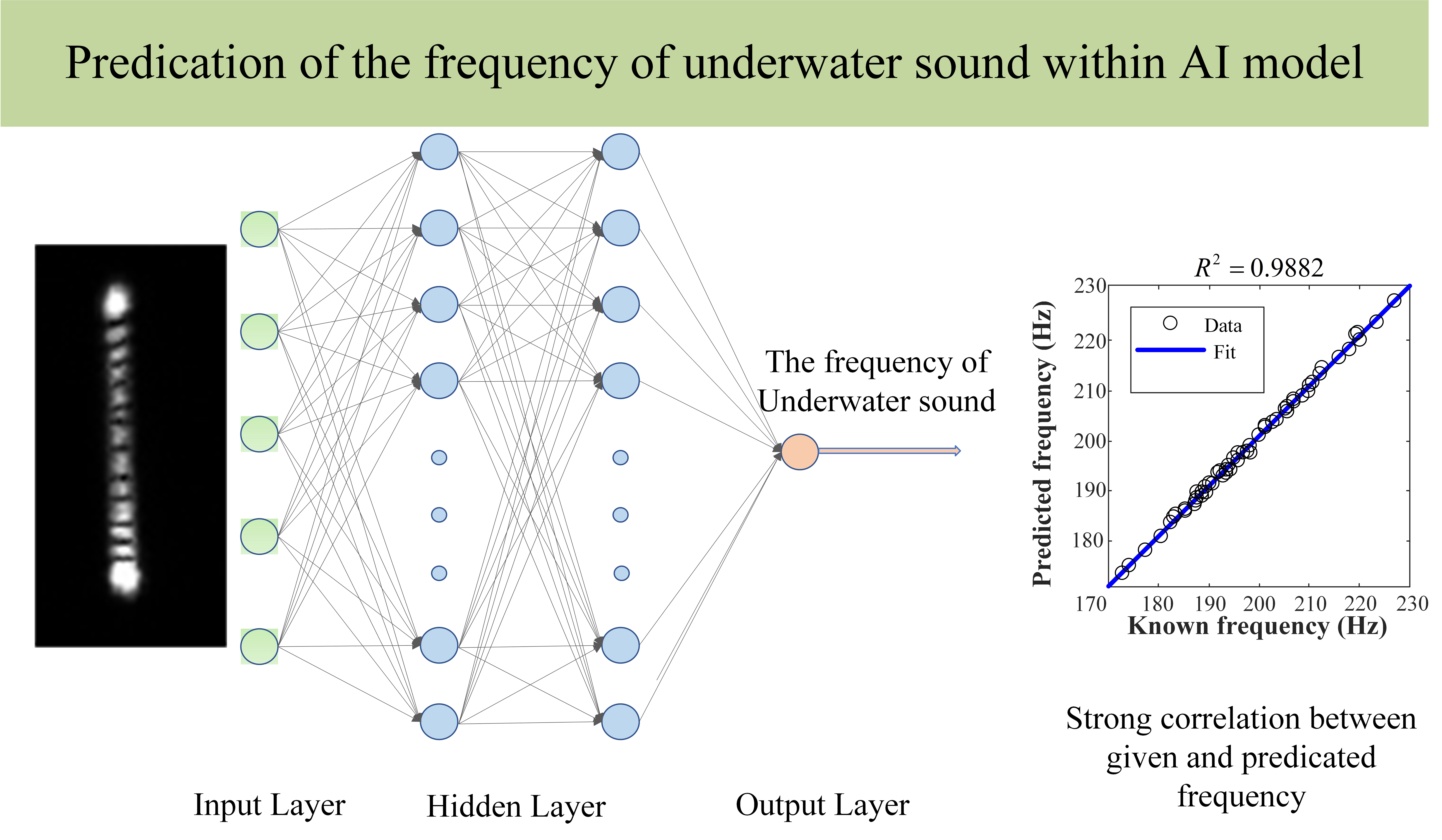
To evaluate underwater sound, a simple non-invasive optical technique based on self-interference to detect low-frequency underwater acoustic signals was demonstrated. Clear self-interference fringes of a laser beam reflected from the surface capillary wave transformed from a low-frequency underwater acoustic signal by a cylinder were observed. This study was also aimed at developing an artificial neural network (ANN) model with input from an optical pattern. The relationship between the optical pattern and the frequency of underwater sound was established, and an optimal combination of hyper-parameters was obtained. By analyzing the fringe region and the fringe interval, the frequency of the underwater acoustic signal and its relative amplitude were measured. A model based on physical optics modified the fringe distribution function, and the theoretical fit with the modified function was in good agreement with experimental observation. The BP-ANN model exhibited good performance in establishing the relationship between the optical pattern and underwater sound.

Archives, libraries, and commercial firms are utilizing new advanced imaging methods for research into cultural heritage objects. New technical systems, including the latest multispectral (MSI) and x-ray fluorescence (XRF) imaging systems and higher resolution cameras raise major challenges for not only the integration of new technologies, but also the ability to store, manage and access large amounts of data in archives and libraries. Recent advanced imaging of ancient Syriac palimpsests (parchment manuscripts with hidden texts embedded within them) demonstrated an approach that utilized multiple imaging techniques and integration and analysis of data from multiple sources. Three palimpsest imaging projects (Archimedes Palimpsest, Syriac Galen Palimpsest, HMML Palimpsest) supported research with a range of advanced imaging techniques with MSI and XRF, requiring implementation and standardization of new digitization and data management practices for the integration, preservation and sharing of advanced image data.