outcomes will help the police department and law enforcement organizations better understand crime issues, map crime incidents onto a geographical map, and supply insight into factors affecting crime that will help them deploy resources and help in their decision-making process.

This paper presents a new quantitative approach to the study of Asian lacquers using surface metrology, and two data science approaches: feature engineering and convolutional deep neural networks, as used in machine vision or image recognition applications. The types of Asian lacquers and additives have a quantifiable impact on the topography of the resulting surface. To understand the unaged and aged characteristics, 15 different formulas of Asian lacquer were prepared using laccol, thitsiol and urushiol with the most common additives: oils, pigments and resins. These were studied with the surface metrology instrumental technique of confocal microscopy.